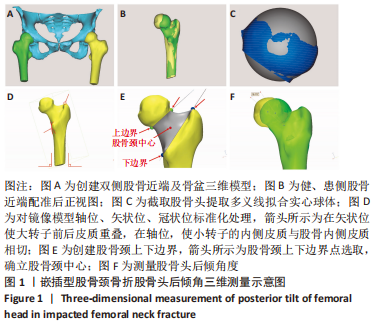
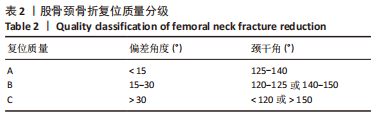
[1] JI C, ZHU Y, LIU S, et al. Incidence and risk of surgical site infection after adult femoral neck fractures treated by surgery: A retrospective case-control study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(11):e14882.
[2] CUELLAR DO, GARCIA VELEZ DA, BLEDSOE G, et al. Hybrid screw fixation for femoral neck fractures: Does it prevent mechanical failure? Injury. 2022;53(8):2839-2845.
[3] CHEN W, LI Z, SU Y, et al. Garden type I fractures myth or reality? A prospective study comparing CT scans with X-ray findings in Garden type I femoral neck fractures. Bone. 2012;51(5):929-932.
[4] AMSELLEM D, PARRATTE S, FLECHER X, et al. Non-operative treatment is a reliable option in over two thirds of patients with Garden I hip fractures. Rates and risk factors for failure in 298 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(5):985-990.
[5] ZHU J, HU H, DENG X, et al. Nomogram for predicting reoperation following internal fixation of nondisplaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):544.
[6] 杜秀鹏, 杨朝晖. 65岁以下嵌插型股骨颈骨折初始畸形程度对颈缩短的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(9):1410-1416.
[7] ZLOWODZKI M, BRINK O, SWITZER J, et al. The effect of shortening and varus collapse of the femoral neck on function after fixation of intracapsular fracture of the hip: a multi-centre cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(11):1487-1494.
[8] DAI Y, NI M, DOU B, et al. Finite element analysis of necessity of reduction and selection of internal fixation for valgus-impacted femoral neck fracture. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022;1-8. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2022.2092727.
[9] FILIPPO M, DRIESSEN A, COLAROSSI G, et al. Bipolar versus monopolar hemiarthroplasty for displaced femur neck fractures: a meta-analysis study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(3):401-410.
[10] ALHO A, BENTERUD JG, RONNINGEN H, et al. Prediction of disturbed healing in femoral neck fracture. Radiographic analysis of 149 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992;63(6):639-644.
[11] PALM H, GOSVIG K, KRASHENINNIKOFF M, et al. A new measurement for posterior tilt predicts reoperation in undisplaced femoral neck fractures. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(3):303-307.
[12] CLEMENT ND, GREEN K, MURRAY N, et al. Undisplaced intracapsular hip fractures in the elderly: predicting fixation failure and mortality. A prospective study of 162 patients. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(4):578-585.
[13] DOLATOWSKI FC, ADAMPOUR M, FRIHAGEN F, et al. Preoperative posterior tilt of at least 20 degrees increased the risk of fixation failure in Garden-I and -II femoral neck fractures. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(3): 252-256.
[14] SONG HK, CHOI HJ, YANG KH. Risk factors of avascular necrosis of the femoral head and fixation failure in patients with valgus angulated femoral neck fractures over the age of 50 years. Injury. 2016;47(12): 2743-2748.
[15] OKIKE K, UDOGWU UN, ISAAC M, et al. Not All Garden-I and II Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly Should Be Fixed. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(20):1852-1859.
[16] SJÖHOLM P, SUNDKVIST J, WOLF O, et al. Preoperative Anterior and Posterior Tilt of Garden I-II Femoral Neck Fractures Predict Treatment Failure and Need for Reoperation in Patients Over 60 Years. JB JS Open Access. 2021;6(4):e21.00045.
[17] KALSBEEK J, VAN WALSUM A, ROERDINK H, et al. More than 20° posterior tilt of the femoral head in undisplaced femoral neck fractures results in a four times higher risk of treatment failure. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022;48(2):1343-1350.
