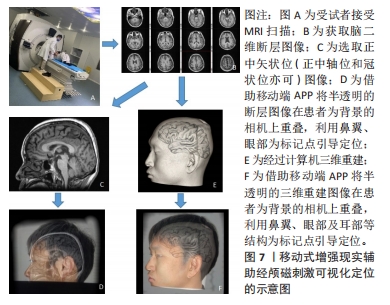
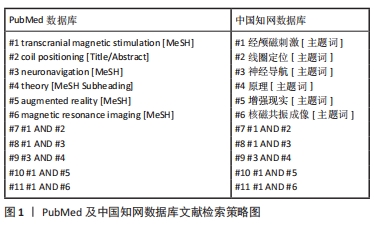
[1] DENG ZD, LISANBY SH, PETERCHEV AV. Electric field depth-focality tradeoff in transcranial magnetic stimulation: simulation comparison of 50 coil designs. Brain Stimul. 2013;6(1):1-13.
[2] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ALEMAN A, BAEKEN C, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): an update (2014-2018). Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(2):474-528.
[3] DE GOEDE AA, TER BRAACK EM, VAN PUTTEN M. Accurate coil positioning is important for single and paired pulse TMS on the subject level. Brain Topogr. 2018;31(6):917-930.
[4] 万振宽.重复经颅磁刺激(含定位导航系统)技术及临床应用[J].中国医疗设备,2011,26(1):99-101.
[5] 王辉.经颅磁刺激线圈定位方法研究[J].集成技术,2013,2(4):49-55.
[6] 周天鹏,张广浩,吴昌哲,等.经颅磁刺激定位方法的研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2017,36(6):741-748.
[7] BARKER AT, JALINOUS R, FREESTON IL. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985;1(8437):1106-1107.
[8] GEORGE MS, WASSERMANN EM, WILLIAMS WA, et al. Daily repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) improves mood in depression. Neuroreport. 1995; 6(14):1853-1856.
[9] SCHLUTER ND, RUSHWORTH MF, PASSINGHAM RE, et al. Temporary interference in human lateral premotor cortex suggests dominance for the selection of movements. A study using transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain. 1998;121(5): 785-799.
[10] MOTTAGHY FM, GANGITANO M, SPARING R, et al. Segregation of areas related to visual working memory in the prefrontal cortex revealed by rTMS. Cereb Cortex. 2002;12(4):369-375.
[11] KOCH G, FRANCA M, ALBRECHT UV, et al. Effects of paired pulse TMS of primary somatosensory cortex on perception of a peripheral electrical stimulus. Exp Brain Res. 2006;172(3):416-424.
[12] KLEM GH, LÜDERS HO, JASPER HH, et al. The ten-twenty electrode system of the international federation. the international federation of clinical neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl. 1999;52:3-6.
[13] BOROOJERDI B, FOLTYS H, KRINGS T, et al. Localization of the motor hand area using transcranial magnetic stimulation and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Neurophysiol. 1999;110(4):699-704.
[14] SOEIRO J, CLÁUDIO AP, CARMO MB, et al. Visualizing the brain on a mixed reality smartphone application. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015;2015:5090-5093.
[15] EFTEKHAR B. A smartphone app to assist scalp localization of superficial supratentorial lesions--technical note. World Neurosurg. 2016;85:359-363.
[16] HOU Y, MA L, ZHU R, et al. A low-cost iphone-assisted augmented reality solution for the localization of intracranial lesions. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e159185.
[17] ALSHOMER F, ALAZZAM A, ALTURKI A, et al. Smartphone-assisted augmented reality in craniofacial surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9(8):e3743.
[18] SHU XJ, WANG Y, XIN H, et al. Real-time augmented reality application in presurgical planning and lesion scalp localization by a smartphone. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2022;164(4):1069-1078.
[19] ROSSINI PM, BURKE D, CHEN R, et al. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;126(6):1071-1107.
[20] HERWIG U, SATRAPI P, SCHÖNFELDT-LECUONA C. Using the international 10-20 EEG system for positioning of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Topogr. 2003;16(2):95-99.
[21] STEINMETZ H, FÜRST G, FREUND HJ. Variation of perisylvian and calcarine anatomic landmarks within stereotaxic proportional coordinates. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1990;11(6):1123-1130.
