中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (33): 5333-5339.doi: 10.12307/2024.655
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
全膝关节置换中Brainlab Knee 3导航辅助间隙平衡技术的应用优势
孙敬华,齐志明,阮文礼,张家国,杨智桐
- 大连市第二人民医院,辽宁省大连市 116100
Application advantages of Brainlab Knee 3 navigation combined with gap balance in total knee arthroplasty
Sun Jinghua, Qi Zhiming, Ruan Wenli, Zhang Jiaguo, Yang Zhitong
- Dalian Second People’s Hospital, Dalian 116100, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
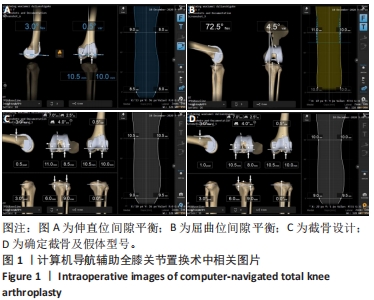
计算机导航手术:计算机导航系统使用无源光学跟踪技术,导航探针及相关手术器械实时获得手术区域关节的解剖、肢体机械轴线、器械所处的位置等相关三维信息数据,通过计算机建模方式引导术者手术的一种方法,可以提高手术的准确性,减少人为失误,导航尤其适用于严重关节畸形患者和需要进行个体化截骨的特殊患者。冠状面胫骨组件角:胫骨假体关节面内外侧连线和膝关节中心与股骨头中心连线的夹角,它是评估胫骨假体安放准确与否的重要指标,小于90°为内翻,大于90°为外翻。
背景:近年来,计算机导航技术辅助关节置换逐渐受到医疗领域的关注。文献报道计算机导航在全膝关节置换中的应用临床效果不一。为了探索新一代Brainlab Knee 3导航系统的临床效果,进行了此项研究。
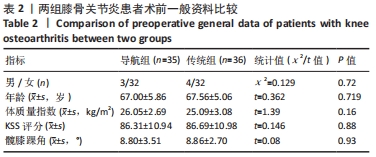
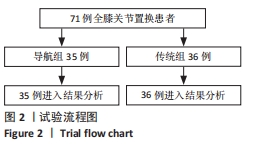
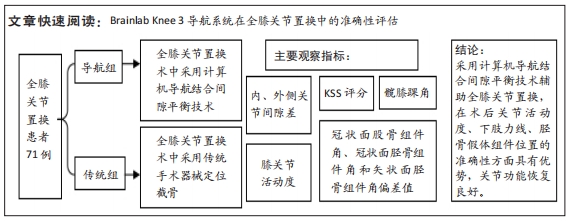
目的:分析计算机导航系统(Brainlab Knee 3)结合间隙平衡技术在全膝关节置换中的应用效果。方法:2020年11月至2021年5月大连市第二人民医院关节外科收治71例行全膝关节置换患者,导航组35例,术中采用计算机导航结合间隙平衡技术行全膝关节置换;传统组36例,术中采用传统手术器械定位截骨。比较两组患者术中内、外侧关节间隙差;膝关节活动度、 KSS评分;髋膝踝角;冠状面股骨组件角、冠状面胫骨组件角和矢状面胫骨组件角偏差值。
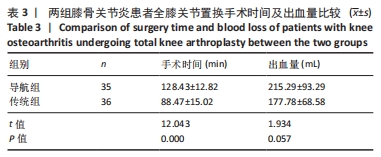
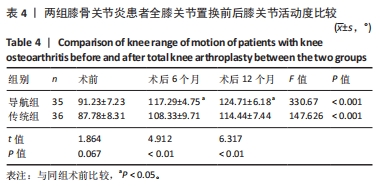
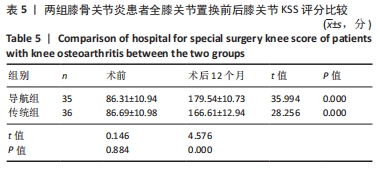
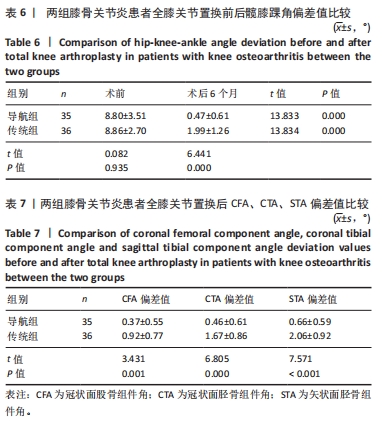
结果与结论:①导航组伸直位内外侧间隙差0,1,2 mm的患者分别为19,14,2例;屈膝90°位内外侧间隙差0,1,2 mm的患者分别为18,15,2例。传统组伸直位内外侧间隙差0,1,2 mm的患者分别为10,20,6例;屈膝90°位内外侧间隙差0,1,2 mm的患者分别为10,15,8例。②导航组手术时间长于传统组(P < 0.05),导航组有2例患者术后形成下肢肌间静脉血栓,传统组患者均无并发症。③置换后6,12个月两组患者膝关节活动度均明显增加,导航组膝关节活动度高于传统组(P < 0.05)。④置换后12个月两组患者KSS评分均明显增加,导航组KSS评分高于传统组(P < 0.05)。⑤置换后6个月髋膝踝角、冠状面股骨组件角、冠状面胫骨组件角、矢状面胫骨组件角偏差值均显著小于传统组(P < 0.05)。⑥结果表明,采用计算机导航结合间隙平衡技术辅助全膝关节置换对关节活动度、下肢力线、胫骨假体组件位置的准确性方面具有优势,置换后关节功能恢复良好。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1500-3792 (孙敬华)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: