中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (12): 1846-1851.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0202
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
川芎嗪干预早期膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨Ⅱ型胶原纤维α1基因与血管内皮生长因子mRNA及miR20b的表达
谢平金1,2,3,余 翔1,2,4,柴生颋2,3,曹学伟5,孙 赫1,2,5,陈群群2,3,梁桂洪1,2,3
- 1广州中医药大学岭南医学研究中心中医骨伤科学实验室,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510405;3广州中医药大学第三附属医院骨科,广东省广州市 510240;4广州中医药大学第一附属医院骨科,广东省广州市 510405;5广东省中医院骨科,广东省广州市 510240
Ligustrazine for early-stage knee osteoarthritis in rats: changes in the expression levels of type II collagen fiber alpha 1, vascular endothelial growth factor and miR20b in the cartilage
Xie Ping-jin1, 2, 3, Yu Xiang1, 2, 4, Chai Sheng-ting2, 3, Cao Xue-wei5, Sun He1, 2, 5, Chen Qun-qun2, 3, Liang Gui-hong1, 2, 3
- 1the Lab of Orthopedics and Traumatology of Chinese Medicine of Lingnan Medical Research Center of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240, Guangdong Province, China; 4Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 5Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
川芎嗪:是从活血化瘀类中药川芎中提取的一种有效活性生物碱,具有扩张血管、镇静镇痛、改善微循环、增强免疫等作用。课题组前期研究亦发现川芎嗪能明显降低骨关节炎关节液中NO、前列腺素E2水平,对减轻骨性关节炎的炎症有一定作用。
木瓜蛋白酶:是一种蛋白水解酶。木瓜蛋白酶是番木瓜中含有的一种低特异性蛋白水解酶,木瓜蛋白酶对动植物蛋白具有较强的水解能力,其诱导大鼠膝骨性关节炎具有成功率高、时间短、重复性好等特点。已有研究表明,木瓜蛋白酶关节腔注射可作为诱导早期膝骨关节炎大鼠模型的方法。
文题释义:
川芎嗪:是从活血化瘀类中药川芎中提取的一种有效活性生物碱,具有扩张血管、镇静镇痛、改善微循环、增强免疫等作用。课题组前期研究亦发现川芎嗪能明显降低骨关节炎关节液中NO、前列腺素E2水平,对减轻骨性关节炎的炎症有一定作用。
木瓜蛋白酶:是一种蛋白水解酶。木瓜蛋白酶是番木瓜中含有的一种低特异性蛋白水解酶,木瓜蛋白酶对动植物蛋白具有较强的水解能力,其诱导大鼠膝骨性关节炎具有成功率高、时间短、重复性好等特点。已有研究表明,木瓜蛋白酶关节腔注射可作为诱导早期膝骨关节炎大鼠模型的方法。
.jpg) 文题释义:
川芎嗪:是从活血化瘀类中药川芎中提取的一种有效活性生物碱,具有扩张血管、镇静镇痛、改善微循环、增强免疫等作用。课题组前期研究亦发现川芎嗪能明显降低骨关节炎关节液中NO、前列腺素E2水平,对减轻骨性关节炎的炎症有一定作用。
