• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
低氧环境振动训练条件下2型糖尿病骨质疏松大鼠骨质代谢及胰岛素敏感性
程加秋1,张庭然2
- 1重庆幼儿师范高等专科学校,重庆市 404047;2西南大学体育学院,重庆市 400715
Effects of hypoxia and vibration training on bone metabolism and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis rats
Cheng Jia-qiu1, Zhang Ting-ran2
- 1Chongqing Preschool Education College, Chongqing 404047, China; 2College of Sports of Southwest University, Chongqing 4000715, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
低氧训练:指在运动周期里,利用低氧仓(人工模拟)或高海拔地区(自然条件)制造的低氧条件刺激对机体进行刺激,诱发生物学应激反应同时结合运动来增加机体的缺氧程度,激发机体潜力机能,从而产生一系列有利于提高运动能力的抗缺氧生理反应和适应,有大量研究表明低氧刺激有利于缓解胰岛素抵抗现象。
振动训练:指利用振动设备制造不稳定的运动环境,同时对机体产生频率和幅度的扰动刺激,以达到促进肌力、神经肌肉的协调能力及平衡训练的效果。最新研究表明,全身振动训练能够作为辅助练习手段减少身体脂肪量,降低内脏脂肪组织的方法水平,同时能够改善骨密度。
文题释义:
低氧训练:指在运动周期里,利用低氧仓(人工模拟)或高海拔地区(自然条件)制造的低氧条件刺激对机体进行刺激,诱发生物学应激反应同时结合运动来增加机体的缺氧程度,激发机体潜力机能,从而产生一系列有利于提高运动能力的抗缺氧生理反应和适应,有大量研究表明低氧刺激有利于缓解胰岛素抵抗现象。
振动训练:指利用振动设备制造不稳定的运动环境,同时对机体产生频率和幅度的扰动刺激,以达到促进肌力、神经肌肉的协调能力及平衡训练的效果。最新研究表明,全身振动训练能够作为辅助练习手段减少身体脂肪量,降低内脏脂肪组织的方法水平,同时能够改善骨密度。
.jpg) 文题释义:
低氧训练:指在运动周期里,利用低氧仓(人工模拟)或高海拔地区(自然条件)制造的低氧条件刺激对机体进行刺激,诱发生物学应激反应同时结合运动来增加机体的缺氧程度,激发机体潜力机能,从而产生一系列有利于提高运动能力的抗缺氧生理反应和适应,有大量研究表明低氧刺激有利于缓解胰岛素抵抗现象。
振动训练:指利用振动设备制造不稳定的运动环境,同时对机体产生频率和幅度的扰动刺激,以达到促进肌力、神经肌肉的协调能力及平衡训练的效果。最新研究表明,全身振动训练能够作为辅助练习手段减少身体脂肪量,降低内脏脂肪组织的方法水平,同时能够改善骨密度。
文题释义:
低氧训练:指在运动周期里,利用低氧仓(人工模拟)或高海拔地区(自然条件)制造的低氧条件刺激对机体进行刺激,诱发生物学应激反应同时结合运动来增加机体的缺氧程度,激发机体潜力机能,从而产生一系列有利于提高运动能力的抗缺氧生理反应和适应,有大量研究表明低氧刺激有利于缓解胰岛素抵抗现象。
振动训练:指利用振动设备制造不稳定的运动环境,同时对机体产生频率和幅度的扰动刺激,以达到促进肌力、神经肌肉的协调能力及平衡训练的效果。最新研究表明,全身振动训练能够作为辅助练习手段减少身体脂肪量,降低内脏脂肪组织的方法水平,同时能够改善骨密度。摘要
背景:利用低氧干预缓解2型糖尿病胰岛素抵抗的方案已被众多学者推荐,但是低氧因素对糖尿病患者造成骨质疏松的风险导致方案存在争议。
目的:探讨低氧环境下振动训练对2型糖尿病骨质疏松大鼠骨密度、骨结构力学、骨质代谢、胰岛素敏感性等的影响。
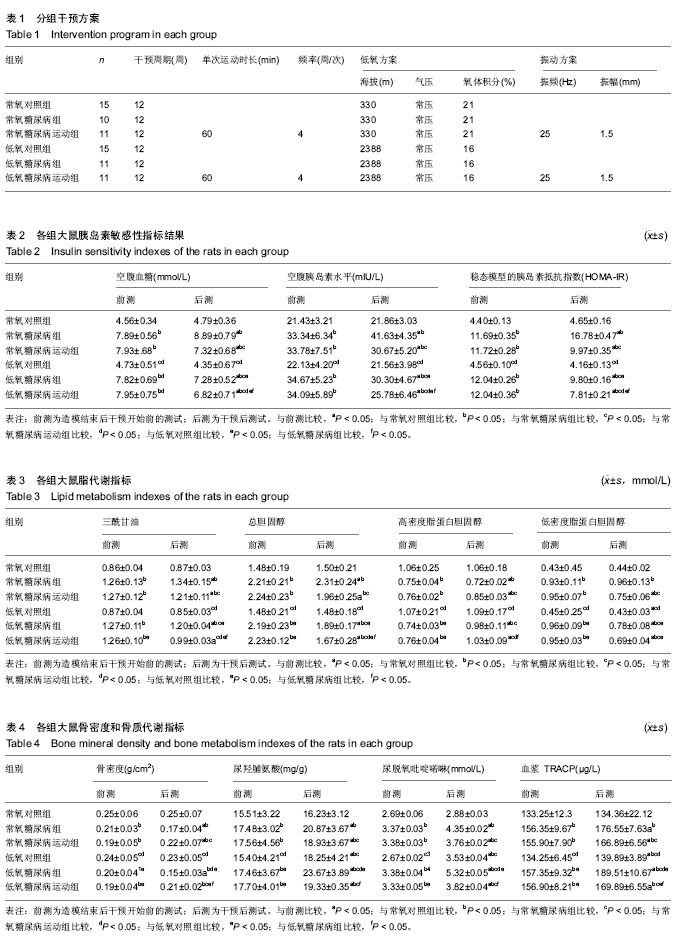
方法:90只清洁级SD大鼠随机分出60只大鼠进行高脂饲料喂食,30只大鼠正常喂食,饲养8周后,高脂饲料喂食组的60只大鼠注射链脲佐菌素,构建2型糖尿病骨质疏松动物模型,4周后对所有大鼠进行糖代谢、胰岛素敏感性、骨质代谢、骨密度前测和评价造模情况;正常喂食的30只大鼠随机分为常氧对照组、低氧对照组,造模成功的2型糖尿病骨质疏松大鼠随机分为低氧糖尿病组、低氧糖尿病振动训练组(低氧糖尿病运动组)、常氧糖尿病组、常氧糖尿病运动组,利用低氧仓和powerplate振动训练平台执行低氧和振动方案,进行为期12周干预。干预后对所有大鼠胰岛素敏感性指标、代谢指标、骨密度、骨质代谢进行检测。
结果与结论:①12周干预后低氧糖尿病运动组大鼠空腹胰岛素水平、空腹血糖、稳态模型的胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR)、均显著优于常氧糖尿病组、低氧糖尿病组、常氧糖尿病运动组(P < 0.05);②常氧糖尿病运动组和低氧糖尿病运动组大鼠骨密度、最大应力、最大载荷、断裂载荷、弹性模量显著低于常氧对照组和低氧对照组(P < 0.05);振动训练后各项指标显著提高(P < 0.05);③结果说明,低氧环境能够促进2型糖尿病大鼠胰岛素敏感性提升,改善糖、脂代谢,但也能够导致骨密度下降,骨质代谢异常,骨吸收增加;低氧环境下进行振动训练能够显著改善糖尿病骨质疏松大鼠的胰岛素敏感性;并能够避免低氧因素对大鼠造成骨密度下降、骨质代谢异常和骨生物力学性质的风险。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-7835-8470(程加秋)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
低氧训练:指在运动周期里,利用低氧仓(人工模拟)或高海拔地区(自然条件)制造的低氧条件刺激对机体进行刺激,诱发生物学应激反应同时结合运动来增加机体的缺氧程度,激发机体潜力机能,从而产生一系列有利于提高运动能力的抗缺氧生理反应和适应,有大量研究表明低氧刺激有利于缓解胰岛素抵抗现象。
振动训练:指利用振动设备制造不稳定的运动环境,同时对机体产生频率和幅度的扰动刺激,以达到促进肌力、神经肌肉的协调能力及平衡训练的效果。最新研究表明,全身振动训练能够作为辅助练习手段减少身体脂肪量,降低内脏脂肪组织的方法水平,同时能够改善骨密度。
文题释义:
低氧训练:指在运动周期里,利用低氧仓(人工模拟)或高海拔地区(自然条件)制造的低氧条件刺激对机体进行刺激,诱发生物学应激反应同时结合运动来增加机体的缺氧程度,激发机体潜力机能,从而产生一系列有利于提高运动能力的抗缺氧生理反应和适应,有大量研究表明低氧刺激有利于缓解胰岛素抵抗现象。
振动训练:指利用振动设备制造不稳定的运动环境,同时对机体产生频率和幅度的扰动刺激,以达到促进肌力、神经肌肉的协调能力及平衡训练的效果。最新研究表明,全身振动训练能够作为辅助练习手段减少身体脂肪量,降低内脏脂肪组织的方法水平,同时能够改善骨密度。