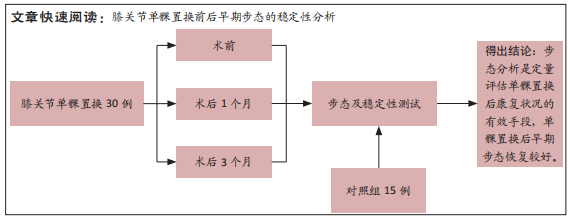
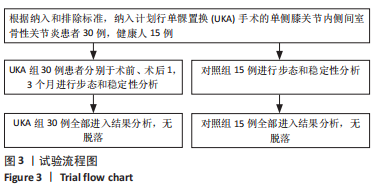
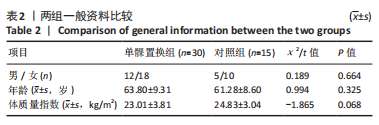
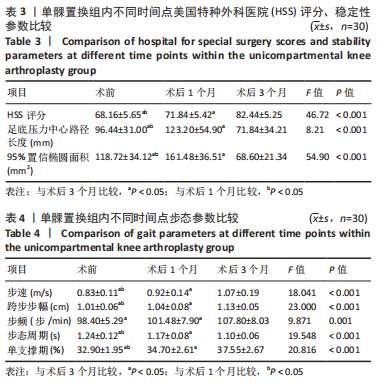
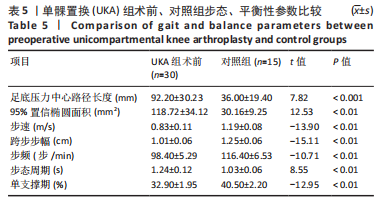
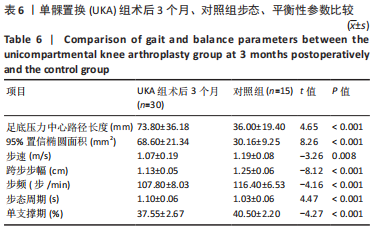
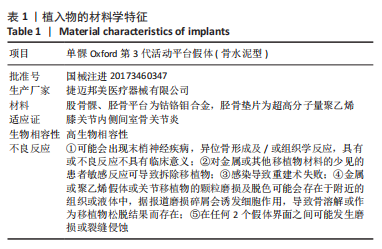
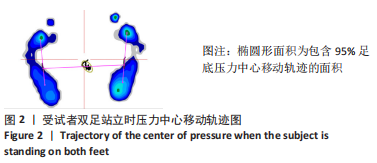
[1] WILSON HA, MIDDLETON R, ABRAM SGF, et al. Patient relevant outcomes of unicompartmental versus total knee replacement: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2019;364:l352.
[2] BANNURU RR, OSANI MC, VAYSBROT EE, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11):1578-1589.
[3] 边焱焱, 程开源, 常晓, 等. 2011至2019年中国人工髋膝关节置换手术量的初步统计与分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(21):1453-1460.
[4] Vissers MM, de Groot IB, Reijman M, et al. Functional capacity and actual daily activity do not contribute to patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11:121.
[5] Bach CM, Nogler M, Steingruber IE, et al. Scoring systems in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(399):184-196.
[6] 李远栋, 刘爱峰, 张君涛, 等. 步态分析在膝关节骨性关节炎中的应用研究进展[J]. 国际生物医学工程杂志,2020,43(1):75-79.
[7] 吴东, 杨敏之, 曹正, 等. 膝关节单髁置换术研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(2):145-150.
[8] Chang A, Hurwitz D, Dunlop D, et al. The relationship between toe-out angle during gait and progression of medial tibiofemoral osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(10):1271-1275.
[9] 张启栋, 郭万首, 刘朝晖, 等. 内翻畸形膝骨关节炎软骨磨损的临床研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(23):2345-2350.
[10] Kim KT, Lee S, Lee JI, et al. Analysis and Treatment of Complications after Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28(1):46-54.
[11] El-Galaly A, Kappel A, Nielsen PT, et al. Revision Risk for Total Knee Arthroplasty Converted from Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Comparison with Primary and Revision Arthroplasties, Based on Mid-Term Results from the Danish Knee Arthroplasty Registry. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(22):1999-2006.
