中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (27): 4397-4404.doi: 10.12307/2024.546
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白和信号通路在运动防治肌少症中的作用
郭 辉,孔健达,田春兰
- 曲阜师范大学体育科学学院,山东省济宁市 272000
-
收稿日期:2023-10-07接受日期:2023-11-06出版日期:2024-09-28发布日期:2024-01-29 -
通讯作者:田春兰,硕士,教授,硕士生导师,曲阜师范大学体育科学学院,山东省济宁市 272000 -
作者简介:郭辉,男,1997年生,山东省人,汉族,曲阜师范大学体育科学学院在读硕士,主要从事运动训练及其生理生化机制研究。 -
基金资助:山东省社会科学规划研究项目一般项目(17CTYJ10),项目负责人:田春兰
The role of mitochondrial autophagy-related receptor proteins and signaling pathways in the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia through exercise
Guo Hui, Kong Jianda, Tian Chunlan
- School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-07Accepted:2023-11-06Online:2024-09-28Published:2024-01-29 -
Contact:Tian Chunlan, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Guo Hui, Master candidate, School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Social Science Planning Research Project (General Project), No. 17CTYJ10 (to TCL)
摘要:
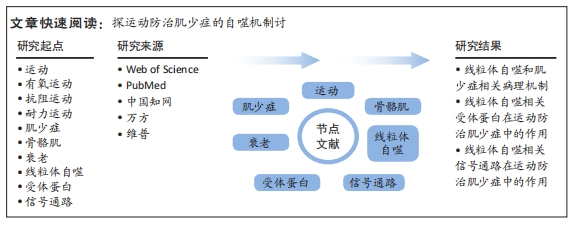
文题释义:
线粒体自噬:是一种特殊形式的自噬过程,指的是细胞通过将旧或损坏的线粒体包裹在自噬泡中,然后将其降解和回收的过程。肌少症:是一种随着年龄增长而出现的健康问题,其特征为骨骼肌组织量和功能的逐渐减少,可能导致肌肉无力、脆弱骨折和身体功能下降,其可能由多种因素引起,包括年龄相关的代谢变化、慢性疾病、营养不良和缺乏运动等。
背景:肌少症是一种衰老相关的退行性综合征,线粒体自噬和运动防治肌少症已被证明密切相关,但尚缺乏详细介绍其中具体的受体蛋白和信号通路在运动防治肌少症中作用的综述。
目的:综述详细介绍线粒体自噬相关具体的受体蛋白和信号通路在运动防治肌少症中的作用。方法:在2023-02-01/04-01之间进行了文献检索,检索文献时限从各数据库建库至2023年4月,数据库包括Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网、万方和维普。涵盖了“肌少症,衰老,老年,线粒体,线粒体功能,蛋白,通路”等关键词,严格按照纳入和排除标准进行筛选,最终纳入文献76篇进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①肌少症是随着年龄增长肌肉质量和功能下降的疾病,其发生机制涉及神经肌肉功能下降、慢性炎症、酸碱失衡和线粒体功能障碍等。②线粒体自噬是细胞清除受损线粒体的重要过程,其中相关受体蛋白以及信号通路参与线粒体自噬的调控,运动可以通过调节这些受体蛋白和信号通路的活性,促进线粒体自噬的发生,对防治肌少症具有重要作用。③运动通过调控多个通路来促进线粒体自噬,包括上调AMPK、磷酸化ULK1、降低线粒体能量、增加与AMBRA1相关蛋白的表达、调控PINK1/Parkin通路等,从而改善肌少症引发的线粒体功能障碍;此外,运动还能激活mTOR通路促进肌肉生长和增加对葡萄糖的摄取,预防和治疗肌少症。④未来需要进一步深入研究运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白和信号通路的具体作用机制和调控途径,开展更多的人体临床研究,以推动该领域的进一步发展。
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-4769-443X(郭辉);https://orcid.org/0009-0000-1899-0194(田春兰)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
郭 辉, 孔健达, 田春兰. 线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白和信号通路在运动防治肌少症中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(27): 4397-4404.
Guo Hui, Kong Jianda, Tian Chunlan. The role of mitochondrial autophagy-related receptor proteins and signaling pathways in the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia through exercise[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4397-4404.
2.2 线粒体自噬和肌少症相关病理机制 肌少症是一种衰老相关的退行性综合征,与线粒体自噬密切相关[10-14]。线粒体自噬是细胞通过选择性地降解和清除受损或老化的线粒体来维持细胞内线粒体的质量和功能[5,10-11]。其中,FUNDC1、AMBRA1和PHBs是参与线粒体自噬调控的重要受体蛋白,它们通过与其他蛋白因子相互作用,并参与一系列信号通路的调节[7]。PINK1/Parkin通路通过识别和标记受损的线粒体,并通过产生泛素链来促进线粒体的自噬[8]。AMPK/PGC-1α通路参与调节线粒体的数量、合成和质量,以维持线粒体的正常代谢和功能[9]。BNIP3/NIX通路通过连接自噬体和线粒体,起到清除受损线粒体的作用[8]。运动能够通过调控这些受体蛋白和信号通路的表达和活性,促进线粒体自噬的发生,对于预防和治疗肌少症具有重要作用[1]。下文将重点论述运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关的受体蛋白和信号通路。
2.3 线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白在运动防治肌少症中的作用 线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白在肌少症预防和治疗中起着重要作用。FUNDC1是一种位于外线粒体膜上的蛋白质,通过与LC3结合实现线粒体自噬的功能。在缺氧条件下,FUNDC1被去磷酸化,增加与LC3的相互作用并诱导线粒体自噬。FUNDC1还通过激活AMPK-ULK1信号通路参与线粒体自噬。运动可以通过激活AMPK和磷酸化ULK1来诱导线粒体自噬,改善肌肉中FUNDC1的丧失导致的线粒体能量和运动能力降低以及线粒体自噬缺陷。此外,FUNDC1还参与脂肪利用、增加运动能力、线粒体质量控制和维持代谢稳态。AMBRA1是与线粒体自噬调节密切相关的蛋白质,通过与BCL-2的相互作用在线粒体自噬中发挥着关键作用。AMBRA1还与Parkin和ULK1等蛋白质因子相互作用,对线粒体质量控制和线粒体自噬的启动和进程起调节作用。运动可以下调AMBRA1的表达水平,增加与AMBRA1相关的线粒体自噬相关蛋白的表达,从而改善肌少症。PHBs是线粒体自噬的受体蛋白,主要位于线粒体内膜中。PHBs可以调控PINK1/Parkin通路,启动和促进线粒体自噬。运动能够增加PHBs的表达,防治肌少症引发的线粒体功能障碍。综上,运动通过调控线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白的表达和功能,实现对肌少症的预防和治疗作用。运动的效果与运动时间和强度直接相关,可以通过激活特定的信号通路和调控因子来诱导线粒体自噬,增加线粒体功能,改善肌少症的症状。线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白运动防治肌少症中作用的机制图见图3。
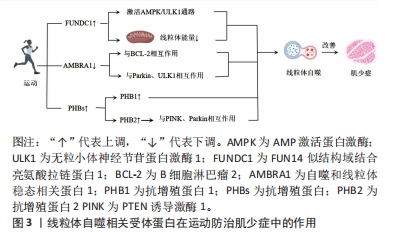