木瓜蛋白酶:是一种蛋白水解酶。木瓜蛋白酶是番木瓜中含有的一种低特异性蛋白水解酶,木瓜蛋白酶对动植物蛋白具有较强的水解能力,其诱导大鼠膝骨性关节炎具有成功率高、时间短、重复性好等特点。已有研究表明,木瓜蛋白酶关节腔注射可作为诱导早期膝骨关节炎大鼠模型的方法。
文题释义:
川芎嗪:是从活血化瘀类中药川芎中提取的一种有效活性生物碱,具有扩张血管、镇静镇痛、改善微循环、增强免疫等作用。课题组前期研究亦发现川芎嗪能明显降低骨关节炎关节液中NO、前列腺素E2水平,对减轻骨性关节炎的炎症有一定作用。
木瓜蛋白酶:是一种蛋白水解酶。木瓜蛋白酶是番木瓜中含有的一种低特异性蛋白水解酶,木瓜蛋白酶对动植物蛋白具有较强的水解能力,其诱导大鼠膝骨性关节炎具有成功率高、时间短、重复性好等特点。已有研究表明,木瓜蛋白酶关节腔注射可作为诱导早期膝骨关节炎大鼠模型的方法。摘要
背景:课题组前期研究发现川芎嗪能明显降低骨关节炎关节液中NO、前列腺素E2水平,对减轻骨性关节炎的炎症有一定作用,但具体机制还不清楚。
目的:观察川芎嗪治疗膝骨关节炎模型关节软骨中Ⅱ型胶原纤维α1基因、血管内皮生长因子mRNA及miR20b表达水平,并探讨川芎嗪治疗早期膝骨关节炎大鼠的作用机制。
方法:健康雄性SD大鼠随机分为正常组、模型组、川芎嗪高剂量组、川芎嗪低剂量组、阳性对照组,后4组通过木瓜蛋白酶关节腔注射制作早期膝骨关节炎大鼠模型。造模后川芎嗪高、低剂量组分别灌胃川芎嗪100 mg/kg和50 mg/kg,阳性对照组灌服塞来昔布24 mg/kg;正常组、模型组灌服等量生理盐水。干预6周后取材,分别行鼠软骨大体组织学评分、qRT-PCR检测软骨Ⅱ型胶原纤维α1基因、血管内皮生长因子mRNA及miR20b的表达水平。
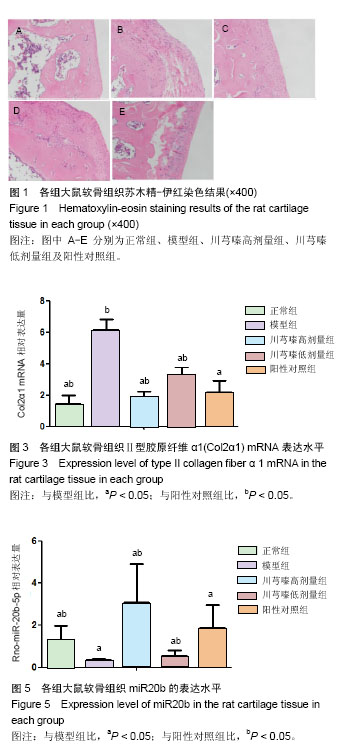
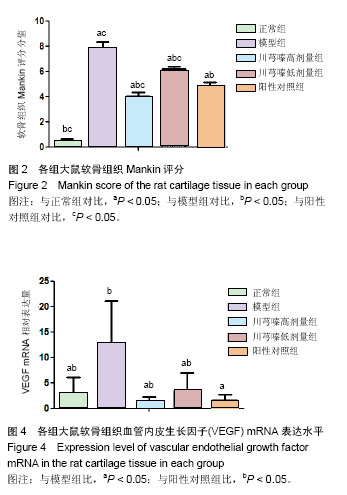
结果与结论:①软骨Mankin评分:川芎嗪高、低剂量组和阳性对照组均较正常组高(P < 0.05),较模型组低(P < 0.05),且川芎嗪高剂量组<阳性对照组<川芎嗪低剂量组;②川芎嗪各剂量组和阳性对照组的Ⅱ型胶原纤维α1基因、血管内皮生长因子mRNA表达较正常组上调(P < 0.05),较模型组下调(P < 0.05),且川芎嗪高剂量组<阳性对照组<川芎嗪低剂量组;③川芎嗪各剂量组、阳性对照组及正常组的miR20b表达均较模型组上调(P < 0.05),其中川芎嗪低剂量组<阳性对照组<川芎嗪高剂量组;④提示:川芎嗪对早期膝骨关节炎大鼠治疗具有积极作用,可能通过上调软骨中miR20b从而抑制血管内皮生长因子mRNA的表达,促进软骨的修复。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-9554-9033(谢平金)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
川芎嗪:是从活血化瘀类中药川芎中提取的一种有效活性生物碱,具有扩张血管、镇静镇痛、改善微循环、增强免疫等作用。课题组前期研究亦发现川芎嗪能明显降低骨关节炎关节液中NO、前列腺素E2水平,对减轻骨性关节炎的炎症有一定作用。
木瓜蛋白酶:是一种蛋白水解酶。木瓜蛋白酶是番木瓜中含有的一种低特异性蛋白水解酶,木瓜蛋白酶对动植物蛋白具有较强的水解能力,其诱导大鼠膝骨性关节炎具有成功率高、时间短、重复性好等特点。已有研究表明,木瓜蛋白酶关节腔注射可作为诱导早期膝骨关节炎大鼠模型的方法。
文题释义:
川芎嗪:是从活血化瘀类中药川芎中提取的一种有效活性生物碱,具有扩张血管、镇静镇痛、改善微循环、增强免疫等作用。课题组前期研究亦发现川芎嗪能明显降低骨关节炎关节液中NO、前列腺素E2水平,对减轻骨性关节炎的炎症有一定作用。
木瓜蛋白酶:是一种蛋白水解酶。木瓜蛋白酶是番木瓜中含有的一种低特异性蛋白水解酶,木瓜蛋白酶对动植物蛋白具有较强的水解能力,其诱导大鼠膝骨性关节炎具有成功率高、时间短、重复性好等特点。已有研究表明,木瓜蛋白酶关节腔注射可作为诱导早期膝骨关节炎大鼠模型的方法。