[12] Kahlenberg CA, Richardson SS, Gruskay JA, et al. Trends in Utilization of Total and Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty in the United States. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(10):1138-1141.
[13] Kuo AC, Giori NJ, Bowe TR, et al. Comparing Methods to Determine the Minimal Clinically Important Differences in Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Veterans Undergoing Elective Total Hip or Knee Arthroplasty in Veterans Health Administration Hospitals. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(5):404-411.
[14] 邬波, 柳椰, 杜明昌, 等. 膝关节单髁置换治疗膝内侧间室骨关节炎的疗效观察[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(2):123-125,131.
[15] Khanna G, Singh JA, Pomeroy DL, et al. Comparison of patient-reported and clinician-assessed outcomes following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2011;93(20):e117.
[16] Studenski S, Perera S, Patel K, et al. Gait speed and survival in older adults. JAMA. 2011;305(1):50-58.
[17] 瞿晓娜, 张腾宇, 王喜太, 等. 行走速度对步态参数影响的实验研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(3):257-259.
[18] McKean KA, Landry SC, Hubley-Kozey CL, et al. Gender differences exist in osteoarthritic gait. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007;22(4):400-409.
[19] Casartelli NC, Item-Glatthorn JF, Bizzini M, et al. Differences in gait characteristics between total hip, knee, and ankle arthroplasty patients: a six-month postoperative comparison. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:176.
[20] 柯鹏辉, 尹宗生, 陆鸣, 等. 单髁与全膝关节置换术后步态与平衡能力比较[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020,14(1):11-16.
[21] Nha KW, Shon OJ, Kong BS, et al. Gait comparison of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty during level walking. PloS One. 2018;13(8):e0203310.
[22] 郭甲瑞. 单髁与全膝关节置换术对单侧膝骨关节炎患者步态和运动学参数影响研究[J]. 人民军医,2021,64(4):318-320.
[23] Kim MK, Yoon JR, Yang SH, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty fails to completely restore normal gait patterns during level walking. Knee surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(11):3280-3289.
[24] 中国老年保健医学研究会老龄健康服务与标准化分会, 《中国老年保健医学》杂志编辑委员会. 中国老年人跌倒风险评估专家共识(草案) [J]. 中国老年保健医学,2019,17(4):47-48,50.
[25] 徐欣, 温子星. 人体动态稳定性控制理论在老年人防跌倒中的应用[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2017,23(11):1254-1257.
[26] Baumann F, Bahadin O, Krutsch W, et al. Proprioception after bicruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty is comparable to unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(6):1697-1704.
[27] Zhang W, Low LF, Schwenk M, et al. Review of Gait, Cognition, and Fall Risks with Implications for Fall Prevention in Older Adults with Dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2019;48:17-29.
[28] Henry M, Baudry S. Age-related changes in leg proprioception: implications for postural control. J Neurophysiol. 2019;122(2):525-538.
[29] Schultz RA, Miller DC, Kerr CS, et al. Mechanoreceptors in human cruciate ligaments. A histological study. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(7):1072-1076.
[30] Zhang C, Sun W, Yu B, et al. Effects of exercise on ankle proprioception in adult women during 16 weeks of training and eight weeks of detraining. Res Sports Med. 2015;23(1):102-113.
[31] Sadeghi H, Hakim MN, Hamid TA, et al. The effect of exergaming on knee proprioception in older men: A randomized controlled trial. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2017;69:144-150.
[32] Soleimani R, Jalali MM, Mirbolook AR. Predictors of Fear of Falling among Iranian Older Adults with Hip Fracture and Controls. Clin Gerontol. 2020;43(4):391-399.
[33] Mueller MJ, Maluf KS. Tissue adaptation to physical stress: a proposed “Physical Stress Theory” to guide physical therapist practice, education, and research. Phys Ther. 2002;82(4):383-403.
[34] Fetzer GB, Callaghan JJ, Templeton JE, et al. Posterior cruciate-retaining modular total knee arthroplasty: a 9- to 12-year follow-up investigation. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(8):961-966. |