2.3.1 FUNDC1 是一种位于外线粒体膜上的蛋白质,作为一种有氧条件下调节哺乳动物线粒体清除的线粒体自噬受体,与LC3结合实现其功能[15]。FUNDC1还在内质网-线粒体接触位点接口起调节作用。在缺氧条件下,FUNDC1被去磷酸化,增加与LC3的相互作用并诱导线粒体自噬[16]。FUNDC1还通过激活AMPK-ULK1信号通路参与线粒体自噬[17]。运动通过激活AMPK能量感受器和磷酸化ULK1来诱导线粒体自噬[18]。肌肉中FUNDC1的丧失会导致线粒体能量和运动能力降低,以及线粒体自噬缺陷[18]。衰老与BNIP3L、FUNDC1和NIX引起的mtDNA损伤积累和线粒体自噬程序破坏有关[19]。研究表明,跑步机运动和抗阻训练可以激活肌肉中的AMPK/Ulk1依赖的自噬,并减少肌细胞凋亡。FUNDC1还参与脂肪利用、增加运动能力、线粒体质量控制和维持代谢稳态[15-19]。
研究表明,运动能够影响FUNDC1的表达,从而促进线粒体自噬。在一项研究中,GAO等[15]发现,运动能够调节FUNDC1的表达,并通过激活AMPK-ULK1途径来诱导线粒体自噬,他们还观察到,脉冲电刺激能够诱导线粒体自噬,并可能潜在地激活AMPK-ULK1途径,从而进一步促进FUNDC1的表达。此外,FU等[18]认为FUNDC1相关的缺陷性线粒体自噬作用可能与MAPK信号通路和炎症反应以及代谢紊乱有关。另外,LAKER等[17]发现,急性跑步运动会引起小鼠骨骼肌中的线粒体氧化应激,并在运动后的6 h触发线粒体自噬,这个过程与FUNDC1相关,发生在Ampk酪氨酸172位点磷酸化和类似unc-51的自噬激活激酶1(Ulk1)在丝氨酸555位点磷酸化之前。通过在小鼠骨骼肌中表达显性负性和常活性的Ampk,研究还证明Ulk1的激活依赖于Ampk。此外,研究人员还发现运动诱导的代谢适应需要Ulk1的参与。此外,于亮等[20]发现,运动可以提高LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ比值,降低p62蛋白的表达水平,增加FUNDC1和ULK1蛋白的表达水平以及AMPKα的磷酸化水平;与进行4周中等强度运动(M-ex)的组相比,进行4周高强度运动(Hi-ex)的组在这些蛋白表达上变化幅度更大。
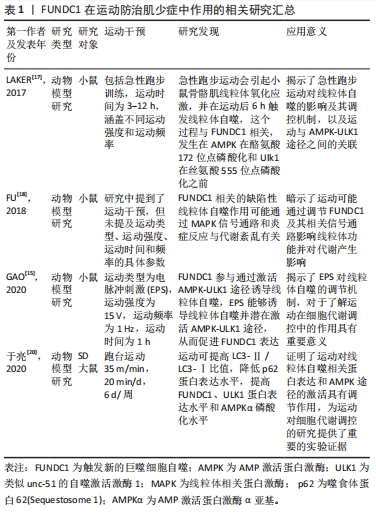
综上所述,运动通过调控FUNDC1并激活AMPK-ULK1途径诱导线粒体自噬,从而改善肌少症。此外,运动的效果与运动时间和强度直接相关。这些研究结果揭示了运动对于线粒体自噬的诱导机制可能是通过AMPK-ULK1通路影响FUNDC1表达而实现的。FUNDC1在运动防治肌少症中作用的相关研究见表1。
2.3.2 AMBRA1 是与细胞自噬调节密切相关的蛋白质,它在在线粒体自噬中起着重要的作用[21]。研究发现,AMBRA1与B细胞淋巴瘤-2(BCL-2)蛋白的相互作用在在线粒体自噬中发挥着关键作用[22]。AMBRA1与BCL-2之间的相互作用可以调节BCL-2的功能,并影响细胞的凋亡过程[22]。研究还发现,AMBRA1过表达可以抑制B细胞淋巴瘤细胞的增殖和生存,这说明AMBRA1与BCL-2的相互作用在抑制B细胞淋巴瘤中具有重要的生物学功能[23]。
除了与BCL-2的相互作用外,AMBRA1还与其他蛋白质因子在在线粒体自噬中发生相互作用。AMBRA1与Parkin和ULK1等蛋白质的相互作用对线粒体质量控制过程发挥着重要作用[24]。AMBRA1通过与Parkin相互作用促进Parkin对线粒体的定位和选择性降解。此外,AMBRA1与ULK1的相互作用调节线粒体自噬的启动和进程[24]。AMBRA1与ULK1的结合有助于线粒体自噬的启动,通过与ULK1相互作用,AMBRA1促进ULK1的激活和定位到线粒体,从而启动线粒体自噬[25]。AMBRA1还通过与ULK1形成复合物,调节线粒体自噬的进程,增强ULK1在线粒体上膜结构形成的能力,促进线粒体自噬的进行[26]。
运动对AMBRA1的调控也具有重要的影响。GAMBAROTTO等[27]的研究结果表明,游泳运动可以下调小鼠腓肠肌中AMBRA1的表达水平,当AMBRA1缺失时,肌纤维生长延缓,线粒体自噬受抑制,泛素蛋白积累增加,细胞增殖不平衡和细胞凋亡增加。此外,运动还能增加与AMBRA1相关的线粒体自噬相关蛋白,如Beclin-1和Parkin。衰老会引发肌少症,导致Beclin-1和AMBRA1的表达水平以及自噬体和自噬水平降低,但运动可以恢复这些蛋白的表达和自噬水平[28]。另外,研究发现,老年小鼠肌肉中AMBRA1的表达上升,Beclin-1、ATG7和肌肉特异性RING指蛋白1的表达水平上调[29]。同时,只有老年训练小鼠的腓肠肌质量/体质量比显著增加。运动能够增加与AMBRA1相关的自噬相关蛋白,如Beclin-1和Parkin,进而增加由耐力训练和体力活动引起的线粒体密度[30]。
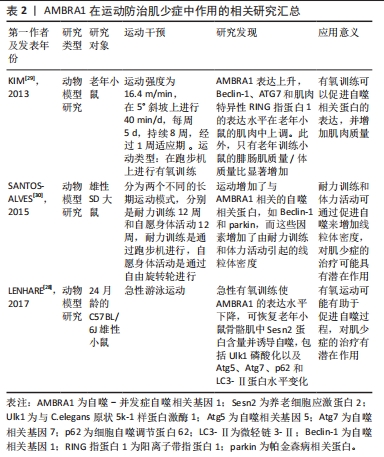
综上所述,AMBRA1是线粒体自噬的关键蛋白质。当AMBRA1表达水平较低时,会抑制线粒体自噬,并影响与之相关的调控因子的功能。运动通过下调AMBRA1表达水平来防治肌少症,并增加与AMBRA1相关的线粒体自噬相关蛋白的表达。表2总结了AMBRA1在运动防治肌少症中的作用及相关研究。
2.3.3 PHBs PHBs亦可作为线粒体自噬的受体蛋白,主要位于线粒体内膜中[31]。PHBs主要包括PHB1和PHB2。YAN等[32]的研究认为,PHB2能够稳定PINK1的表达和增加线粒体中的Parkin表达,进而激活PINK1/Parkin通路介导线粒体自噬;同时,PHB2能够调控PINK1/Parkin通路,但PARL影响PHB2的活性,PHB2介导去极化线粒体中PINK1稳定表达时需要PARL-PGAM5轴(presenilin-associated rhomboid-like protein-phosphoglycerate mutase family member 5 axis)来调控,此时PHB2与磷酸甘油酸变位酶5(phosphoglycerate mutase family member 5,PGAM5)结合可以避免线粒体早老素相关菱形蛋白(presenilin-associated rhomboid-
like protein,PARL)对PHB2活性的影响;PHB2在线粒体去极化后倾向于和PARL结合,合成释放PGAM5,PINK1附着在线粒体外膜上,激活线粒体自噬[33]。PINK1亦能够调控Parkin在线粒体中募集,并促进线粒体外膜蛋白的泛素化和降解,进而激活线粒体自噬。然而,线粒体外膜破裂时,PHB2和LC3在线粒体内膜相互作用[34]。另外,YAN等[32]还认为,线粒体基质中未折叠蛋白的积累亦会刺激Parkin向线粒体中募集。当PHB2表达水平过高时,Parkin表达水平升高激活线粒体自噬。PHB1和PHB2介导线粒体自噬通过维持线粒体功能保护性地提高线粒体寿命,反之,线粒体寿命减少[35]。PHBs在高能细胞中表达,PHBs复合物刺激ATP合酶复合物能够导致线粒体功能发生障碍,PHB1表达增加能够提升复合物Ⅰ的活性[36]。另外,PHB2能够稳定线粒体呼吸复合体的亚单位,PHB复合物下调会降低呼吸链中其他复合物的活性,而且PHBs功能受限与衰老有关[37],PHB2表达增加时能够降低造血细胞特异蛋白1相关蛋白X1(hematopoietic cell specific protein 1-associated protein X1,HAX1)的活性,HAX1是一种抗凋亡蛋白,其能够抑制线粒体结构的完整性,并增加Caspase 9/3的活性[38]。PHBs表达水平较低时能导致线粒体受损,影响线粒体结构的完整性,进而导致复合物Ⅰ的活性降低并增加活性氧含量[39]。YAN等[32]认为,PHBs亦能够和Parkin相互作用,Parkin介导线粒体损伤时能够促进PHB2复合物与LC3-Ⅱ蛋白结合,进而促进线粒体自噬,并可能有助于其在衰老过程中的作用。PHB1表达水平升高时可促进mtDNA复制表达PGC-1α、复合物Ⅳ、核因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2,NRF2)、视神经萎缩蛋白(optic atrophy 1,OPA1)、DRP1和线粒体转录因子A(mitochondrial transcription factor A,TFAM)等线粒体蛋白[40]。
运动能够调控PHBs诱导线骨骼肌线粒体自噬。运动能够增加PHB1、PHB2、苹果酸脱氢酶、三磷酸异构酶、ATP合酶(复合物Ⅳ)和异柠檬酸脱氢酶等表达,进而防治肌少症引发的线粒体功能障碍[8]。GU等[41]发现,慢性有氧训练通过保护老年大鼠的主动脉线粒体功能减轻主动脉硬化和内皮功能障碍,慢性有氧训练能够增加老年小鼠的PHB、ATP形成、mtDNA含量和复合物Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ的活性,同时降低活性氧,改善线粒体受损情况。方雯等[40]发现,一次性力竭运动8周后PHB1表达的增加与ATP含量和v-复合物活性呈正相关,与活性氧水平呈负相关。
