| [1] 刘农虞,任天培,向宇.“筋针”对软组织损伤即刻镇痛效果临床观察[J].中国针灸,2015,35(9):927-929. [2] 郑寒丹,赵继梦,吴璐一,等.温针灸镇痛的临床应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(42):6855-6860.[3] 何巍,温先荣,童元元,等.近10年国内针灸临床试验研究病种计量分析[J].上海针灸杂志,2014,33(4):375-376.[4] 赵勇,方维,张宽,等.铍针治疗肩胛肌筋膜炎53例[J].中国针灸, 2014,34(2):177-178.[5] 郭保君,余思奕,胡幼平.刃针临床应用及作用机制研究进展[J].湖南中医杂志,2016,32(6):210-212.[6] 朱国庆,苏慧.松筋针治疗经筋痹痛症的临床应用(慢性软组织损伤肌筋膜病)[C].第八届全国中青年针灸推拿学术研讨会论文集.2008:32-36.[7] 王莉,袁仕国,刘飞,等.新型针具治疗肌筋膜痛的研究进展[J].中国疗养医学,2017,2626(7):697-701.[8] 袁铭,董宝强,林星星.长圆针解结法治疗神经根型颈椎病随机对照研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2017,19(8):181-184.[9] 迟永传,董宝强,林星星.针刺结筋病灶点治疗慢性踝关节扭伤随时对照研究[J].中医药临床杂志,2017,29(4);540-542.[10] 王翔,刘顺怡,石瑛,等.针刀松解术治疗膝骨关节炎的临床观察[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(4);345-349.[11] 谭兴乐,张宝燕,苏霞辉,等.松筋针与小针刀治疗慢性腰臀部肌筋膜炎临床研究[J].中国现代医生,2008,46(21):129-130.[12] 王慧敏,曾浩彬,陈文治,等.刃针松解术治疗颈性眩晕[J].广东医学,2012,33(3):366-368.[13] 苏鑫童,刘元石,杨涛,等.长圆针治疗偏瘫肩手综合征Ⅰ期的疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(2):153-155.[14] 丁永国,甄龙龙,张骋,等.以银质针为主治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后复发28例体会[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2013,19(8):511-512.[15] Weidner N. Chapter14. Measuring intratumoral microvessel density. Methods Enzymol. 2008;444:305-323. [16] Flanders KC, Sullivan CD, Fujii M, et al. Mice lacking Smad3 are protected againstcutaneous injury induced by ionizing radiation. Am J Pathol. 2002;160(3):1057-1068.[17] 张义,权伍成,尹萍,等.针刀疗法的适应症和优势病种的文献分析[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(25):3185-3186.[18] 赵军,王庆甫,马玉峰,等.针刀联合玻璃酸钠与单纯玻璃酸钠治疗膝骨关节炎疗效的Meta分析[J].中国中医骨伤杂志, 2014,22(2): 15-20.[19] 张义,权伍成,尹萍,等.基于文献计量学的针刀疗法现状分析[J].中华中医药学刊,2010,28(6):1189-1190.[20] Reinke JM, Sorg H.Wound Repair and Regeneration. Eur Surg Res. 2012;49(1):35-43. [21] 陈燕,谢利红,章杰,等.炎性反应及免疫反应与病理性瘢痕研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(5):640-644.[22] Witko-Sarsat V, Rieu P, Descamps-Latscha B, et al. Neutrophils: molecules, functions and pathophysiological aspects. Lab Invest. 2000;80(5):617-653.[23] He L,Li G, Feng X, et al. Effect of energy compound on skeletal muscle strain injury and regeneration in rats. Ind Health. 2008;46(5):506-512.[24] Farnebo S, Lars-Erik K, Ingrid S, et al. Continuous assessment of concentrations of cytokines in experimental injuries of the extremity. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2009;2(4): 354-362.[25] 刘树坤,于晓华,吴耀义,等.SD大鼠骨骼肌钝挫伤早期的组织病理变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(24):4371-4375.[26] McLoughlin TJ, Mylona E, Hornberger TA, et al. Inflammatory cells in rat skeletal muscle are elevated after electrically stimulated contractions. J Appl Physiol. 2003;94(3):876-882.[27] Martin P, Hopkinson-Woolley J, McCluskey J. Growth factors and cutaneous wound repair. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1992; 4(1):25-44.[28] 苏顺清,于冶,张一鸣.成纤维细胞与细胞外基质在皮肤创伤修复中的相互作用及其调控[J].中华创伤杂志,2000,16(6):25-26.