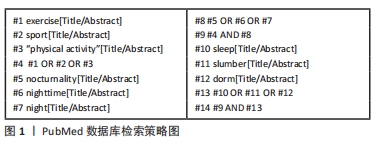
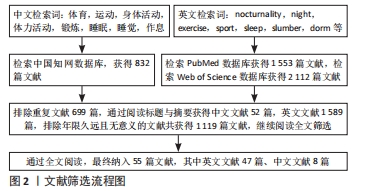
[1] STUTZ J, EIHOLZER R, SPENGLER CM. Effects of Evening Exercise on Sleep in Healthy Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(2):269-287.
[2] CHAPUT JP, MCHILL AW, COX RC, et al. The role of insufficient sleep and circadian misalignment in obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(2):82-97.
[3] BLOOMBERG M, BROCKLEBANK L, HAMER M, et al. Joint associations of physical activity and sleep duration with cognitive ageing: longitudinal analysis of an English cohort study. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023;4(7):e345-e53.
[4] YUE T, LIU X, GAO Q, et al. Different Intensities of Evening Exercise on Sleep in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nat Sci Sleep. 2022;14:2157-2177.
[5] RAMOS-CAMPO DJ, ÁVILA-GANDíA V, LUQUE AJ, et al. Effects of hour of training and exercise intensity on nocturnal autonomic modulation and sleep quality of amateur ultra-endurance runners. Physiol Behav. 2019;198:134-139.
[6] 韩芳.人为什么要睡眠?[J].科学通报,2018,63(1):16-21.
[7] 邓佳慧,黄筱琳,刘晓星,等.中国睡眠医学的过去、现在和未来[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2023,55(3):567-573.
[8] TROYNIKOV O, WATSON CG, NAWAZ N. Sleep environments and sleep physiology: A review. J Therm Biol. 2018;78:192-203.
[9] VON ECONOMO C. Sleep as a problem of localization. Nerv Ment Dis.1930;71:249-259.
[10] MORUZZI G, MAGOUN HW. Brain stem reticular formation and activation of the EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1949;1(4):455-473.
[11] VANINI G, TORTEROLO P. Sleep-Wake Neurobiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1297:65-82.
[12] BORBéLY A. The two-process model of sleep regulation: Beginnings and outlook. J Sleep Res. 2022;31(4):e13598.
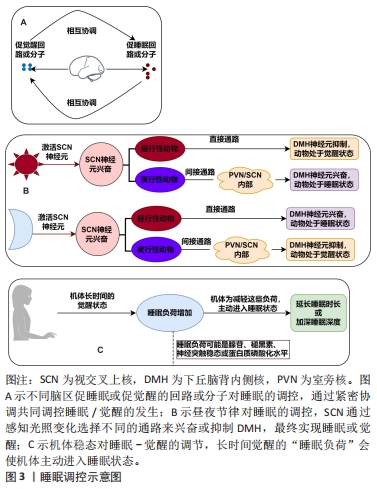
[13] 崔素颖,秦宇,张永鹤.睡眠调控与睡眠调节药物研究进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2022,36(11):801-811.
[14] ZADA D, SELA Y, MATOSEVICH N, et al. Parp1 promotes sleep, which enhances DNA repair in neurons. Mol Cell. 2021;81(24):4979-4993.e7.
[15] WANG Z, MA J, MIYOSHI C, et al. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of the molecular substrates of sleep need. Nature. 2018;558(7710):435-439.
[16] DUHART JM, INAMI S, KOH K. Many faces of sleep regulation: beyond the time of day and prior wake time. FEBS J. 2023;290(4):931-950.
[17] FIFEL K, YANAGISAWA M, DEBOER T. Mechanisms of Sleep/Wake Regulation under Hypodopaminergic State: Insights from MitoPark Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(5):e2203170.
[18] BAEKELAND F, LASKY R. Exercise and sleep patterns in college athletes. Percept Mot Skills. 1966;23(3):1203-1207.
[19] UCHIDA S, SHIODA K, MORITA Y, et al. Exercise effects on sleep physiology. Front Neurol. 2012;3:48.
[20] 赵春玲,欧阳松云,陈兰兰,等.有氧运动对原发性失眠病人睡眠质量、睡眠结构及炎症因子的影响[J].护理研究,2022,36(1):154-157.
[21] PLEKHANOVA T, ROWLANDS AV, DAVIES M, et al. Effect of exercise on sleep and bi-directional associations with accelerometer-assessed physical activity in men with obesity. Appl Physiol Nutr Me. 2021;46(6):597-605.
[22] WANG XW, YOUNGSTEDT SD. Sleep quality improved following a single session of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise in older women: Results from a pilot study. J Sport Health Sci. 2014;3(4):338-342.
[23] SIU PM, YU AP, TAM BT, et al. Effects of Tai Chi or Exercise on Sleep in Older Adults With Insomnia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037199.
[24] 谢璞,马园艳,聂应军.运动锻炼对老年人睡眠干预效果分析——基于Meta系统综述[J].武汉体育学院学报,2023,57(7):69-78.
[25] 龚明俊,谭思洁,孙亚麒,等.运动干预睡眠障碍成年人的睡眠结构的Meta分析[J].首都体育学院学报,2021,33(3):276-284.
[26] PESONEN AK, KAHN M, KUULA L, et al. Sleep and physical activity - the dynamics of bi-directional influences over a fortnight. Bmc Public Health. 2022;22(1):1160.
