中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (20): 3123-3129.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0296
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
多西环素在纤维连接蛋白诱导髓核细胞退变过程中的作用
张海飞,赵 广,张治宇
- 中国医科大学附属第四医院骨外科,辽宁省沈阳市 100032
Role of doxycycline in the fibronectin-induced degeneration of nucleus pulposus cells
Zhang Hai-fei, Zhao Guang, Zhang Zhi-yu
- Department of Orthopedics, the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 100032, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
多西环素:是四环素类抗生素,可以非特异性抑制基质金属蛋白酶。正因为此特性,它已开始用于血管外科、神经科、循环科、呼吸科等多种疾病的预防和治疗的研究中。多西环素可以通过细胞因子和细胞因子受体调控胶原酶来抑制蛋白水解从而保护关节软骨,据此该文探讨多西环素是否可以通过类似机制抑制间盘退变。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路:丝裂原活化蛋白激酶属于一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可在多种不同的信号转导途径中充当一种共同的信号转导成分,且在细胞周期调控中发挥重要的作用。已有基础研究证实在退变椎间盘中丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路发挥了重要作用。
文题释义:
多西环素:是四环素类抗生素,可以非特异性抑制基质金属蛋白酶。正因为此特性,它已开始用于血管外科、神经科、循环科、呼吸科等多种疾病的预防和治疗的研究中。多西环素可以通过细胞因子和细胞因子受体调控胶原酶来抑制蛋白水解从而保护关节软骨,据此该文探讨多西环素是否可以通过类似机制抑制间盘退变。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路:丝裂原活化蛋白激酶属于一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可在多种不同的信号转导途径中充当一种共同的信号转导成分,且在细胞周期调控中发挥重要的作用。已有基础研究证实在退变椎间盘中丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路发挥了重要作用。
.jpg) 文题释义:
多西环素:是四环素类抗生素,可以非特异性抑制基质金属蛋白酶。正因为此特性,它已开始用于血管外科、神经科、循环科、呼吸科等多种疾病的预防和治疗的研究中。多西环素可以通过细胞因子和细胞因子受体调控胶原酶来抑制蛋白水解从而保护关节软骨,据此该文探讨多西环素是否可以通过类似机制抑制间盘退变。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路:丝裂原活化蛋白激酶属于一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可在多种不同的信号转导途径中充当一种共同的信号转导成分,且在细胞周期调控中发挥重要的作用。已有基础研究证实在退变椎间盘中丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路发挥了重要作用。
文题释义:
多西环素:是四环素类抗生素,可以非特异性抑制基质金属蛋白酶。正因为此特性,它已开始用于血管外科、神经科、循环科、呼吸科等多种疾病的预防和治疗的研究中。多西环素可以通过细胞因子和细胞因子受体调控胶原酶来抑制蛋白水解从而保护关节软骨,据此该文探讨多西环素是否可以通过类似机制抑制间盘退变。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路:丝裂原活化蛋白激酶属于一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可在多种不同的信号转导途径中充当一种共同的信号转导成分,且在细胞周期调控中发挥重要的作用。已有基础研究证实在退变椎间盘中丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路发挥了重要作用。摘要
背景:多西环素在阻止间盘退变方面有一定的作用,但是其在椎间盘中抑制基质金属蛋白酶的机制并未完全阐明。
目的:从分子内信号传导角度采用细胞实验来阐明多西环素抑制间盘内基质金属蛋白酶的作用机制。
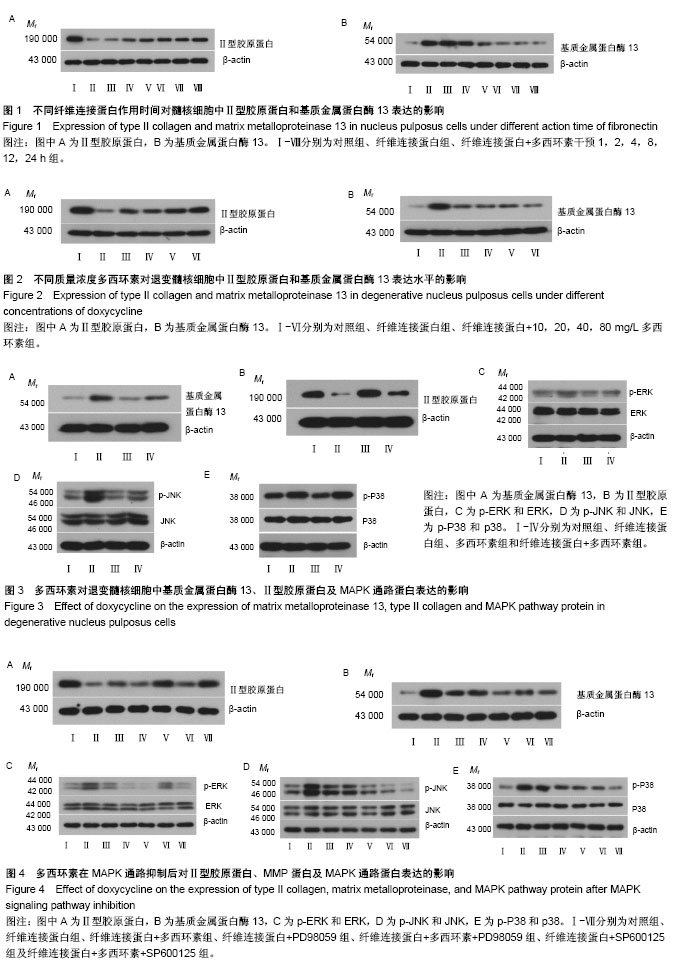
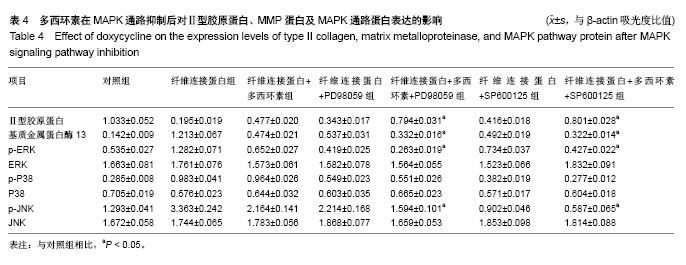
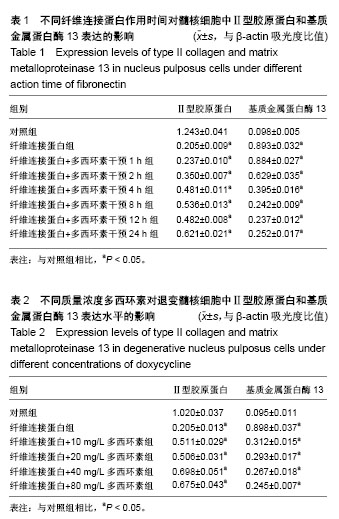
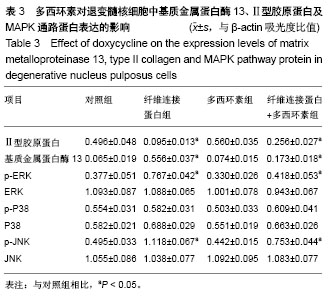
方法:体外培养人间盘髓核细胞,在培养液中加入相对分子质量为45 000纤维连接蛋白片段制造退变模型。在退变模型中按照不同作用时间及不同作用浓度分组,均通过Western blot方法检测各组Ⅱ型胶原和基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白的表达情况。然后在10 mg/L多西环素作用24 h后,Western blot方法测定各组ERK1/2、p-ERK1/2、P38、p-P38、JNK、p-JNK 蛋白表达水平,并根据以上实验结果选择ERK及JNK通路抑制后,Western blot检测多西环素对MAPK通路蛋白表达的影响。
结果与结论:①纤维连接蛋白可以诱导髓核细胞退变,表现为基质金属蛋白酶13表达增加、Ⅱ型胶原表达降低。多西环素可以抑制纤维连接蛋白诱导的退变髓核细胞基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,但并不呈时间依赖性和剂量依赖性;②多西环素作用于经纤维连接蛋白诱导的髓核细胞后可以抑制其ERK1/2及JNK磷酸化,双重抑制有效地阻断了ERK1/2及JNK在髓核细胞中的激活,与多西环素或MAPK抑制剂单独作用相比,这种联合作用协同地增强了对ERK及JNK磷酸化的抑制作用。因此多西环素可能通过阻断ERK1/2及JNK在髓核细胞中的激活来抑制金属基质蛋白酶表达,进而减少细胞外基质降解,具有预防和治疗间盘退变的潜在作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2818-6404(张治宇)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
多西环素:是四环素类抗生素,可以非特异性抑制基质金属蛋白酶。正因为此特性,它已开始用于血管外科、神经科、循环科、呼吸科等多种疾病的预防和治疗的研究中。多西环素可以通过细胞因子和细胞因子受体调控胶原酶来抑制蛋白水解从而保护关节软骨,据此该文探讨多西环素是否可以通过类似机制抑制间盘退变。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路:丝裂原活化蛋白激酶属于一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可在多种不同的信号转导途径中充当一种共同的信号转导成分,且在细胞周期调控中发挥重要的作用。已有基础研究证实在退变椎间盘中丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路发挥了重要作用。
文题释义:
多西环素:是四环素类抗生素,可以非特异性抑制基质金属蛋白酶。正因为此特性,它已开始用于血管外科、神经科、循环科、呼吸科等多种疾病的预防和治疗的研究中。多西环素可以通过细胞因子和细胞因子受体调控胶原酶来抑制蛋白水解从而保护关节软骨,据此该文探讨多西环素是否可以通过类似机制抑制间盘退变。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路:丝裂原活化蛋白激酶属于一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可在多种不同的信号转导途径中充当一种共同的信号转导成分,且在细胞周期调控中发挥重要的作用。已有基础研究证实在退变椎间盘中丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路发挥了重要作用。