综上所述,运动能够上调骨骼肌中PHBs的表达,而PHBs介导线粒体自噬能够减少肌少症引发的线粒体功能障碍,同时增加能量产生复合物的耦合,进而防治肌少症引发的不良反应。PHBs在运动防治肌少症中作用的相关研究见表3。
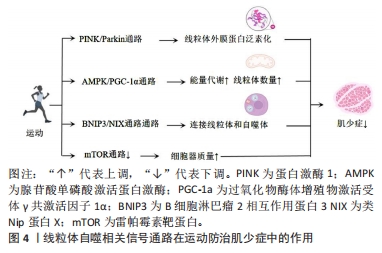
2.4 线粒体自噬相关信号通路在运动防治肌少症中的作用 线粒体自噬相关信号通路在运动防治肌少症中起着重要作用。运动可以调节这些通路的活性,改善线粒体功能和结构,从而预防和治疗肌少症。PINK1/Parkin通路由PINK1和Parkin等蛋白构成,可以调节线粒体功能失调。当线粒体受损时,PINK1会进入线粒体内膜并聚集在线粒体外膜上,然后与Parkin相互作用,最终触发线粒体自噬。研究表明,PINK1和Parkin的表达水平会受到运动的调控,增加它们的表达可改善肌少症,在调节受损线粒体的清除和功能恢复中起着重要作用。AMPK/PGC-1α通路与肌少症密切相关,通过激活该通路可以防止肌少症的发生。研究表明,运动能够激活AMPK/PGC-1α通路,降低蛋白质降解,改善线粒体质量,从而防止肌少症。此外,AMPK/PGC-1α通路还能调节线粒体的数量、合成和质量,确保线粒体的正常代谢和功能。BNIP3/NIX通路是一种与线粒体自噬相关的信号通路,通过连接线粒体和自噬体促进线粒体的清除。运动能够调节BNIP3/NIX通路的活性,促进线粒体自噬,并改善线粒体功能和结构,从而预防和治疗肌少症。mTOR通路与线粒体自噬在肌少症中起着重要作用。运动可以通过降低mTOR信号和刺激自噬来改善肌少症。研究表明,运动可以激活mTOR通路,促进蛋白质合成和肌肉生长,同时提高对葡萄糖的摄取,从而预防和治疗肌少症。然而,对于运动、信号通路和肌少症之间的直接证据仍有限,需要进一步的研究来支持这些结论。线粒体自噬相关信号通路在运动防治肌少症中作用的机制图见图4。
2.4.1 PINK1/Parkin通路 该通路主要由PINK1和Parkin等蛋白构成,这些蛋白能够靶向调控线粒体功能失调[8]。当线粒体受损后,线粒体膜电位发生去极化,PINK1进入线粒体内膜且表达受限,使蛋白质集中在线粒体外膜上,并由细胞质吸收蛋白质,最终到达线粒体外膜。依赖磷酸化诱导PINK1能够抑制Parkin表达[41]。Parkin被激活后,通过电压依赖表达VDAC1,并产生泛素(Ub)和多泛素(Poly-Ub)链,Poly-Ub链随后被PINK1磷酸化并介导线粒体自噬,进而实现线粒体外膜蛋白泛素化[42]。
Poly-Ub链在线粒体蛋白上磷酸化后,通过泛素和P62、视神经蛋白(optineurin,OPTN)和核点蛋白52(nuclear domain 10 protein 52,NDP52)等蛋白结合来识别,并通过与LC3的相互作用自噬受损的线粒体[43]。另外,Parkin在自噬受损的线粒体时新形成的自噬体,同时与LC3连接[44]。
运动对PINK1/Parkin通路具有一定的影响,并可作用于肌少症。GOUSPILLOU等[45]发现,抑制Parkin蛋白的表达会导致老年小鼠模型肌肉质量的减少,进而影响小鼠的身体功能,然而,增加Parkin的表达却可以改善老年小鼠的骨骼肌功能,这表明Parkin在调节肌少症中起着重要的作用。Parkin可以促使丝裂蛋白的蛋白酶体降解,增加裂变并抑制线粒体融合,从而将受损线粒体与健康的线粒体网络分离出来[46]。此外,PINK1可以间接激活DRP1,加速受损线粒体的降解[45]。然而,当PINK1和Parkin表达水平较低时,会导致线粒体功能失调和碎片化的积累,因此PINK1/Parkin通路很可能是调控受损线粒体的重要靶点[47]。此外,PINK1/Parkin通路的生物利用度降低可能表明线粒体衰老和功能障碍[48]。ROMANELLO等[49]认为,在PINK1/Parkin通路相关基因缺失后,线粒体自噬受限,伴随着线粒体功能障碍、骨骼肌损伤以及寿命缩短。然而,当PINK1,Parkin和DRP1的表达水平较高时,可以促进线粒体自噬,减少与年龄相关的肌肉功能障碍并延长寿命。此外, ZHAO等[50]发现,运动可以增加小鼠骨骼肌中PINK1和Parkin蛋白的mRNA表达,通过线粒体融合/裂变信号通路改善线粒体功能。当运动不足时,会导致线粒体功能异常和肌原纤维损伤,而PINK1和DRP1的表达水平能够激活线粒体自噬。另外,运动对骨骼肌中PINK1和Parkin具有一定影响,结果显示运动可以提高衰老过程中PINK1和Parkin的表达水平[51-53]。此外,使用AMPK敲除小鼠的研究显示,PINK1和Parkin的表达水平会降低,而运动可以降低AMPK的表达水平[52-53],这表明运动可以通过AMPK使PINK1和Parkin的表达水平升高,进而改善线粒体自噬来防治肌少症。
总之,PINK1/Parkin通路在调控线粒体功能失调方面具有重要作用,该通路的调控水平对机体的肌肉质量和功能产生影响,尤其在肌少症进展中体现。另外,运动亦被证实可以调节该通路,并改善线粒体功能进而防治肌少症。PINK1/Parkin通路在运动防治肌少症中作用的相关研究进展,见表4。

2.4.2 AMPK/PGC-1α通路 肌少症和AMPK/PGC-1α通路密切相关,激活AMPK/PGC-1α通路能够防止肌少症的发生[9]。研究发现,疲劳可能是通过AMPK/PGC-1α信号通路引起腓肠肌肌少症和线粒体功能障碍,慢性约束应力导致线粒体损伤并阻断保护性线粒体自噬,长期进行运动能够激活AMPK/ PGC-1α通路,减少蛋白质降解,改善线粒体质量,进而防治肌少症[54]。另外,在线粒体自噬过程中,AMPK/PGC-1α通路能够通过多种途径发挥作用。一方面,AMPK/PGC-1α通路能够调节线粒体的数量和合成,进而增加线粒体的生物合成和产生[55]。另一方面,AMPK/PGC-1α通路还能够调节线粒体的质量和功能,如清除累积的受损线粒体、减少线粒体生成的反应性氧化物等,以维持线粒体正常的代谢和功能[56]。另外,AMPK/PGC-1α通路还能够通过调节蛋白质酶降解途径,如热休克蛋白70(heat shock protein 70,HSP70)等的表达,参与线粒体自噬的质量控制和调节代谢反应的平衡[57]。
AMPK/PGC-1α通路与肌少症和运动在线粒体自噬方面之间存在着密切的联系。终身有氧训练可以通过AMPK/PGC-1α信号通路降低蛋白质降解并改善线粒体质量控制,从而延缓肌少症[52]。急性运动会激活信号传导通路,最终汇聚于PGC-1α,导致钙依赖性蛋白激酶/钙调素(CaMK)的激活以及对多种应激物如活性氧敏感的p38MAPK的激活,以及AMPK的磷酸化[52]。定期终身有氧训练通过激活AMPK/PGC-1α信号通路促进线粒体生物发生[52,58]。运动会提高细胞内钙离子水平并引起能量失衡,通过激活AMPK、CaMK和MAPK来刺激线粒体生物发生[59]。AMPK、CaMKII和MAPK是运动引起PGC-1α活化的上游介导因子,有助于对PGC-1α的正调控[59]。这些发现表明,运动可提高细胞内能量代谢,激活多种细胞内应激物,并通过PGC-1α信号调控提升细胞内钙离子浓度来诱导线粒体生物发生、增殖和肌肉细胞分化,通过增加NRF1/2/TFAM和AKT/mTOR通路实现。
综上所述,运动能够调控AMPK/PGC-1α通路激活线粒体自噬,并提高细胞内钙浓度,对肌少症有防治的效果。然而,由于当前对于运动、AMPK/PGC-1α通路和肌少症3者在线粒体自噬中的直接证据有限,无法进一步拓展这些方面,需要更多研究来支撑,见表5。
2.4.3 BNIP3/NIX通路 该通路是一种线粒体自噬相关的信号通路,主要由BNIP3和NIX分别作用于肌少症。BNIP3和NIX可以结合LC3,并连接线粒体和自噬体[47]。BNIP3和NIX位于线粒体表面,BNIP3/NIX通路能够引起线粒体去极化,导致骨骼肌中线粒体自噬发生[60]。BNIP3/NIX通路亦能够增加线粒体自噬早期阶段线粒体中DRP1的数量,进而导致Parkin的分裂和募集[61]。另外,BNIP3/NIX通路能够结合Beclin-2,分解Beclin-1/Beclin-2相互作用,使Beclin-1激活线粒体自噬,且BNIP3/NIX通路在线粒体外膜上发生磷酸化形成同型二聚体,并和LC3结合[62]。另外,线粒体自噬发生频率较高和BNIP3表达水平较高时,能够抑制低氧状态并降低由运动引起的氧化应激,进而对骨骼肌细胞起到保护作用[63]。
