中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (20): 3223-3228.doi: 10.12307/2024.389
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
三维数字儿童蒙医针刺穴位可视化系统的研发
刘宇航1,孙瑞芬2,木日根吉雅3,王 星4,5,李志军4,刘亚楠1,郝韵腾1,蔡永强5,张少杰4,5,李 琨4,5
- 1内蒙古医科大学研究生院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000;2内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院影像中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000;3内蒙古医科大学蒙医药学院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010020;4内蒙古医科大学基础医学院解剖学教研室,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010110;5内蒙古医科大学数字医学中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010059
Development of a three-dimensional digital children’s acupuncture point visualization system of Mongolian medicine
Liu Yuhang1, Sun Ruifen2, Mu Rigen Jiya3, Wang Xing4, 5, Li Zhijun4, Liu Yanan1, Hao Yunteng1, Cai Yongqiang5, Zhang Shaojie4, 5, Li Kun4, 5
- 1Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Imaging Center, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 3School of Mongolian Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010020, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 4Department of Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 5Digital Medical Center of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
可视化:是利用计算机图形学和图像处理技术,将数据转换成图形或图像在屏幕上显示出来,并进行交互处理的理论、方法和技术。蒙医针刺穴位:是指蒙医传统疗法在治疗疾病时,利用针具刺激人体表面可达疗效的特定部位。
背景:目前中医成人针刺穴位数字化、可视化系统相关报道日益增多,且中医儿童针刺穴位数字化、可视化系统及蒙医训练针刺手法仿真系统已有报道,但蒙医面向儿童群体此类系统尚未见报道。
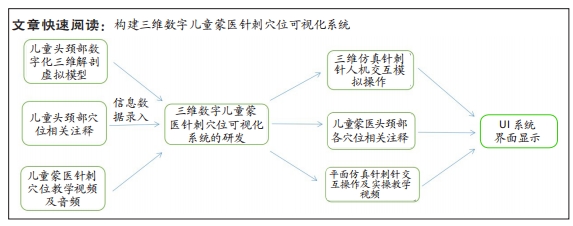
目的:研发蒙医儿童针刺穴位仿真系统,希望供临床教学、施术手法练习及针刺安全性研究使用。方法:在学龄前男童断层解剖数据集基础上运用PhotoShop 2021与Digihuman Reconstruction System软件完成儿童三维数字化虚拟解剖模型及内部多器官组织的构建;通过Unity数据库语言编制蒙医顶会穴等27个穴位的相关注释信息库;在儿童3D打印头颈部树脂模型上选用蒙医金针、银针录制针刺穴位教学视频;在Unity3D 软件中整合儿童解剖模型、穴位注释信息库及针刺操作视频并编写代码,成功创建集仿真针刺训练、临床教学及针刺安全性研究等多功能于一体的三维数字儿童蒙医针刺穴位可视化系统。
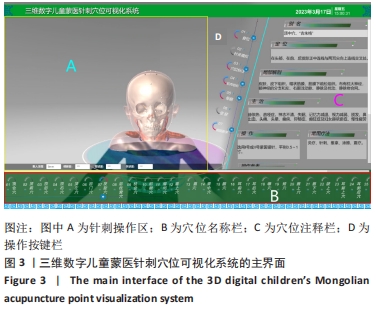
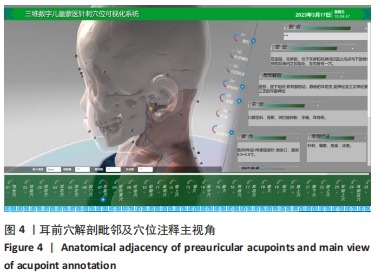
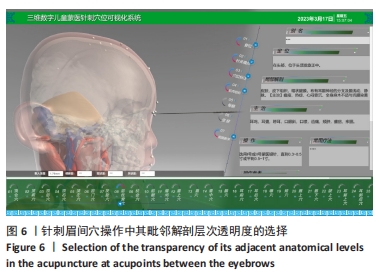
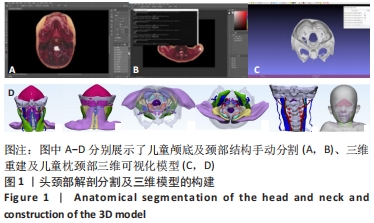
结果与结论:①该研究基于真实儿童标本,为减少二维分割错误,采用手动逐层分割断面图像法,最大程度确保3D模型精度的前提下,使用3D 软件 Digihuman Reconstruction System提取和保存独立分割数据,与PhotoShop.2021软件共同完成儿童头颈部外层皮肤与其内部骨性结构、颈脊髓、血管和神经、肌肉及韧带等数十个解剖结构的三维重建后,于MeshLab软件中完成各独立结构基本形态和整体轮廓完整性核验工作,并利用3-matic research 13.0软件进行最终精细化调校及解剖位置确认,成功模拟还原学龄前儿童头颈部真实解剖形态。②该研究运用Unity3D 软件将儿童三维模型、针刺操作视频和穴位注释库三者整合,成功构建三维数字儿童蒙医针刺穴位可视化系统。③该研究以中国学龄前男童真实连续断层超薄数据集为基础,实现了中国首个蒙医儿童头颈部针刺穴位三维数字化、可视化系统的研发,较既往针刺软著更贴合亚洲儿童解剖形态学发育特点,在蒙医针刺安全性研究、临床教学及针刺模拟训练等领域具有极高应用价值。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2984-3859(刘宇航);https://orcid.org/0009-0006-3957-488X(刘宇航);
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1205-7624(张少杰);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8329-3368(李琨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: