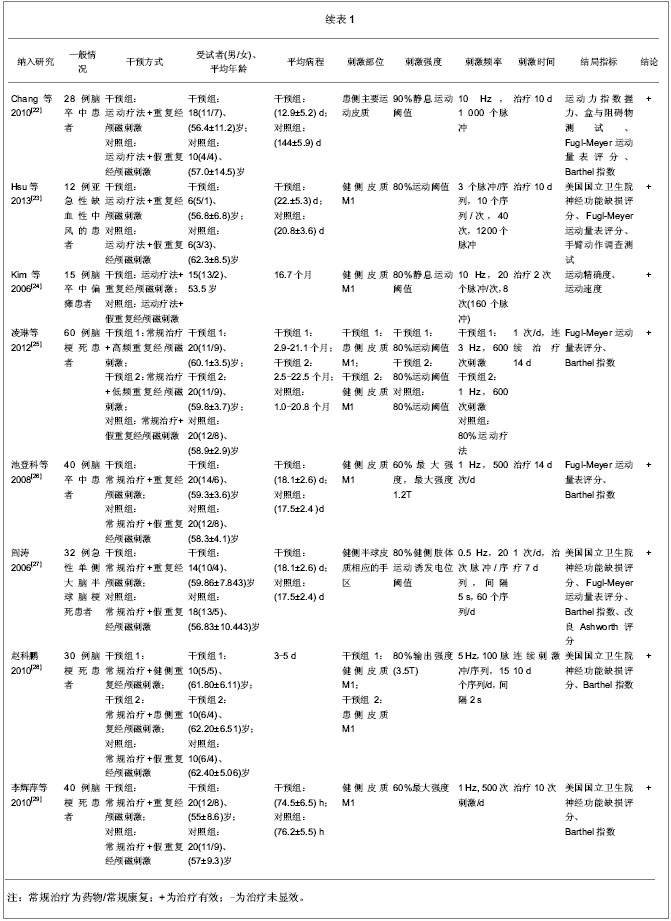
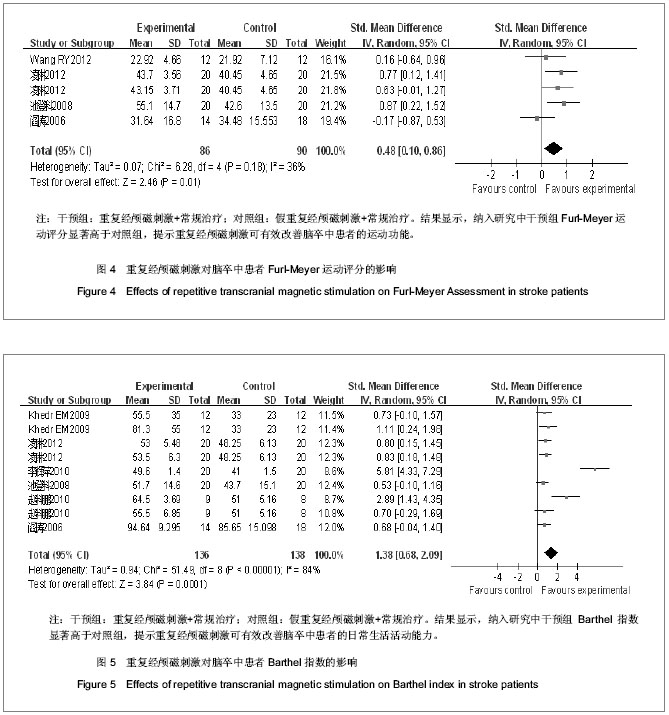
| [1] 吴兆苏,姚崇华,赵冬. 我国人群脑卒中发病率、死亡率的流行病学研究[J] . 中华流行病学杂志,2003,24(1):236-239.[2] 王伊龙,王拥军,吴敌,等. 中国卒中防治研究现状[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2007,2(1):20-37.[3] 姚滔涛,王宁华,陈卓铭. 脑卒中运动功能训练的循证医学研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(6):565-570.[4] Barker AT, Jalinous R, Freeston IL. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985;325(8437): 1106-1107.[5] 王晓明,谢建平,周树舜.重复经颅磁刺激技术及其临床应用进展[J].国外医学:物理医学与康复学分册, 2004, 24(1): 43-45.[6] Griškova I, Höppner J, Rukš?nas O, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: the method and application. Medicina (Kaunas). 2006;42(10): 792-804.[7] Conforto AB, Anjos SM, Saposnik G, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in mild to severe hemiparesis early after stroke: a proof of principle and novel approach to improve motor function. J Neurology. 2012;259(7): 1399-1405.[8] Khedr EM, Abdel-Fadeil MR, Farghali A, et al. Role of 1 and 3 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function recovery after acute ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurology. 2009;16(12): 1323-1330.[9] Khedr EM, Ahmed MA, Fathy N, et al. Therapeutic trial of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation after acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2005;65(3): 466-468.[10] Fregni F, Boggio PS, Valle AC, et al. A sham-controlled trial of a 5-day course of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the unaffected hemisphere in stroke patients. Stroke. 2006; 37(8): 2115-2122.[11] Seniów J, Bilik M, Le?niak M, et al. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Combined With Physiotherapy in Rehabilitation of Poststroke Hemiparesis A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Repair. 2012;26(9): 1072-1079.[12] Khedr EM, Etraby AE, Hemeda M, et al. Long‐term effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor function recovery after acute ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;121(1): 30-37.[13] Malcolm MP, Triggs WJ, Light KE, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation as an adjunct to constraint-induced therapy: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;86(9): 707-715.[14] Takeuchi N, Chuma T, Matsuo Y, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of contralesional primary motor cortex improves hand function after stroke. Stroke. 2005;36(12): 2681-2686.[15] Takeuchi N, Tada T, Toshima M, et al. Inhibition of the unaffected motor cortex by 1 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation enhances motor performance and training effect of the paretic hand in patients with chronic stroke. J Rehabil Med. 2008;40(4): 298-303.[16] Sasaki N, Mizutani S, Kakuda W, et al. Comparison of the effects of high-and low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on upper limb hemiparesis in the early phase of stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013; 22(4): 413-418.