[18] YAMAMOTO T, KOBAYASHI Y, NONOMIYA H. Undisplaced femoral neck fractures need a closed reduction before internal fixation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(1):73-78.
[19] PAPADELIS E, CHAUDHRY YP, HAYES H, et al. Evaluation of the Posterior Tilt Angle in Predicting Failure of Nondisplaced Femoral Neck Fractures After Internal Fixation: A Systematic Review. J Orthop Trauma. 2022; 2023;37(2):e89-e94.
[20] SHIN WC, MOON NH, JANG JH, et al. Three-dimensional analyses to predict surgical outcomes in non-displaced or valgus impaction fractures of the femoral neck: A multicenter retrospective study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(5):991-998.
[21] WANG T, SUN J, ZHA G, et al. Analysis of Risk Factors for Femoral Head Necrosis After Internal Fixation in Femoral Neck Fractures. Orthopedics. 2014;37(12):e1117-e1123.
[22] PAPAPIETRO N, DI MARTINO A, NICCOLI G, et al. Trabecular metal screw implanted for avascular necrosis of the femoral head may complicate subsequent arthroplasty surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(6):931-938.
[23] LAMBERS FM, KOCH K, KUHN G, et al. Trabecular bone adapts to long-term cyclic loading by increasing stiffness and normalization of dynamic morphometric rates. Bone. 2013;55(2):325-334.
[24] HOELSBREKKEN SE, DOLATOWSKI FC. The influence of the hips position on measurements of posterior tilt in a valgus-impacted femoral neck fracture. Injury. 2017;48(10):2184-2188.
[25] ZAMORA T, KLABER I, ANANIAS J, et al. The influence of the CT scan in the evaluation and treatment of nondisplaced femoral neck fractures in the elderly. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(2):920543104.
[26] WU S, WANG W, ZHANG B, et al. A three-dimensional measurement based on CT for the posterior tilt with ideal inter-and intra-observer reliability in non-displaced femoral neck fractures. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2021;24(16):1854-1861.
[27] DU C, MA X, ZHANG T, et al. Reunderstanding of Garden Type I Femoral Neck Fractures by 3-dimensional Reconstruction. Orthopedics. 2013; 36(6):820-825.
[28] NANTY L, CANOVAS F, RODRIGUEZ T, et al. Femoral neck shortening after internal fixation of Garden I fractures increases the risk of femoral head collapse. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(5):999-1004.
[29] CUI S, ZHAO L, WANG Y, et al. Blood biomarkers related to osteonecrosis of femoral head by internal fixation after Garden I femoral neck fracture: a cohort study. Injury. 2021;52(11):3427-3433.
[30] MIN BW, KIM SJ. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head after osteosynthesis of femoral neck fracture. Orthopedics. 2011;34(5):349.
[31] SEO GS, DIEUDONNE G, MOONEY SA, et al. Unexplained “massive osteolysis of femoral head” (MOFH) after acetabular fracture: occurrence and suggested patho-etiology. Acta Radiol. 2017;58(6): 710-718.
[32] IKEMURA S, YAMASHITA A, HARADA T, et al. Clinical and imaging features of a subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head after internal fixation of a femoral neck fracture: a comparison with those of post-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1060):20150725.
[33] STEINBERG EL, ALBAGLI A, SNIR N, et al. Addressing posterior tilt displacement during surgery to lower failure risk of sub-capital Garden types 1 and 2 femoral fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(8):1885-1893.
[34] 张雅文, 侯国进, 周方, 等. Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折闭合复位内固定术后缺血性股骨头坏死的多因素分析[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2020,20(12):1057-1062.
[35] PEI F, ZHAO R, LI F, et al. Osteonecrosis of femoral head in young patients with femoral neck fracture: a retrospective study of 250 patients followed for average of 7.5 years. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020; 15(1):238.
[36] SZITA J, CSERHATI P, BOSCH U, et al. Intracapsular femoral neck fractures: the importance of early reduction and stable osteosynthesis. Injury. 2002;33 Suppl 3:C41-C46. |