[27] 赵文瑞,李陈渝,陈军君,等.失眠障碍与过度觉醒:来自静息态脑电和睡眠脑电的证据[J].中国科学:生命科学,2020,50(3):270-286.
[28] VALDEZ P. Circadian Rhythms in Attention. Yale J Biol Med. 2019;92(1):81-92.
[29] BREUS M. Healthy Sleep Tips. 2023-06-01. https://www.sleepassociation.org/about-sleep/sleep-hygiene-tips/
[30] MILLER DJ, ROACH GD, LASTELLA M, et al. Hit the gym or hit the hay: can evening exercise characteristics predict compromised sleep in healthy adults? Front Physiol. 2023;14:1231835.
[31] RAMOS-CAMPO DJ, ÁVILA-GANDíA V, LUQUE AJ, et al. Effects of hour of training and exercise intensity on nocturnal autonomic modulation and sleep quality of amateur ultra-endurance runners. Physiol Behav. 2019;198:134-139.
[32] ALOULOU A, DUFOREZ F, BIEUZEN F, et al. The effect of night-time exercise on sleep architecture among well-trained male endurance runners. J Sleep Res. 2020;29(6):e12964.
[33] MILLER DJ, SARGENT C, ROACH GD, et al. Moderate-intensity exercise performed in the evening does not impair sleep in healthy males. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(1):80-89.
[34] KAHN M, KORHONEN T, LEINONEN L, et al. Is It Time We Stop Discouraging Evening Physical Activity? New Real-World Evidence From 150,000 Nights. Front Public Health. 2021;9:772376.
[35] BUMAN MP, PHILLIPS BA, YOUNGSTEDT SD, et al. Does nighttime exercise really disturb sleep? Results from the 2013 National Sleep Foundation Sleep in America Poll. Sleep Med. 2014;15(7):755-761.
[36] FRIMPONG E, MOGRASS M, ZVIONOW T, et al. The effects of evening high-intensity exercise on sleep in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. 2021;60:101535.
[37] ODA S, SHIRAKAWA K. Sleep onset is disrupted following pre-sleep exercise that causes large physiological excitement at bedtime. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014;114(9):1789-1799.
[38] ROBEY E, DAWSON B, HALSON S, et al. Effect of evening postexercise cold water immersion on subsequent sleep. Med Sci Sport Exer. 2013;45(7):1394-1402.
[39] CHEIKH M, HAMMOUDA O, GAAMOURI N, et al. Melatonin ingestion after exhaustive late-evening exercise improves sleep quality and quantity, and short-term performances in teenage athletes. Chronobiol Int. 2018;35(9):1281-1293.
[40] CHEIKH M, MAKHLOUF K, GHATTASSI K, et al. Melatonin ingestion after exhaustive late-evening exercise attenuate muscle damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation during intense short term effort in the following day in teenage athletes. Chronobiol Int. 2020; 37(2):236-247.
[41] CHAUVINEAU M, PASQUIER F, GUYOT V, et al. Effect of the Depth of Cold Water Immersion on Sleep Architecture and Recovery Among Well-Trained Male Endurance Runners. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:659990.
[42] RICHARD NA, KOEHLE MS. Optimizing recovery to support multi-evening cycling competition performance. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019;19(6):811-823.
[43] ASEY C, MCBRIDE J, PENTA K. Circadian Rhythm Dysregulation and Restoration: The Role of Melatonin. Nutrients. 2021;13(10):3480.
[44] CAJOCHEN C, KRäUCHI K, WIRZ-JUSTICE A. Role of melatonin in the regulation of human circadian rhythms and sleep. J Neuroendocrinol. 2003;15(4):432-437.
[45] CARLSON LA, POBOCIK KM, LAWRENCE MA, et al. Influence of Exercise Time of Day on Salivary Melatonin Responses. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019;14(3):351-353.
[46] MONTELEONE P, FUSCHINO A, NOLFE G, et al. Temporal relationship between melatonin and cortisol responses to nighttime physical stress in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1992;17(1):81-86.
[47] MARRIN K, DRUST B, GREGSON W, et al. Diurnal variation in the salivary melatonin responses to exercise: relation to exercise-mediated tachycardia. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(11):2707-2714.
[48] 董毅.生物节律与运动[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(4):22-30.
[49] BIGALKE JA, CLEVELAND EL, BARKSTROM E, et al. Core body temperature changes before sleep are associated with nocturnal heart rate variability. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023;135(1):136-145.
[50] SZYMUSIAK R. Body temperature and sleep. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;156:341-351.
[51] KENNY GP, MCGINN R. Restoration of thermoregulation after exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(4):933-944.
[52] THIVEL D, METZ L, JULIAN V, et al. Diet- but not exercise-induced iso-energetic deficit induces compensatory appetitive responses. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2021;75(10):1425-1432.
[53] THIVEL D, FINLAYSON G, MIGUET M, et al. Energy depletion by 24-h fast leads to compensatory appetite responses compared with matched energy depletion by exercise in healthy young males. Br J Nutr. 2018;120(5):583-592.
[54] NORTHEAST RC, VYAZOVSKIY VV, BECHTOLD DA. Eat, sleep, repeat: the role of the circadian system in balancing sleep-wake control with metabolic need. Curr Opin Physiol. 2020;15:183-191.
[55] FLAUSINO NH, DA SILVA PRADO JM, DE QUEIROZ SS, et al. Physical exercise performed before bedtime improves the sleep pattern of healthy young good sleepers. Psychophysiology. 2012;49(2):186-192.
|