[17] Wang RY, Tseng HY, Liao KK, et al. rTMS Combined With Task-Oriented Training to Improve Symmetry of Interhemispheric Corticomotor Excitability and Gait Performance After Stroke A Randomized Trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(3): 222-230.[18] Theilig S, Podubecka J, Bösl K, et al. Functional neuromuscular stimulation to improve severe hand dysfunction after stroke: does inhibitory rTMS enhance therapeutic efficiency? Exp Neurol. 2011;230(1): 149-155.[19] Ackerley SJ, Stinear CM, Barber PA, et al. Combining theta burst stimulation with training after subcortical stroke. Stroke. 2010;41(7):1568-1572.[20] Emara TH, Moustafa RR, Elnahas NM, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation at 1Hz and 5Hz produces sustained improvement in motor function and disability after ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(9):1203-1209.[21] Chang WH, Kim YH, Yoo WK, et al. rTMS with motor training modulates cortico-basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits in stroke patients. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2012;30(3): 179-189.[22] Chang WH, Kim YH, Bang OY, et al. Long-term effects of rTMS on motor recovery in patients after subacute stroke. J Rehabil Med. 2010;42(8): 758-764.[23] Hsu YF, Huang YZ, Lin YY, et al. Intermittent theta burst stimulation over ipsilesional primary motor cortex of subacute ischemic stroke patients: a pilot study. Brain Stimul. 2013;6(2): 166-174.[24] Kim YH, You SH, Ko MH, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation–induced corticomotor excitability and associated motor skill acquisition in chronic stroke. Stroke. 2006;37(6): 1471-1476.[25] 凌琳, 黄国志. 不同频率重复经颅磁刺激对脑梗死患者运动功能影响的研究[J].中华神经医学杂志, 2012, 11(2): 169-172.[26] 池登科, 吴爱玲, 龚凌云, 等. 重复经颅磁刺激在卒中后运动功能康复中的作用[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2008, 6(6): 743-744.[27] 阎涛.经颅磁刺激对急性脑梗死预后的早期评价及治疗的试验研究[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2006.[28] 赵科鹏. 5HZ高频rTMS对急性期脑梗死患者运动功能恢复的影响[D]. 苏州:苏州大学, 2010.[29] 李辉萍, 徐伟, 宋治, 等.重复经颅磁刺激对急性脑梗死患者血清白介素-6水平及神经功能康复的影响[J].中国全科医学, 2010, 13(33): 3709-3711.[30] 庄立. 重复经颅磁刺激改善缺血性脑卒中动功能的作用机制[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2009, 16(3): 213-216.[31] Corti M, Patten C, Triggs W. Repetitive transcranial magneticstimulation of motor cortex after stroke: a focused review. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91(3):254-270.[32] Khedr EM, Fetoh NA. Short- and long-term effect of rTMS on motor function recovery after ischemic stroke. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2010,28(4):545-559.[33] 沈滢, 单春雷, 殷稚飞,等.重复经颅磁刺激在脑卒中后运动功能康复中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2012, 27(12): 1162-1166.[34] 户东梅, 程肖蕊, 周文霞, 等. 重复经颅磁刺激对脑卒中后认知功能障碍治疗的研究进展[J]. 生理科学进展, 2012, 43(6): 411-416. |