运动亦能够调控BNIP3/NIX通路诱导线粒体自噬,进而防治肌少症。其中,LC3、BNIP3、Beclin-1、自噬相关蛋白7(autophagy related gene 7,ATG7)、P62和Parkin等线粒体自噬调节因子的表达和年龄呈负相关性[61-63]。赵永才等[64]发现,运动能够使C57BL/6小鼠的BNIP3和NIX表达水平降低,而BNIP3和NIX的缺失能够导致年龄相关的线粒体心肌病。OGURA等[65]发现,运动能够增加骨骼肌线粒体的自噬,其中LC3-Ⅰ转化为LC3-Ⅱ,并可以加速骨骼肌细胞内代谢废物和受损蛋白的清除,并最终改善骨骼肌系统的功能和结构再生。这说明,BNIP3/NIX通路能够直接与LC3相互作用以吸收自噬体,促进线粒体清除。另外,运动促进BNIP3表达后通过和自噬-溶酶体的相互作用改善骨骼肌的氧化损伤和线粒体损伤[66]。运动增加骨骼肌中BNIP3和NIX的表达,激活BNIP3/NIX通路靶向损伤线粒体,并通过线粒体自噬降解这些受损的线粒体[64],另外,运动过程中骨骼肌收缩,上调OPA1,PINK1,Parkin,BNIP3和NIX的表达,进而改善线粒体质量[67],然而,由于BNIP3水平的增加,慢肌纤维比快肌纤维的线粒体自噬发生频率更高[68]。
总之,BNIP3/NIX通路是一种线粒体自噬相关的信号通路,能够通过连接线粒体和自噬体促进线粒体的清除。运动可以调控BNIP3/NIX通路的活性,防治肌少症以及改善线粒体功能和结构,同时也能够降低氧化应激和损伤。BNIP3/NIX通路在运动防治肌少症中作用的相关研究见表6。
2.4.4 mTOR通路 该通路和线粒体自噬在肌少症中起着重要作用,慢性mTOR激活可能存在,但肌少症的特征仍是合成代谢抵抗[69]。在老年人中,肌肉纤维成分会向慢收缩纤维转变,并且快收缩纤维中葡萄糖转运体GLUT4的表达会减少[70],这会导致在胰岛素岛素刺激下肌肉对葡萄糖的利用能力降低。这种情况通常与代谢紊乱有关,其中胰岛素信号的调节发生了改变(例如,肥胖、糖尿病)。肌少症的存在会加剧这些疾病,并可能成为其一种因素和/或后果,因为肌肉本身是一种内分泌器官,能够释放出控制全身代谢的活性分子。这样的作用在肝硬化患者中也有所描述,认为其中mTOR通路和自噬的改变可能是引起肌少症的介质[71-72]。运动能够调控mTOR通路,从而改善肌少症。研究表明,运动可以通过降低mTOR信号并刺激自噬来更新肌肉结构,提高细胞器整体质量[51]。抗阻训练被认为是预防肌少症的有效干预措施。然而,研究发现,老年人对抗阻训练后肌肉蛋白合成的反应较弱。一项研究假设,在急性抗阻训练后,老年人相比年轻人,具有受损的mTORC1信号传导和肌肉蛋白合成反应,因此,他们得出结论,衰老会损害肌肉收缩诱导的骨骼肌mTORC1信号传导和蛋白质合成[73]。然而,目前尚不完全了解锻炼引起的适应性变化的细胞和分子机制。一项研究发现,对老年大鼠进行跑步机锻炼和训练频率的调整,会对骨骼肌中的胰岛素信号传导等促生化途径产生影响[74]。另一项研究表明,跑步和抗阻训练都可以通过激活mTOR信号通路,促进蛋白质合成和肌肉生长,提高骨骼肌对葡萄糖的摄取[75]。此外,运动还可以通过增加胰岛素敏感性、促进肌肉卫星细胞以及激活PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路,促进肌细胞增殖和蛋白质合成[76]。
综上所述,mTOR通路在肌少症中发挥重要作用,调节肌肉的代谢和结构。运动是一种有效的干预措施,可通过降低mTOR信号和刺激自噬来改善肌肉结构和细胞器质量,从而预防和治疗肌少症。虽然抗阻训练被认为是预防肌少症的有效方法,但老年人对其肌肉蛋白合成的反应较弱。关于运动通过mTOR通路预防和治疗肌少症的相关研究见表7。

| [1] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191):2636-2646. [2] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(4):601. [3] PETERMANN-ROCHA F, BALNTZI V, GRAY SR, et al. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):86-99. [4] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020; 21(3):300-307.e2. [5] LARSSON L, DEGENS H, LI M, et al. Sarcopenia: aging-related loss of muscle mass and function. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(1):427-511. [6] BIOLO G, CEDERHOLM T, MUSCARITOLI M. Muscle contractile and metabolic dysfunction is a common feature of sarcopenia of aging and chronic diseases: from sarcopenic obesity to cachexia. Clin Nutr. 2014;33(5):737-748. [7] URBINA-VARELA R, CASTILLO N, VIDELA LA, et al. Impact of mitophagy and mitochondrial unfolded protein response as new adaptive mechanisms underlying old pathologies: sarcopenia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(20):7704. [8] WANG L, LU G, SHEN HM. The long and the short of PTEN in the regulation of mitophagy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:299. [9] KO YJ, KO IG. Voluntary wheel running exercise improves aging-induced sarcopenia via activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α/fibronectin type iii domain-containing protein 5/adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Int Neurourol J. 2021;25(Suppl 1):S27-S34. [10] 侯国珍,郭琪,韩佩佩.肌少症自噬激活和线粒体质量控制信号途径的研究进展[J].中国医学科学院学报,2022,44(4):709-716. [11] 王岑依,梁计陵,司誉豪等.运动通过调控线粒体质量控制改善肌少症的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(9):1066-1070. [12] ZHU Y, ZHOU X, ZHU A, et al. Advances in exercise to alleviate sarcopenia in older adults by improving mitochondrial dysfunction. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1196426. [13] BELLANTI F, LO BUGLIO A, VENDEMIALE G. Mitochondrial impairment in sarcopenia. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(1):31. [14] DEMONTIS F, PICCIRILLO R, GOLDBERG AL, et al. Mechanisms of skeletal muscle aging: insights from Drosophila and mammalian models. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6(6):1339-1352. [15] GAO J, YU L, WANG Z, et al. Induction of mitophagy in C2C12 cells by electrical pulse stimulation involves increasing the level of the mitochondrial receptor FUNDC1 through the AMPK-ULK1 pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(10):6879-6894. [16] LAMPERT MA, OROGO AM, NAJOR RH, et al. BNIP3L/NIX and FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy is required for mitochondrial network remodeling during cardiac progenitor cell differentiation. Autophagy. 