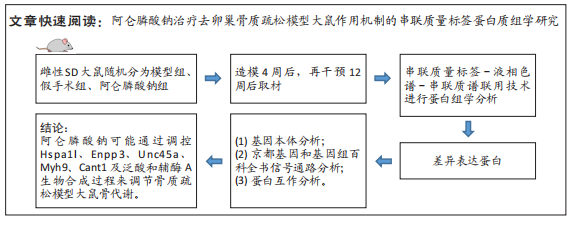
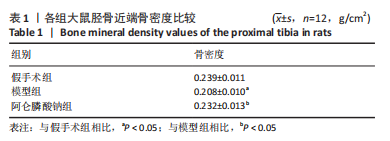
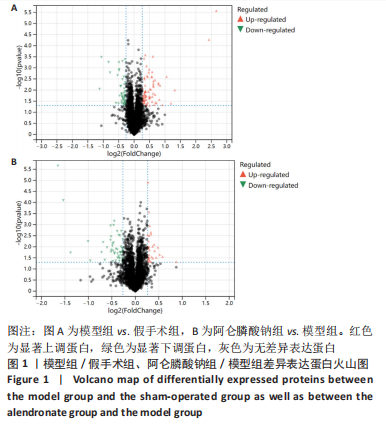
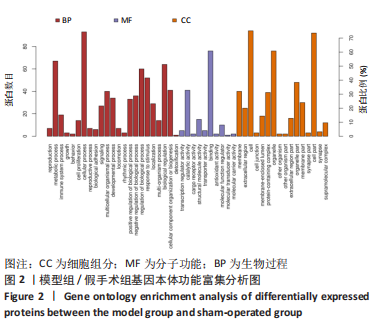
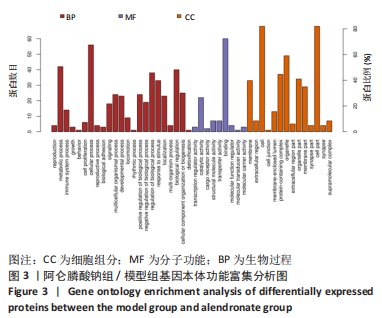
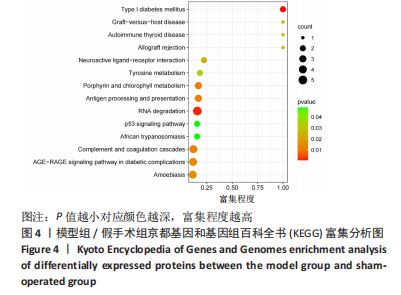
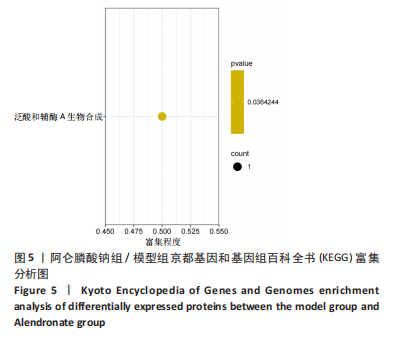
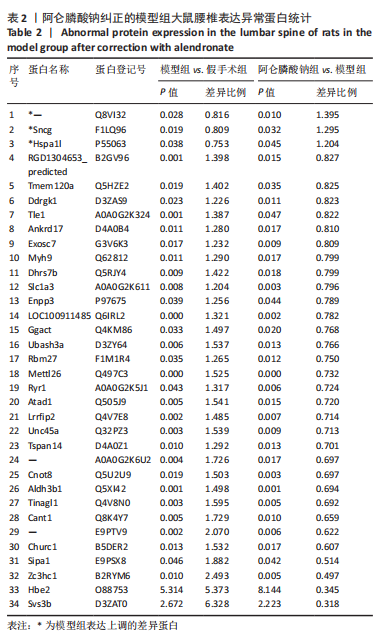
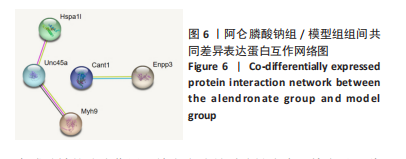
[1] 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2022,15(6):573-611.
[2] 吴惠一,刘颖,兰亚佳, 等.中国绝经女性骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志,2022,22(8):882-890.
[3] WILKINS MR, SANCHEZ JC, GOOLEY AA, et al. Progress with proteome projects: why all proteins expressed by a genome should be identified and how to do it. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1996;13:19-50.
[4] 魏丽英, 李景欣.HPLC法对阿仑膦酸钠成分的测定[J].北方药学, 2021,18(12):1-3.
[5] 赖蔚文, 戴闽, 戴玥.阿仑膦酸钠对大鼠成骨细胞的影响[J].吉林医学,2021,42(3):519-521.
[6] 陈贝贝,郭鱼波,刘海霞,等. 补肾壮骨方对去卵巢大鼠骨结构和骨代谢作用的研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(2):163-168,173.
[7] FU LJ, TANG TT, HAO YQ, et al. Long-term effects of alendronate on fracture healing and bone remodeling of femoral shaft in ovariectomized rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(3):387-392.
[8] 刘文静, 杨娟, 张楚天,等.巴戟天抗去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠的血清代谢组分析[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(3):446-453.
[9] 何丽君, 黄巧文, 马黄璜, 等.淫羊藿苷通过自噬与凋亡途径保护去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的机制探究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2023, 34(2):149-155.
[10] 林若慧, 陈赛楠, 叶云金, 等.基于TMT蛋白质组学分析骨疏康胶囊治疗骨质疏松模型大鼠的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5141-5147.
[11] FAIENZA MF, VENTURA A, MARZANO F, et al. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: the role of immune system cells. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:575936.