[22] CYKOWSKI MD, COULON O, KOCHUNOV PV, et al. The central sulcus: an observer-independent characterization of sulcal landmarks and depth asymmetry. Cereb Cortex. 2008;18(9):1999-2009.
[23] FITZGERALD PB. Targeting repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in depression: do we really know what we are stimulating and how best to do it? Brain Stimul. 2021;14(3):730-736.
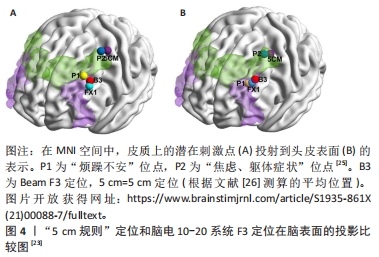
[24] TRAPP NT, BRUSS J, KING JM, et al. Reliability of targeting methods in TMS for depression: beam F3 vs. 5.5 cm. Brain Stimul. 2020;13(3):578-581.
[25] SIDDIQI SH, TAYLOR SF, COOKE D, et al. Distinct symptom-specific treatment targets for circuit-based neuromodulation. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177(5):435-446.
[26] SHIRLY S, RAMESH K. Review on 2D and 3D MRI image segmentation techniques. Curr Med Imaging Rev. 2019;15(2):150-160.
[27] FOX MD, BUCKNER RL, WHITE MP, et al. Efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation targets for depression is related to intrinsic functional connectivity with the subgenual cingulate. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;72(7):595-603.
[28] TIAN Q, BILGIC B, FAN Q, et al. Improving in vivo human cerebral cortical surface reconstruction using data-driven super-resolution. Cereb Cortex. 2021;31(1): 463-482.
[29] OSECHINSKIY S, KRUGGEL F. PDE-based reconstruction of the cerebral cortex from MR images. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc.2010;2010:4278-4283.
[30] FAN Y, YAO X, XU X. A robust automated surface-matching registration method for neuronavigation. Med Phys. 2020;47(7):2755-2767.
[31] SEDRAK M, ALAMINOS-BOUZA AL, SRIVASTAVA S. Coordinate systems for navigating stereotactic space: how not to get lost. Cureus. 2020;12(6):e8578.
[32] WANG F, DONG Z, REESE TG, et al. Echo planar time-resolved imaging (EPTI). Magn Reson Med. 2019;81(6):3599-3615.
[33] MAURER CJ, FITZPATRICK JM, WANG MY, et al. Registration of head volume images using implantable fiducial markers. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1997;16(4):447-462.
[34] MONGEN MA, WILLEMS P. Current accuracy of surface matching compared to adhesive markers in patient-to-image registration. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2019; 161(5):865-870.
[35] WANG MN, SONG ZJ. Classification and analysis of the errors in neuronavigation. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(4):1131-1143.
[36] YOUNG IM, OSIPOWICZ K, MACKENZIE A, et al. Comparison of consistency between image guided and craniometric transcranial magnetic stimulation coil placement. Brain Stimul. 2022;15(6):1465-1466.
[37] NIEMINEN AE, NIEMINEN JO, STENROOS M, et al. Accuracy and precision of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Neural Eng. 2022. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aca71a.
[38] CAULFIELD KA, FLEISCHMANN HH, COX CE, et al. Neuronavigation maximizes accuracy and precision in TMS positioning: Evidence from 11,230 distance, angle, and electric field modeling measurements. Brain Stimul. 2022;15(5):1192-1205.
[39] DENG ZD, ROBINS PL, DANNHAUER M, et al. Comparison of coil placement approaches targeting dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in depressed adolescents receiving repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: an electric field modeling study. medRxiv. 2023. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1858.
[40] PAN F, SHEN Z, JIAO J, et al. Neuronavigation-guided rTMS for the treatment of depressive patients with suicidal ideation: a double-blind, randomized, sham-controlled trial. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020;108(4):826-832.
[41] ATTAL N, POINDESSOUS-JAZAT F, DE CHAUVIGNY E, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for neuropathic pain: a randomized multicentre sham-controlled trial. Brain. 2021;144(11):3328-3339.
[42] BARWOOD CH, MURDOCH BE, WHELAN BM, et al. The effects of low frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) and sham condition rTMS on behavioural language in chronic non-fluent aphasia: short term outcomes. NeuroRehabilitation. 2011;28(2):113-128.
[43] HEBEL T, GÖLLNITZ A, SCHOISSWOHL S, et al. A direct comparison of neuronavigated and non-neuronavigated intermittent theta burst stimulation in the treatment of depression. Brain Stimul. 2021;14(2):335-343.
[44] PIZZAGALLI DA, ROBERTS AC. Prefrontal cortex and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47(1):225-246.
[45] SUTHERLAND J, BELEC J, SHEIKH A, et al. Applying modern virtual and augmented reality technologies to medical images and models. J Digit Imaging. 2019;32(1):38-53.
[46] GUO Y, XU S, LI X, et al. Preliminary study on Sina (Sina Intraoperative Neurosurgical Assist) APP assisted localization of supratentorial lesions by smart phone. J Clin Neurosci. 2019;62:277-281.
[47] DOGAN I, EROGLU U, OZGURAL O, et al. Visualization of superficial cerebral lesions using a smartphone application. Turk Neurosurg. 2018;28(3):349-355.
[48] HOPMAN H, CHAN S, CHU W, et al. Personalized prediction of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation clinical response in medication-refractory depression data. Data Brief. 2021;37:107264.
[49] ZHANG Z, ZHANG H, XIE CM, et al. Task-related functional magnetic resonance imaging-based neuronavigation for the treatment of depression by individualized repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the visual cortex. Sci China Life Sci. 2021;64(1):96-106.
[50] ALEXANDER B, LAYCOCK R, CREWTHER DP, et al. An fMRI-neuronavigated chronometric TMS investigation of V5 and intraparietal cortex in motion driven attention. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017;11:638.
[51] HERWIG U, ABLER B, SCHÖNFELDT-LECUONA C, et al. Verbal storage in a premotor-parietal network: evidence from fMRI-guided magnetic stimulation. Neuroimage. 2003;20(2):1032-1041.
[52] WU SW, MALONEY T, GILBERT DL, et al. Functional MRI-navigated repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over supplementary motor area in chronic tic disorders. Brain Stimul. 2014;7(2):212-218.
[53] PITTS LL, ROGERS L, WANG X, et al. Functionally navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation to evoke lingual pressure in stroke survivors with dysphagia and healthy adults: a proof of concept trial. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2020;27(4):241-250.
[54] SEIFERT F, FUCHS O, NICKEL FT, et al. A functional magnetic resonance imaging navigated repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation study of the posterior parietal cortex in normal pain and hyperalgesia. Neuroscience. 2010;170(2):670-677.
[55] ROSCOE O BRADY RJ, GONSALVEZ I, LEE I, et al. Cerebellar-prefrontal network connectivity and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2019; 176(7):512-520.
[56] LUO X, HU Y, WANG R, et al. Individualized rTMS treatment for depression using an fMRI-based targeting method. J Vis Exp. 2021. doi: 10.3791/62687.
[57] CAO Z, XIAO X, ZHAO Y, et al. Targeting the pathological network: feasibility of network-based optimization of transcranial magnetic stimulation coil placement for treatment of psychiatric disorders. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:1079078.
[58] GRATTON C, LAUMANN TO, NIELSEN AN, et al. Functional brain networks are dominated by stable group and individual factors, not cognitive or daily variation. Neuron. 2018;98(2):439-452.
[59] GORDON EM, LAUMANN TO, GILMORE AW, et al. Precision functional mapping of individual human brains. Neuron. 2017;95(4):791-807.
[60] CASH R, COCCHI L, LV J, et al. Personalized connectivity-guided DLPFC-TMS for depression: Advancing computational feasibility, precision and reproducibility. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021;42(13):4155-4172.
[61] MOMI D, OZDEMIR RA, TADAYON E, et al. Perturbation of resting-state network nodes preferentially propagates to structurally rather than functionally connected regions. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):12458.
[62] MOMI D, OZDEMIR RA, TADAYON E, et al. Network-level macroscale structural connectivity predicts propagation of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neuroimage. 2021;229:117698.
[63] GEETER ND, DUPRÉ L, CREVECOEUR G. Modeling transcranial magnetic stimulation from the induced electric fields to the membrane potentials along tractography-based white matter fiber tracts. J Neural Eng. 2016;13(2):26028. |