2019;15(7):1182-1198. [17] LAKER RC, DRAKE JC, WILSON RJ, et al. Ampk phosphorylation of Ulk1 is required for targeting of mitochondria to lysosomes in exercise-induced mitophagy. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):548. [18] FU T, XU Z, LIU L, et al. Mitophagy directs muscle-adipose crosstalk to alleviate dietary obesity. Cell Rep. 2018;23(5):1357-1372. [19] TRIOLO M, HOOD DA. Manifestations of age on autophagy, mitophagy and lysosomes in skeletal muscle. Cells. 2021;10(5):1054. [20] 于亮,史霄雨,刘子铭等.运动时长和强度对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自噬的影响及其机制[J].生理学报,2020,72(5):631-642. [21] LI X, LYU Y, LI J, WANG X. AMBRA1 and its role as a target for anticancer therapy. Front Oncol. 2022;12:946086. [22] SUN WL, HE LY, LIANG L, et al. Ambra1 regulates apoptosis and chemosensitivity in breast cancer cells through the Akt-FoxO1-Bim pathway. Apoptosis. 2022;27(5-6):329-341. [23] XU HD, QIN ZH. Beclin 1, Bcl-2 and Autophagy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:109-126. [24] DI RIENZO M, ROMAGNOLI A, CICCOSANTI F, et al. AMBRA1 regulates mitophagy by interacting with ATAD3A and promoting PINK1 stability. Autophagy. 2022;18(8):1752-1762. [25] LI W, HE P, HUANG Y, et al. Selective autophagy of intracellular organelles: recent research advances. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):222-256. [26] IORIO R, CELENZA G, PETRICCA S. Mitophagy: molecular mechanisms, new concepts on parkin activation and the emerging role of AMPK/ULK1 axis. Cells. 2021;11(1):30. [27] GAMBAROTTO L, METTI S, CHRISAM M, et al. Ambra1 deficiency impairs mitophagy in skeletal muscle. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(4):2211-2224. [28] LENHARE L, CRISOL BM, SILVA VRR, et al. Physical exercise increases Sestrin 2 protein levels and induces autophagy in the skeletal muscle of old mice. Exp Gerontol. 2017; 97:17-21. [29] KIM YA, KIM YS, OH SL, et al. Autophagic response to exercise training in skeletal muscle with age. J Physiol Biochem. 2013;69(4):697-705. [30] SANTOS-ALVES E, MARQUES-ALEIXO I, RIZO-ROCA D, et al. Exercise modulates liver cellular and mitochondrial proteins related to quality control signaling. Life Sci. 2015; 135:124-130. [31] STRAPPAZZON F, DI RITA A, PESCHIAROLI A, et al. HUWE1 controls MCL1 stability to unleash AMBRA1-induced mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27(4):1155-1168. [32] YAN C, GONG L, CHEN L, et al. PHB2 (prohibitin 2) promotes PINK1-PRKN/Parkin-dependent mitophagy by the PARL-PGAM5-PINK1 axis. Autophagy. 2020;16(3):419-434. [33] WANG K, QI Y, WANG X, et al. GOLPH3 promotes glioma progression by enhancing PHB2-mediated autophagy. Am J Cancer Res. 2021;11(5):2106-2123. [34] BLOTTNER D, CAPITANIO D, TRAUTMANN G, et al. Nitrosative redox homeostasis and antioxidant response defense in disused vastus lateralis muscle in long-term bedrest (toulouse cocktail study). Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(3):378. [35] HERNANDO-RODRÍGUEZ B, ARTAL-SANZ M. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms and the PHB (prohibitin) complex. Cells. 2018;7(12):238. [36] 齐洁,牛书妍,李纯,等.运动对高脂膳食诱导的IR小鼠骨骼肌线粒体内膜蛋白PHB2表达和线粒体自噬的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2022,45(7):104-112. [37] FAN Y, MURGIA M, LINDER MI, et al. HAX1-dependent control of mitochondrial proteostasis governs neutrophil granulocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(9): e153153. [38] LÓPEZ-LLUCH G. Mitochondrial activity and dynamics changes regarding metabolism in ageing and obesity. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017;162:108-121. [39] SIGNORILE A, SGARAMELLA G, BELLOMO F, et al. Prohibitins: a critical role in mitochondrial functions and implication in diseases. Cells. 2019;8(1):71. [40] 方雯,李泽,刘晓华,等.