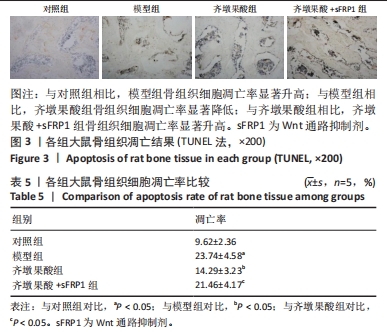
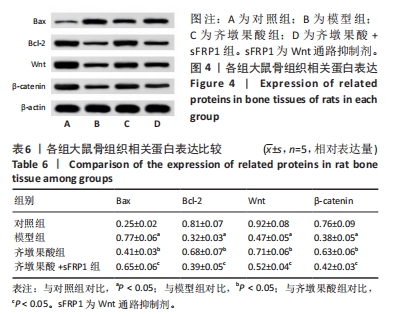
[1] YANG F, ZHANG X, SONG T, et al. Huogu injection alleviates SONFH by regulating adipogenic differentiation of BMSCs via targeting the miR-34c-5p/MDM4 pathway. Gene. 2022;838:146705.
[2] PENG P, NIE Z, SUN F, et al. Glucocorticoids induce femoral head necrosis in rats through the ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(1):312-321.
[3] HUA KC, YANG XG, FENG JT, et al. The efficacy and safety of core decompression for the treatment of femoral head necrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):306.
[4] HOFMANN A, FISCHER B, SCHLEIFENBAUM S, et al. Atraumatic femoral head necrosis: a biomechanical, histological and radiological examination compared to primary hip osteoarthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(11):3093-3099.
[5] CASTELLANO JM, RAMOS-ROMERO S, PERONA JS. Oleanolic Acid: Extraction, Characterization and Biological Activity. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):623.
[6] SHU B, ZHAO Y, WANG Y, et al. Oleanolic Acid Enhances Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Osteogenic Potential by Inhibition of Notch Signaling. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7002.
[7] ZHAO D, SHU B, WANG C, et al.Oleanolic acid exerts inhibitory effects on the late stage of osteoclastogenesis and prevents bone loss in osteoprotegerin knockout mice. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(1):152-164.
[8] ZHU D, WANG Z, ZHANG G, et al. Periostin promotes nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2022;36(7):e22369.
[9] MARINI F, GIUSTI F, PALMINI G, et al. Role of Wnt signaling and sclerostin in bone and as therapeutic targets in skeletal disorders. Osteoporos Int. 2023;34(2):213-238.
[10] SHEN J, SUN Y, LIU X, et al. EGFL6 regulates angiogenesis and osteogenesis in distraction osteogenesis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):415.
[11] WANG Y, ZHANG X, SHAO J, et al. Adiponectin regulates BMSC osteogenic differentiation and osteogenesis through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3652.
[12] YUAN S, ZHANG C, WANG B. Neohesperidin promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via BMP2-Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(2):187-201.
[13] LIU S, HUANG Y, WANG C, et al. Epimedium protects steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head in rats by inhibiting autophagy. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(6):5047-5052.
[14] ZHAO D, LI X, ZHAO Y, et al. Oleanolic acid exerts bone protective effects in ovariectomized mice by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2018;137(1):76-85.
[15] ZHANG C, ZOU YL, MA J, et al. Apoptosis associated with Wnt/β-catenin pathway leads to steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:132.
[16] LIU Y, SHE GR, CHEN SX. Magnetic resonance image diagnosis of femoral head necrosis based on ResNet18 network. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;208:106254.
[17] PENG P, NIE Z, SUN F, et al. Glucocorticoids induce femoral head necrosis in rats through the ROS/JNK/c-Jun pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(1):312-321.
[18] YANG N, SUN H, XUE Y, et al. Inhibition of MAGL activates the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway to attenuate glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(6):e447-e456.
[19] WEI Q, YAN Q, LIN D, et al. Symptomatic femoral head necrosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective case-control study. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022; 10(6):e633.
[20] YU Y, WANG S, ZHOU Z. Cartilage Homeostasis Affects Femoral Head Necrosis Induced by Methylprednisolone in Broilers. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4841.
[21] SUREDA A, MONSERRAT-MESQUIDA M, PINYA S, et al. Hypotensive Effects of the Triterpene Oleanolic Acid for Cardiovascular Prevention. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2021; 14(6):935-942.
[22] WU Y, GAO LJ, FAN YS, et al. Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis on the Action Mechanism of Oleanolic Acid to Alleviate Osteoporosis. ACS Omega. 2021;6(42):28410-28420.
[23] ADHIKARI N, NEUPANE S, ARYAL YP, et al. Effects of oleanolic acid acetate on bone formation in an experimental periodontitis model in mice. J Periodontal Res. 2019; 54(5):533-545.
[24] CAO S, TIAN XL, YU WX, et al. Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid Improve Bone Properties and Calcium Balance and Modulate Vitamin D Metabolism in Aged Female Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1435.
[25] XIE BP, SHI LY, LI JP, et al. Oleanolic acid inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via ER alpha/miR-503/RANK signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;117:109045.
[26] CUEVAS PL, AELLOS F, DAWID IM, et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Craniomaxillofacial Osteocytes. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(2):228-240.
[27] 林天烨, 吴智明, 张文胜, 等. 复方生脉成骨胶囊修复激素性股骨头坏死的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):200-207.
[28] ZHANG M, GAO Y, LI Q, et al. Downregulation of DNA methyltransferase-3a ameliorates the osteogenic differentiation ability of adipose-derived stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):397.
[29] CHEN XJ, SHEN YS, HE MC, et al. Polydatin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cells by activating the BMP2-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108746.
[30] SHEN G, REN H, SHANG Q, et al. Foxf1 knockdown promotes BMSC osteogenesis in part by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. EBioMedicine. 2020;52:102626.
|