[12] 蔡美煌, 洪世顺, 陈胜男.骨康胶囊联合阿仑膦酸钠对骨质疏松性压缩性骨折患者PKP术后骨愈合和骨代谢的影响[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2022,22(10):1181-1183+1188.
[13] 柯太平.阿仑膦酸钠加阿法骨化醇对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨密度及骨代谢标志物的改善作用[J].中外医学研究,2023,21(5):111-115.
[14] 李禹潼, 程之强. 阿仑膦酸钠治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的临床疗效观察[J].中国现代药物应用,2020,14(19):139-141.
[15] 沈力, 章振林.两种阿仑膦酸钠制剂对原发性骨质疏松症患者骨密度和骨转换指标的影响比较[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2020,13(6):522-528.
[16] SAAG KG, SHANE E, BOONEN S, et al. Teriparatide or alendronate in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(20): 2028-2039.
[17] 叶子丰, 戎宽, 张信成, 等.基于OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路探讨益肾健骨方防治绝经后骨质疏松的作用机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(1):23-28+57.
[18] 董伟. 共培养体系中阿仑膦酸钠对破骨细胞相关基因表达的影响[J]. 口腔生物医学,2013,4(2):111.
[19] 沈云玲, 魏静, 徐小宇.阿仑膦酸钠通过调控NF-κB和MAPK信号通路改善大鼠骨质疏松的发展[J].实用药物与临床,2020,23(5): 391-395.
[20] 陈赛楠, 李生强, 谢丽华, 等.续苓健骨方联合阿仑膦酸钠调控EphB4/EphrinB2双向通路对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(5):637-642.
[21] GIULIANI N, PEDRAZZONI M, NEGRI G, et al. Bisphosphonates stimulate formation of osteoblast precursors and mineralized nodules in murine and human bone marrow cultures in vitro and promote early osteoblastogenesis in young and aged mice in vivo. Bone. 1998; 22(5):455-461.
[22] 冯尔宥, 林煜, 张怡元, 等.阿仑膦酸钠对成骨细胞BMP-2信号通路的影响[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2014,53(3):430-435.
[23] HOU JL, YANG WY, ZHANG Q, et al. Integration of Metabolomics and Transcriptomics to Reveal the Metabolic Characteristics of Exercise-Improved Bone Mass. Nutrients. 2023;15(7):1694.
[24] XUE J, HAN Y, BANIASADI H, et al. TMEM120A is a coenzyme A-binding membrane protein with structural similarities to ELOVL fatty acid elongase. Elife. 2021;10:e71220.
[25] BONET IJM, ARALDI D, BOGEN O, et al. Involvement of TACAN, a Mechanotransducing Ion Channel, in Inflammatory But Not Neuropathic Hyperalgesia in the Rat. J Pain. 2021;22(5):498-508.
[26] RAMAKRISHNAN AB, SINHA A, FAN VB, et al. The Wnt Transcriptional Switch: TLE Removal or Inactivation? Bioessays. 2018;40(2):10.1002/bies.201700162.
[27] YU G, CHEN Y, HU Y, et al. Roles of transducin-like enhancer of split (TLE) family proteins in tumorigenesis and immune regulation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1010639.
[28] ALI SA, ZAIDI SK, DOBSON JR, et al. Transcriptional corepressor TLE1 functions with Runx2 in epigenetic repression of ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(9):4165-4169.
[29] HONG D, CHEN HX, YU HQ, et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis of dexamethasone-induced effects on osteoblast differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cells using SILAC. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(7):2175-2186.
[30] BORZA R, SALGADO-POLO F, MOOLENAAR WH, et al. Structure and function of the ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (ENPP) family: Tidying up diversity. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(2):101526.
[31] 胡雅婷, 朱天啸, 徐新月. 嘌呤能受体对骨组织代谢及功能影响的研究进展[J].延安大学学报(医学科学版),2022,20(2):80-86.
[32] HARRISON N, KOO CZ, TOMLINSON MG. Regulation of ADAM10 by the TspanC8 Family of Tetraspanins and Their Therapeutic Potential. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6707.
[33] 樊俊, 吴陈欢, 程中华. 解整合素金属蛋白酶10与激素性股骨头坏死患者骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖及成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(10):1507-1513.
[34] 李敏启, 杜娟, 杨盼盼, 等. 氧化应激调控骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2021,59(6):16-24.
[35] YOON YM, KIM HJ, LEE JH, et al. Melatonin Enhances Mitophagy by Upregulating Expression of Heat Shock 70 kDa Protein 1L in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells under Oxidative Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(18):4545.
[36] LI G, YANG J, YANG C, et al. PTENα regulates mitophagy and maintains mitochondrial quality control. Autophagy. 2018;14(10):1742-1760.
[37] WITHERSPOON JW, MEILLEUR KG. Review of RyR1 pathway and associated pathomechanisms. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016; 4(1):121.
[38] ZAIDI M, MOONGA BS, HUANG CL. Calcium sensing and cell signaling processes in the local regulation of osteoclastic bone resorption. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2004;79(1):79-100.
[39] KODAMA K, TAKAHASHI H, OIJI N, et al. CANT1 deficiency in a mouse model of Desbuquois dysplasia impairs glycosaminoglycan synthesis and chondrocyte differentiation in growth plate cartilage. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(6):1096-1103.
[40] ZHAO G, ZHONG H, RAO T, et al. Metabolomic Analysis Reveals That the Mechanism of Astaxanthin Improves the Osteogenic Differentiation Potential in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:3427430.
[41] MA Z, WEI Y, ZHANG L, et al. GCTOF-MS Combined LC-QTRAP-MS/MS Reveals Metabolic Difference Between Osteoarthritis and Osteoporotic Osteoarthritis and the Intervention Effect of Erxian Decoction. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:905507. |