| [1] Yoon DS, Lee YK, Ha YC, et al.Inadequate Dietary Calcium and Vitamin D Intake in Patients with Osteoporotic Fracture.J Bone Metab. 2016;23(2):55-61.[2] Marcelli C,Chavoix C,Dargent-Molina P. Beneficial effects of vitamin D on falls and fractures: is cognition rather than bone or muscle behind these benefits?. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(1):1-10.[3] Khosla S,Bilezikian JP,Dempster DW, et al. Benefits and risks of bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(7):2272-2282.[4] Li YT, Cai HF, Zhang ZL.Timing of the initiation of bisphosphonates after surgery for fracture healing: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(2):431-441.[5] Adami S, Libanati C, Boonen S, et al. Denosumab treatment in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis does not interfere with fracture-healing: results from the FREEDOM trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2012;94(23):2113-2119.[6] Brewer L,Williams D,Moore A.Current and future treatment options in osteoporosis.Eur J Clin Pharmacol.2011;67(4):321-331.[7] Pickar JH, Komm BS. Selective estrogen receptor modulators and the combination therapy conjugated estrogens/bazedoxifene: A review of effects on the breast. Post Reprod Health.2015;21(3):112-121.[8] Ellis AJ,Hendrick VM, Williams R, et al. Selective estrogen receptor modulators in clinical practice: a safety overview. Expert Opin Drug Saf.2015;14(6):921-934.[9] Mcclung MR. New management options for osteoporosis with emphasis on SERMs. Climacteric.2015;18 Suppl 2:56-61.[10] Park SB, Kim CH, Hong M, et al. Effect of a selective estrogen receptor modulator on bone formation in osteoporotic spine fusion using an ovariectomized rat model. Spine J.2016;16(1):72-81.[11] Chaki O.[Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)].Nihon Rinsho.2015;73(10):1673-1681.[12] Spiro AS, Khadem S, Jeschke A, et al. The SERM raloxifene improves diaphyseal fracture healing in mice.J Bone Miner Metab. 2013;31(6): 629-636.[13] Umland EM, Karel L, Santoro N. Bazedoxifene and Conjugated Equine Estrogen: A Combination Product for the Management of Vasomotor Symptoms and Osteoporosis Prevention Associated with Menopause. Pharmacotherapy.2016;36(5):548-561.[14] Cheung WH,Miclau T,Chow SK,et al.Fracture healing in osteoporotic bone. Injury.2016;47 Suppl 2:S21-S26.[15] Tsartsalis AN,Dokos C,Kaiafa GD,et al.Statins, bone formation and osteoporosis: hope or hype?. Hormones (Athens).2012;11(2):126-139.[16] Ibrahim N, Mohamed N, Shuid AN.Update on statins: hope for osteoporotic fracture healing treatment. Curr Drug Targets.2013; 14(13):1524-1532.[17] Abdul-Majeed S, Mohamed N, Soelaiman IN. A review on the use of statins and tocotrienols, individually or in combination for the treatment of osteoporosis. Curr Drug Targets.2013;14(13):1579-1590.[18] Tan J, Fu X,Sun CG,et al.A single CT-guided percutaneous intraosseous injection of thermosensitive simvastatin/poloxamer 407 hydrogel enhances vertebral bone formation in ovariectomized minipigs. Osteoporos Int.2016;27(2):757-767.[19] Sun LM, Lin M C, Muo CH, et al. Calcitonin nasal spray and increased cancer risk: a population-based nested case-control study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2014;99(11):4259-4264.[20] Giannotti S,Bottai V,Dell'Osso G,et al. Atrophic femoral nonunion successfully treated with teriparatide. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 2:S291-S294.[21] Bhandari M, Jin L, See K, et al. Does Teriparatide Improve Femoral Neck Fracture Healing: Results From A Randomized Placebo-controlled Trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(5):1234-1244.[22] Miyakoshi N, Aizawa T, Sasaki S, et al. Healing of bisphosphonate- associated atypical femoral fractures in patients with osteoporosis: a comparison between treatment with and without teriparatide. J Bone Miner Metab.2015;33(5):553-559.[23] Reginster JY, Brandi ML, Cannata-Andia J, et al.The position of strontium ranelate in today's management of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(6):1667-1671.[24] Komrakova M,Weidemann A,Dullin C, et al. The Impact of Strontium Ranelate on Metaphyseal Bone Healing in Ovariectomized Rats.Calcif Tissue Int.2015;97(4):391-401.[25] Alegre DN, Ribeiro C, Sousa C, et al. Possible benefits of strontium ranelate in complicated long bone fractures. Rheumatol Int.2012; 32(2):439-443.[26] Negri AL, Spivacow FR. Healing of subtrochanteric atypical fractures after strontium ranelate treatment. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab.2012; 9(3):166-169.[27] Chapurlat R.Cathepsin K inhibitors and antisclerostin antibodies. The next treatments for osteoporosis?.Joint Bone Spine.2016;83(3):254-256.[28] Langdahl B,Binkley N,Bone H,et al.Odanacatib in the treatment of postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density: Five years of continued therapy in a phase 2 study. J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(11): 2251-2258.[29] Padhi D,Allison M,Kivitz AJ,et al.Multiple doses of sclerostin antibody romosozumab in healthy men and postmenopausal women with low bone mass: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(2):168-178.[30] Mcclung MR,Grauer A, Boonen S, et al.Romosozumab in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med.2014;370(5):412-420. |
.jpg)

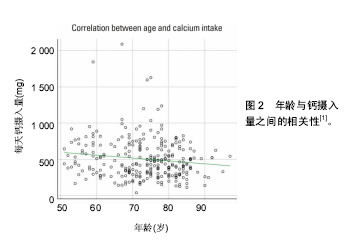
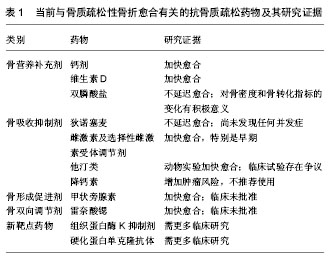
.jpg)
.jpg)