一次性力竭运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自噬的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2017,33(6):544-549. [41] GU Q, WANG B, ZHANG XF, MA YP, et al. Chronic aerobic exercise training attenuates aortic stiffening and endothelial dysfunction through preserving aortic mitochondrial function in aged rats. Exp Gerontol. 2014;56:37-44. [42] LIU D, FAN YB, TAO XH, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in sarcopenia: updated overview of mechanisms and interventions. Aging Dis. 2021;12(8):2016-2030. [43] 王香香,凌江红,王煜姣,等.Pink1/Parkin信号通路调控线粒体自噬的研究进展[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2022,41(4):919-926. [44] 陈林波,马凯丽,陈佺,等.线粒体自噬的分子机制[J].中国科学:生命科学, 2019,49(9):1045-1053. [45] GAOUSPILLOU G, GODIN R, PIQUEREAU J, et al. Protective role of Parkin in skeletal muscle contractile and mitochondrial function. J Physiol. 2018;596(13):2565-2579. [46] ZHONG J, LI M, XU J, et al. Roflupram attenuates α-synuclein-induced cytotoxicity and promotes the mitochondrial translocation of Parkin in SH-SY5Y cells overexpressing A53T mutant α-synuclein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022;436:115859. [47] DULAC M, LEDUC-GAUDET JP, REYNAUD O, et al. Drp1 knockdown induces severe muscle atrophy and remodelling, mitochondrial dysfunction, autophagy impairment and denervation. J Physiol. 2020;598(17):3691-3710. [48] DRAKE JC, WILSON RJ, YAN Z. Molecular mechanisms for mitochondrial adaptation to exercise training in skeletal muscle. FASEB J. 2016;30(1):13-22. [49] ROMANELLO V. The interplay between mitochondrial morphology and myomitokines in aging sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):91. [50] ZHAO N, ZHANG X, LI B, et al. Treadmill exercise improves PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy activity against Alzheimer’s disease pathologies by upregulated SIRT1-FOXO1/3 Axis in APP/PS1 mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(1):277-291. [51] ZENG Z, LIANG J, WU L, et al. Exercise-induced autophagy suppresses sarcopenia through Akt/mTOR and Akt/FoxO3a signal pathways and AMPK-mediated mitochondrial quality control. Front Physiol. 2020;11:583478. [52] LIANG J, ZHANG H, ZENG Z, et al. Lifelong aerobic exercise alleviates sarcopenia by activating autophagy and inhibiting protein degradation via the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Metabolites. 2021;11(5):323. [53] LIU S, YU C, XIE L, et al. Aerobic exercise improves mitochondrial function in sarcopenia mice through sestrin2 in an AMPKα2-dependent manner. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2021;76(7):1161-1168. [54] WANG Z, XIA T, JIN S, et al. Chronic restraint stress-induced muscle atrophy leads to fatigue in mice by inhibiting the AMPK signaling pathway. Biomedicines. 2021;9(10):1321. [55] SCARPULLA RC. Metabolic control of mitochondrial biogenesis through the PGC-1 family regulatory network. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(7):1269-1278. [56] HARDIE DG. AMPK--sensing energy while talking to other signaling pathways. Cell Metab. 2014;20(6):939-952. [57] 冯丽丽,李博文,田振军.运动激活SESN2/AMPK/PGC-1α通路改善心梗诱导的骨骼肌减少[J].北京体育大学学报,2021,44(5):128-137. [58] LIAO ZY, CHEN JL, XIAO MH, et al. The effect of exercise, resveratrol or their combination on Sarcopenia in aged rats via regulation of AMPK/Sirt1 pathway. Exp Gerontol. 2017;98: 177-183. [59] MEMME JM, HOOD DA. Molecular basis for the therapeutic effects of exercise on mitochondrial defects. Front Physiol. 2021;11:615038. [60] ALIZADEH PAHLAVANI H. Exercise therapy for people with sarcopenic obesity: myokines and adipokines as effective actors. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:811751. [61] ESTEBAN-MARTÍNEZ L, BOYA P. BNIP3L/NIX-dependent mitophagy regulates cell differentiation via metabolic reprogramming. Autophagy. 2018;14(5):915-917. [62] NEY PA. Mitochondrial autophagy: origins, significance, and role of BNIP3 and NIX. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1853(10 Pt B):2775-2783. [63] AVERSA Z, PIN F, LUCIA S, et al. Autophagy is induced in the skeletal muscle of cachectic cancer patients. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30340. [64] 赵永才,黄涛.运动训练及饮食限制对小鼠骨骼肌线粒体内膜蛋白PHB2表达和线粒体自噬的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2019,35(4):363-365. [65] OGURA Y, IEMITSU M, NAITO H, et al. Single bout of running exercise changes LC3-II expression in rat cardiac muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414(4):756-760. [66] SPRINGER MZ, MACLEOD KF. In brief: mitophagy: mechanisms and role in human disease. J Pathol. 2016;240(3):253-255. [67] BALAN E, SCHWALM C, NASLAIN D, et al. Regular endurance exercise promotes fission, mitophagy, and oxidative phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle independently of age. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1088. [68] JU JS, JEON SI, PARK JY, et al. Autophagy plays a role in skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in an endurance exercise-trained condition. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66(5):417-430. [69] VAINSHTAIN A, SANDRI M. Signaling pathways that control muscle mass. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4759. [70] PETERSEN KF, MORINO K, ALVES TC, et al. Effect of aging on muscle mitochondrial substrate utilization in humans [published correction appears in Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Oct 20;112(42):E5762]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(36):11330-11334. [71] ANAND A, NAMBIRAJAN A, KUMAR V, et al. Alterations in autophagy and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways mediate sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022;12(2):510-518. [72] PARK SS, SEO YK, KWON KS. Sarcopenia targeting with autophagy mechanism by exercise. BMB Rep. 2019;52(1):64-69. [73] FRY CS, DRUMMOND MJ, GLYNN EL, et al. Aging impairs contraction-induced human skeletal muscle mTORC1 signaling and protein synthesis. Skelet Muscle. 2011;1(1):11. [74] PASINI E, LE DOUAIRON LAHAYE S, FLATI V, et al. Effects of treadmill exercise and training frequency on anabolic signaling pathways in the skeletal muscle of aged rats. Exp Gerontol. 2012;47(1):23-28. [75] 张杰.跑台和抗阻运动对骨骼肌葡萄糖摄取和mTOR信号通路的影响[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(9):4263-4269. [76] 赵瑞朋.运动对骨骼肌葡萄糖摄取和蛋白质合成信号通路的影响[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(9):4283-4288. |
| [1] | 吴 菁, 姚英策, 杨晓巍, 薛博士, 赵建斌, 杨 辰, 栾天峰, 周志鹏. 肌力训练与神经肌肉电刺激干预髌股关节痛患者下肢功能和生物力学的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [2] | 杨毅峰, 叶 楠, 王 琳, 郭帅成, 黄 健. 右美托咪定抗缺血再灌注损伤的信号通路[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [3] | 魏 娟, 李 婷, 郇梦婷, 谢 颖, 谢舟煜, 韦庆波, 吴云川. 静力性训练改善2型糖尿病骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [4] | 娄 国, 张 艳, 付常喜. 内皮型一氧化氮合酶在运动预适应改善心肌缺血-再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [5] | 岳 云, 王佩佩, 袁兆鹤, 何生存, 贾戌生, 刘 倩, 李占涛, 付慧玲, 宋 斐, 贾孟辉. 巴豆霜干预脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠皮质区JNK/p38 MAPK及神经元凋亡的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [6] | 王 继, 张 敏, 李文博, 杨中亚, 张 龙. 有氧运动对2型糖尿病大鼠糖脂代谢、骨骼肌炎症和自噬的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [7] | 刘 鑫, 胡 满, 赵文杰, 张 钰, 孟 博, 杨 盛, 彭 晴, 张 亮, 王静成. 镉暴露激活PI3K/Akt信号通路诱导椎间盘纤维环细胞衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [8] | 周邦瑜, 李 杰, 阮玉山, 耿福能, 李绍波. 美洲大蠊研粉干预脊髓半横断大鼠运动功能和自噬蛋白Beclin-1的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [9] | 阮 蓉, 娄旭佳, 金其贯, 章立冰, 徐 尚, 胡玉龙. 白藜芦醇可调控运动性疲劳大鼠的糖异生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1229-1234. |
| [10] | 潘小龙, 樊飞燕, 应春苗, 刘飞祥, 张运克. 中药抑制间充质干细胞衰老的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [11] | 孔健达, 穆玉晶, 朱 磊, 李志林, 陈世娟. 骨骼肌再生过程中卫星细胞调控机制及其生态位信号的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1105-1111. |
| [12] | 刘麒薇, 张俊辉, 杨 袁, 王金娟. 脐带间充质干细胞治疗多囊卵巢综合征的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [13] | 杨毅峰, 黄 健, 叶 楠, 王 琳. 全膝关节置换中的缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [14] | 张克凡, 石 辉. 细胞因子治疗骨关节炎的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [15] | 刘志杨, 傅泽铤, 夏 雨, 丁海丽. 运动性骨骼肌损伤中时钟基因BMAL1与MyoD的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 510-515. |
当前,部分综述介绍了线粒体自噬和肌少症的相关性[10-13]。这些综述总结了与肌少症相关的骨骼肌流失的影响和潜在分子机制,强调了自噬和线粒体质量控制在肌少症中的重要性,并提出了改善线粒体功能的治疗方案,还介绍了运动对线粒体生物合成、融合/分裂动力学、线粒体自噬等方面的影响。然而,尚缺乏对运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬中具体受体蛋白和信号通路在作用机制方面的详细介绍,尤其是运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关的受体蛋白和信号通路,如FUNDC1、AMBRA1、PHBs、PINK1/Parkin通路、AMPK/PGC-1α通路、BNIP3/NIX通路和雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mechanistic target of rapamycin,mTOR)通路等的作用,这使得当前对于线粒体自噬在肌少症中的详细调控机制和参与的受体蛋白以及信号通路的了解还非常有限。因此,该综述将重点关注运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关的受体蛋白和信号通路,旨在为进一步理解肌少症的预防和治疗机制提供参考依据。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一、二作者于2023-02-01/04-01进行文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2023年4月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网、万方和维普数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词:“肌少症,肌少症,衰老,老年,线粒体,线粒体功能,蛋白,通路”等;英文检索词:“Sarcopenia,Muscle wasting,Aging,Elderly,Mitochondrial dysfunction,impaired mitochondrial function,Mitochondrial autophagy,Mitophagy,Receptor proteins”等。
1.1.5 检索策略 运用布尔逻辑运算符“OR”和“AND”分别将检索词连接进行检索。以PubMed和中国知网数据库为例,文献检索的详细策略见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①随机对照试验、单因素研究、综述、案例研究和非随机性历史对照试验等;②内容为肌少症和线粒体自噬相关、运动改善线粒体自噬相关以及运动防治肌少症相关的文献;③经同行专家评审认可并发表的文献;④期刊文献发表时期刊被中国科技论文统计源期刊、北京大学中文核心期刊目录、中国科学引文数据库(含扩展版)、中国社会科学引文索引(含扩展版)、科学引文索引(含扩展版)、工程索引(含扩展版)和PubMed等一个或多个数据库收录。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①研究内容和此次综述主题不相关的文献;②所在期刊无同行评审环节的文献;③学位论文;④论著未被重要数据库收录(如PubMed);⑤重复性研究和低质量文献。
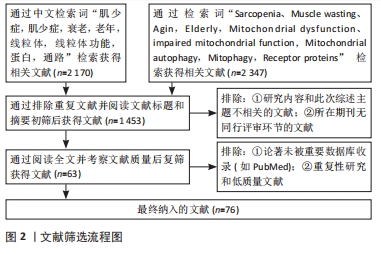
1.3 文献质量评价和数据的提取 文章在数据库初步共检索到文献4 517篇,严格按照纳入和排除标准进行筛选,最终纳入文献76篇。文献筛选流程图见图2。
然而,目前的研究还存在一些问题:①对于运动对肌少症中线粒体自噬的调控机制了解有限,虽然已经发现运动可以激活线粒体自噬,并提高肌肉细胞内线粒体质量,但具体的调控机制和相关受体蛋白的作用机制尚不清楚,尤其这些受体蛋白和信号通路的协同作用;②关于线粒体自噬和肌少症的机制性研究仍缺乏一致的结果,不同的研究使用不同的模型和方法,得出的结论不一致,因此需要更多的研究来验证这些发现。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人研究的特点 该综述区别于以往的研究,在于重点关注运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关的受体蛋白和信号通路的作用机制。对FUNDC1,AMBRA1,PHBs,PINK1/Parkin通路,AMPK/PGC-1α通路,BNIP3/NIX通路和mTOR通路等进行了详细介绍,并探讨了这些信号通路在肌少症中的作用机制。该综述的特点在于综合讨论了运动对线粒体自噬的影响和运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关的受体蛋白和信号通路的作用机制,以及基于综述的研究结果对肌少症的预防和治疗提供了参考依据。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①由于科学研究的不断发展和演变,一些最新的研究尚在同行评审未发表,故该综述可能没有涵盖到最新的研究成果,存在一定的信息滞后性;②由于研究所涉及的不同实验条件、样本大小和数据统计方法等因素的差异,可能会导致结论的不一致或有限的可比性;③综述依赖于已发表的研究文献,如果存在相关研究未被发表或未纳入综述范围内,也会对综述结果产生影响;④由于研究限制、时间和资源限制等原因,综述可能无法展示所有可能的实验设计和方法,且不同研究所采用的实验设计和方法也可能存在差异,这些差异可能会对研究结果产生影响。
3.4 综述的重要意义 该综述对于运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关的受体蛋白和信号通路的研究具有重要意义:①通过对相关受体蛋白和信号通路的介绍,可以更好地了解运动在肌少症中的作用机制,为预防和治疗肌少症提供参考和指导;②该综述提供了一些启示和推动,为未来的研究提供了方向,鼓励进一步的实验和临床研究;③该综述对于全面了解肌少症的发生机制和防治机制具有重要意义,为该领域的进一步发展和探索提供了基础和支持。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 基于对综述的内容和讨论的综合分析,课题专家组对未来的研究提出以下建议:①需要进一步深入研究运动防治肌少症中线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白和信号通路的具体作用机制和调控途径,通过更多的实验证据和研究方法,验证和证实相关蛋白和通路的功能和效果;②建议开展更多的人体临床研究,以验证运动对肌少症的预防和治疗效果,并深入探讨运动对线粒体自噬相关受体蛋白和信号通路的调控,尤其是AMPK/PGC-1α通路在调控线粒体的动力学平衡和稳定性等方面的具体作用;③还建议开展更多与其他肌少症相关的因素和机制的研究,以全面了解肌少症的发生和发展机制;④需要在综述的基础上,进一步深入研究和探索,提出新的假设和实验设计,以推动该领域的进一步发展。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
线粒体自噬:是一种特殊形式的自噬过程,指的是细胞通过将旧或损坏的线粒体包裹在自噬泡中,然后将其降解和回收的过程。肌少症:是一种随着年龄增长而出现的健康问题,其特征为骨骼肌组织量和功能的逐渐减少,可能导致肌肉无力、脆弱骨折和身体功能下降,其可能由多种因素引起,包括年龄相关的代谢变化、慢性疾病、营养不良和缺乏运动等。
近年来,研究人员对肌少症的防治进行了广泛的研究,发现运动是一种防治肌少症的有效解决策略,而线粒体自噬作为一种重要的细胞清除机制在其中发挥了重要作用。线粒体自噬是一种特殊形式的自噬,是细胞通过选择性地降解和清除受损或老化的线粒体来维持细胞内线粒体的质量和功能。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||