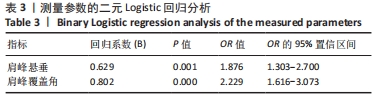
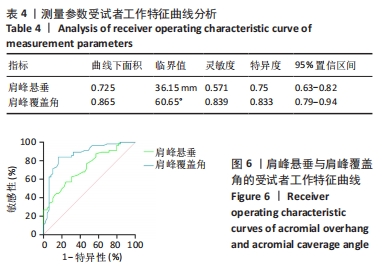
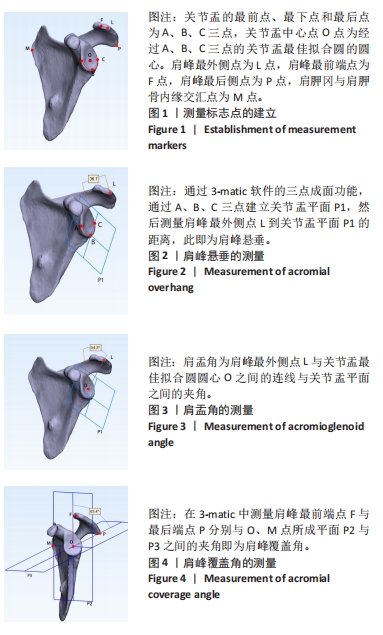
[1] DOIRON-CADRIN P, LAFRANCE S, SAULNIER M, et al. Shoulder rotator cuff disorders: a systematic review of clinical practice guidelines and semantic analyses of recommendations. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101(7):1233-1242.
[2] MOOR B, RÖTHLISBERGER M, MÜLLER D, et al. Age, trauma and the critical shoulder angle accurately predict supraspinatus tendon tears. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(5):489-494.
[3] SAVEH SHEMSHAKI N, KAN HM, BARAJAA M, et al. Muscle degeneration in chronic massive rotator cuff tears of the shoulder: Addressing the real problem using a graphene matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022; 119(33):e2208106119.
[4] FU C, HUANG AH, GALATZ LM, et al. Cellular and molecular modulation of rotator cuff muscle pathophysiology. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(11): 2310-2322.
[5] Borbas P, Hartmann R, Ehrmann C, et al. Acromial morphology and its relation to the glenoid is associated with different partial rotator cuff tear patterns. J Clin Med. 2022;12(1):233.
[6] İncesoy MA, Yıldız Kİ, Türk Öİ, et al. The critical shoulder angle, the acromial index, the glenoid version angle and the acromial angulation are associated with rotator cuff tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29:2257-2263.
[7] Charles S, Neer I. Anterior acromioplasty for the chronic impingement syndrome in the shoulder: a preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972;54(1):41-50.
[8] Bigliani LU, Ticker JB, FLATOW EL, et al. The relationship of acromial architecture to rotator cuff disease. Clin Sports Med. 1991; 10(4):823-838.
[9] Nyffeler RW, Meyer DC. Acromion and glenoid shape: Why are they important predictive factors for the future of our shoulders? EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(5):141-150.
[10] Moor B, Bouaicha S, Rothenfluh D, et al. Is there an association between the individual anatomy of the scapula and the development of rotator cuff tears or osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral joint? A radiological study of the critical shoulder angle. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95(7):935-941.
[11] Smith G, Geelan-Small P, Sawang M. A predictive model for the critical shoulder angle based on a three-dimensional analysis of scapular angular and linear morphometrics. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):1-14.
[12] 马秉贤, 张永. 基于 CT 三维模型分析肩胛下肌腱损伤患者喙突形态和位置的研究 [J]. 中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2021,9(3):229-235.
[13] Van Parys M, Alkiar O, Naidoo N, et al. Three-dimensional evaluation of scapular morphology in primary glenohumeral arthritis, rotator cuff arthropathy, and asymptomatic shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30(8):1803-1810.
[14] Miswan MFBM, Saman MSBA, Hui TS, et al. Correlation between anatomy of the scapula and the incidence of rotator cuff tear and glenohumeral osteoarthritis via radiological study. J Orthop Surg. 2017;25(1):2309499017690317.
