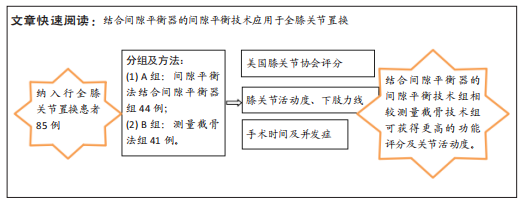
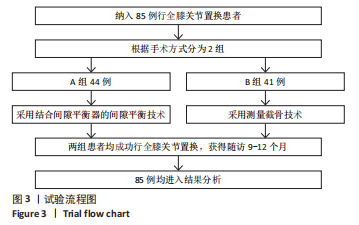
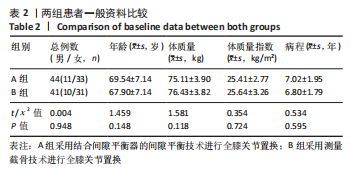
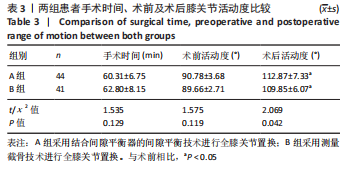
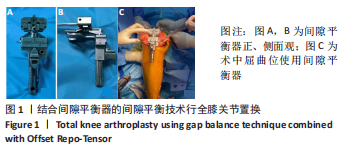
[1] MOON YW, KIM HJ, AHN HS, et al. Comparison of soft tissue balancing, femoral component rotation, and joint line change between the gap balancing and measured resection techniques in primary total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(39):e5006.
[2] HE Q, SUN C, MA J, et al. Is gap balancing superior to measured resection technique in total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis. Arthroplasty. 2020;2(1): 3.
[3] 陆斌, 杨卧龙, 高胜山,等. 测量截骨联合间隙平衡技术在全膝关节置换股骨外旋截骨中的应用 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(15):2323-2328.
[4] 齐志远, 陈秀民, 王在斌,等. 全膝关节置换术中测量截骨与间隙平衡截骨的疗效比较 [J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(2):144-147.
[5] EID AS, NASSAR WA, FAYYAD TA. Total knee replacement with tibial tubercle osteotomy in rheumatoid patients with stiff knee. Int Orthop. 2016;40(11): 2289-2293.
[6] NAGAI K, MURATSU H, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Soft tissue balance changes depending on joint distraction force in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(3):520-524.
[7] BERGER RA, RUBASH HE, SEEL MJ, et al. Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;(286):40-47.
[8] VAIDYA NV, DESHPANDE AN, PANJWANI T, et al. Robotic-assisted TKA leads to a better prosthesis alignment and a better joint line restoration as compared to conventional TKA: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(2):621-626.
[9] WATERSON H, WALKER R, KOOPMANS P, et al. Gap balanced adjusted mechanical alignment versus measured resection mechanical alignment: a randomised controlled trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(4):2141-2151.
[10] TAPASVI SR, SHEKHAR A, PATIL SS, et al. Comparison of Gap Balancing vs Measured Resection Technique in Patients Undergoing Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty: One Technique per Knee. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(3):732-740.
[11] FRANCESCHINI V, NODZO SR, GONZALEZ DELLA VALLE A. Femoral Component Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparison Between Transepicondylar Axis and Posterior Condylar Line Referencing. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(12):2917-2921.
[12] WEBER KL, JEVSEVAR DS, MCGRORY BJ. AAOS Clinical Practice Guideline: Surgical Management of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Evidence-based Guideline. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(8):e94-e96.
[13] 辛雷, 苏佳灿. 膝关节功能评分:现状与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(39):7367-7370.
[14] GUSTKE K. Use of smart trials for soft-tissue balancing in total knee replacement surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(11 Suppl A):147-150.
[15] NAGAI K, MURATSU H, TAKEOKA Y, et al. The Influence of Joint Distraction Force on the Soft-Tissue Balance Using Modified Gap-Balancing Technique in Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(10):2995-2999.
[16] FERREIRA MC, FRANCIOZI CES, KUBOTA MS, et al. Is the Use of Spreaders an Accurate Method for Ligament Balancing? J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(7):2262-2267.
[17] 樊宗庆, 储成顶, 聂宇,等. 全膝关节置换个性化联合间隙平衡[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(20):1830-1835.
[18] GRIFFIN FM, MATH K, SCUDERI GR, et al. Anatomy of the epicondyles of the distal femur: MRI analysis of normal knees. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(3):354-359.
[19] 吴建明, 胡伟, 刘向阳,等. 全膝关节置换中采用测量截骨与间隙平衡技术的对比分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18):2817-2821.
[20] 赵永正, 吕波, 许瀚,等. 全膝关节置换术中软组织平衡测量装置的研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程研究,2021,40(1):100-104.
[21] 柴瑞宝,刘瑞,张子安,等. 间隙平衡与测量截骨技术在全膝关节置换的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(9):804-808.
[22] POILVACHE PL, INSALL JN, SCUDERI GR, et al. Rotational landmarks and sizing of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(331):35-46.
[23] SCHNURR C, NESSLER J, KÖNIG DP. Is referencing the posterior condyles sufficient to achieve a rectangular flexion gap in total knee arthroplasty? Int Orthop. 2009; 33(6):1561-1565.
[24] 洪伟祥. 测量截骨与间隙平衡技术在全膝关节置换术中应用的相关研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2016.
[25] SHETH NP, HUSAIN A, NELSON CL. Surgical Techniques for Total Knee Arthroplasty: Measured Resection, Gap Balancing, and Hybrid. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017; 25(7):499-508.
[26] DENNIS DA. Measured resection: an outdated technique in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2008;31(9):940,943-944.
[27] FEHRING TK. Rotational malalignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(380):72-79.
[28] XIAO Q, LIU B, ZHAO B. Gap balancing improve squat function and knee function: a randomized controlled trial comparing gap balancing and measured resection. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):242.
[29] 苗卫华, 王宏, 李康. 测量截骨联合间隙平衡全膝关节置换治疗膝骨关节炎[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(14):1254-1258.
[30] 高强, 姚运峰. 全膝关节表面置换术后膝前疼痛的原因与治疗方法[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(12):1340-1343.
[31] NAGAI K, MURATSU H, KANDA Y, et al. Intraoperative soft tissue balance using novel medial preserving gap technique in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty: comparison to measured resection technique. Knee Surgery Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11):3474-3481. |