[29] Eming SA, Martin P, Tomic-Canic M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(265):265-266.[30] Wang J, Dodd C, Shankowsky HA, et al. Deep dermal fibroblasts contribute to hypertrophic scarring. Lab Invest. 2008;88(12):1278-1290.[31] Roseborough IE, Grevious MA, Lee RC. Prevention and treatment of excessive dermal scarring. J Natl Med Assoc. 2004;96(1):108-116.[32] 秦全红.成纤维细胞在皮肤创伤愈合中的作用及其调控[J].国外医学(创伤与外科基本问题分册),2000,12(1):33-36+38.[33] McClain SA, Simon M, Jones E, et al. Mesenchymal cell activation is the rate-limiting step of granulation tissue induction. Am J Pathol. 1996;149(4):1257-1270.[34] Frantz FW, Diegelmann RF, Mast BA, et al. Biology of fetal wound healing: collagen biosynthesis during dermal repair. J Pediatr Surg. 1992;27(8):945-948.[35] Nedelec B, Shankowsky H, Scott PG, et al. Myofibroblasts and apoptosis in human hypertrophic scars: the effect of interferon-alpha2b. Surgery. 2001;130(5):798-808.[36] 刘燕,傅跃先,邱林,等.红花对兔耳增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞及Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(37):7296-7300.[37] Somasundaram R, Schuppan D. Type I, II, III, IV, V, and VI collagens serve as extracellular ligands for the isoforms of platelet-derived growth factor (AA, BB, and AB). J Biol Chem. 1996;271(43):26884-26891.[38] Kasemkijwattana C, Kesprayura S, Chaipinyo K, et al. Autologous chondrocytes implantation with three-dimensional collagen scaffold. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009;92(10):1282-1286.[39] de Souza TO, Mesquita DA, Ferrari RA,et al. Phototherapy with low-level laser affects the remodeling of types I and III collagen in skeletal muscle repair. Lasers Med Sci. 2011; 26(6):803-814.[40] Bailey AJ. Molecular mechanisms of ageing in connective tissues. Mech Ageing Dev. 2001;122(7):735-755.[41] Kellett J. Acute soft tissue injuries-a review of the literature. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1986;18(5):489-500.[42] Friedman DW, Boyd CD, Mackenzie JW, et al. Regulation of collagen gene expression in keloids and hypertrophic scars. J Surg Res. 1993;55(2):214-222.[43] 赵星宇,李冬松,王云亭,等.电针在骨骼肌修复中对Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(12):3188-3190. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
软组织松解:是基于古代采用粗大针具针刺治疗经筋痹症的一种方法,是使用特定针具通过对局部病变软组织直接切开、横向剥离、密集针刺、透拨及上挑针体等手法而达到松解局部软组织的作用。
增生性瘢痕:是以成纤维细胞为主的细胞增殖、活性增强,产生大量的胶原蛋白,使包括Ⅰ,Ⅲ型胶原为主的细胞外基质成分在组织中大量沉积,而难以被机体吸收或重塑的病理状态。
文题释义:
软组织松解:是基于古代采用粗大针具针刺治疗经筋痹症的一种方法,是使用特定针具通过对局部病变软组织直接切开、横向剥离、密集针刺、透拨及上挑针体等手法而达到松解局部软组织的作用。
增生性瘢痕:是以成纤维细胞为主的细胞增殖、活性增强,产生大量的胶原蛋白,使包括Ⅰ,Ⅲ型胶原为主的细胞外基质成分在组织中大量沉积,而难以被机体吸收或重塑的病理状态。 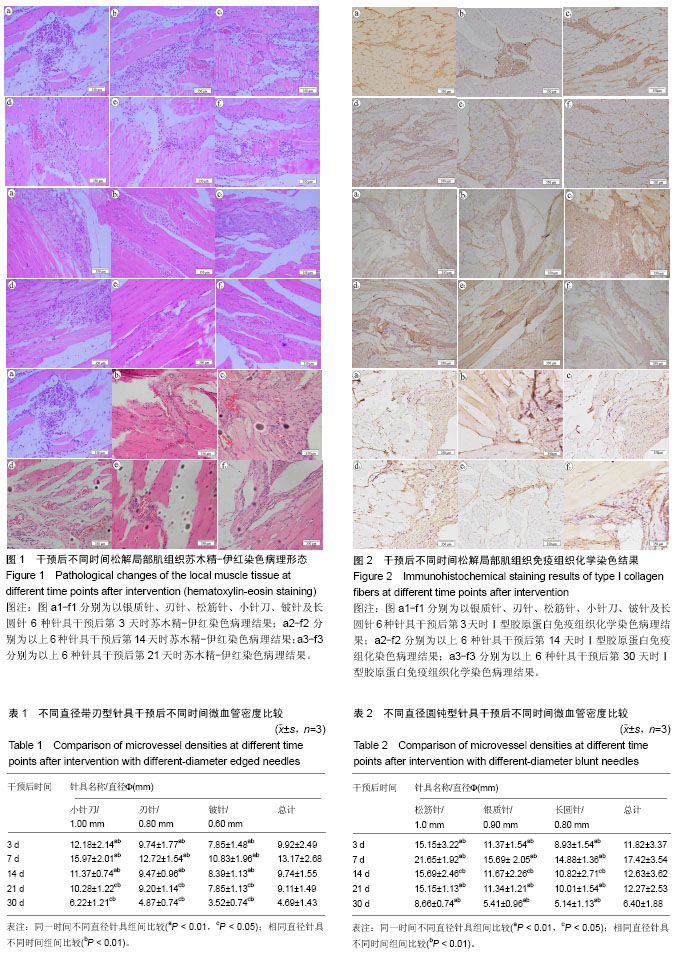

.jpg) 文题释义:
软组织松解:是基于古代采用粗大针具针刺治疗经筋痹症的一种方法,是使用特定针具通过对局部病变软组织直接切开、横向剥离、密集针刺、透拨及上挑针体等手法而达到松解局部软组织的作用。
增生性瘢痕:是以成纤维细胞为主的细胞增殖、活性增强,产生大量的胶原蛋白,使包括Ⅰ,Ⅲ型胶原为主的细胞外基质成分在组织中大量沉积,而难以被机体吸收或重塑的病理状态。
文题释义:
软组织松解:是基于古代采用粗大针具针刺治疗经筋痹症的一种方法,是使用特定针具通过对局部病变软组织直接切开、横向剥离、密集针刺、透拨及上挑针体等手法而达到松解局部软组织的作用。
增生性瘢痕:是以成纤维细胞为主的细胞增殖、活性增强,产生大量的胶原蛋白,使包括Ⅰ,Ⅲ型胶原为主的细胞外基质成分在组织中大量沉积,而难以被机体吸收或重塑的病理状态。