[15] Kim MS, Rhee SM, Jeon HJ, et al. Anteroposterior and Lateral Coverage of the Acromion: Prediction of the Rotator Cuff Tear and Tear Size. Clin Orthop Surg. 2022;14(4):593-602.
[16] Beeler S, Hasler A, Götschi T, et al. Different acromial roof morphology in concentric and eccentric osteoarthritis of the shoulder: a multiplane reconstruction analysis of 105 shoulder computed tomography scans. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(12):e357-e366.
[17] Zeng YM, Xu C, Zhang K, et al. Prediction of Rotator Cuff Injury Associated with Acromial Morphology: A Three‐Dimensional Measurement Study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(5):1394-1404.
[18] Li X, Xu W, Hu N, et al. Relationship between acromial morphological variation and subacromial impingement: a three-dimensional analysis. PLoS One. 2017; 12(4):e0176193.
[19] Liu CT, Miao JQ, Wang H, et al. The association between acromial anatomy and articular-sided partial thickness of rotator cuff tears. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22:1-8.
[20] Passaplan C, Hasler A, Gerber C. The critical shoulder angle does not change over time: a radiographic study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021;30(8):1866-1872.
[21] Codman EA, Akerson IB. The pathology associated with rupture of the supraspinatus tendon. Ann Surg. 1931;93(1):348.
[22] Lindblom K. On pathogenesis of ruptures of the tendon aponeurosis of the shoulder joint. Acta Radiol. 1939;20(6):563-577.
[23] Sürücü S, Aydın M, Çapkın S, et al. Evaluation of bilateral acromiohumeral distance on magnetic resonance imaging and radiography in patients with unilateral rotator cuff tears. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142:175-180.
[24] Mirzayan R, Donohoe S, Batech M, et al. Is there a difference in the acromiohumeral distances measured on radiographic and magnetic resonance images of the same shoulder with a massive rotator cuff tear? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29(6):1145-1151.
[25] Mangi MD, Zadow S, Lim W. Cystic lesions of the humeral head on magnetic resonance imaging: A pictorial review. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022;12(8):4304.
[26] Smith GC. A prospective observational case control study investigating the coronal plane scapular morphological differences in full-thickness posterosuperior cuff tears and primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31(5):e223-e233.
[27] Rojas Lievano J, Bautista M, Woodcock S, et al. Controversy on the association of the critical shoulder angle and the development of degenerative rotator cuff tears: is there a true association? A meta-analytical approach. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(9):2552-2560.
[28] Bjarnison AO, Sørensen TJ, Kallemose T, et al. The critical shoulder angle is associated with osteoarthritis in the shoulder but not rotator cuff tears: a retrospective case-control study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(12):2097-2102.
[29] Daggett M, Werner B, Collin P, et al. Correlation between glenoid inclination and critical shoulder angle: a radiographic and computed tomography study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(12):1948-1953.
[30] Smith GC, Liu V. High critical shoulder angle values are associated with full-thickness posterosuperior cuff tears and low values with primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy. 2022;38(3):709-715. e701.
[31] Karns MR, Jacxsens M, Uffmann WJ, et al. The critical acromial point: the anatomic location of the lateral acromion in the critical shoulder angle. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(1):151-159.
[32] Casier SJ, Van Den Broecke R, Van Houcke J, et al. Morphologic variations of the scapula in 3-dimensions: a statistical shape model approach. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(12):2224-2231.
[33] De Wilde LF, Verstraeten T, Speeckaert W, et al. Reliability of the glenoid plane. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(3):414-422.
[34] Nyffeler RW, Werner CM, Sukthankar A, et al. Association of a large lateral extension of the acromion with rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(4):800-805.
[35] Sakoma Y, Sano H, Shinozaki N, et al. Coverage of the humeral head by the coracoacromial arch: relationship with rotator cuff tears. Acta Med Okayama. 2013;67(6):377-383.
[36] Beeler S, Hasler A, Getzmann J, et al. Acromial roof in patients with concentric osteoarthritis and massive rotator cuff tears: multiplanar analysis of 115 computed tomography scans. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2018;27(10):1866-1876. |