[1] DIBELLO D, TORELLI L, DI CARLO V, et al. Incidence of Congenital Clubfoot: Preliminary Data from Italian CeDAP Registry. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(9):5406.
[2] CADY R, HENNESSEY TA, SCHWEND RM. Diagnosis and Treatment of Idiopathic Congenital Clubfoot. Pediatrics. 2022;149(2):e2021055555.
[3] BINA S, PACEY V, BARNES EH, et al. Interventions for congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;5(5):CD008602.
[4] BASIT S, KHOSHHAL KI. Genetics of clubfoot; recent progress and future perspectives. Eur J Med Genet. 2018;61(2):107-113.
[5] MUSTARI MN, FARUK M, BAUSAT A, et al. Congenital talipes equinovarus: A literature review. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022;81:104394.
[6] BIANCO AM, RAGUSA G, DI CARLO V, et al.What Is the Exact Contribution of PITX1 and TBX4 Genes in Clubfoot Development? An Italian Study. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(11):1958.
[7] CAI G, YANG X, CHEN T, et al. Integrated bioinformatics analysis of potential pathway biomarkers using abnormal proteins in clubfoot. PeerJ. 2020;8:e8422.
[8] LI J, WANG Z, FENG D, et al. Evaluation of genetic susceptibility of common variants in SOX9 in patients with congenital talipes equinovarus in the Han Chinese population.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):276.
[9] LADEMANNF, WEIDNER H, TSOURDI E, et al.Disruption of BMP Signaling Prevents Hyperthyroidism-Induced Bone Loss in Male Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(10):2058-2069.
[10] TODD GM, GAO Z, HYVÖNEN M, et al. Secreted BMP antagonists and their role in cancer and bone metastases. Bone. 2020;(137):115455.
[11] LIM J, TU X, CHOI K, et al. BMP-Smad4 signaling is required for precartilaginous mesenchymal condensation independent of Sox9 in the mouse. Dev Biol. 2015;400(1):132-138.
[12] KIM DK, BANDARA G, CHO YE, et al. Mastocytosis-derived extracellular vesicles deliver miR-23a and miR-30a into pre-osteoblasts and prevent osteoblastogenesis and bone formation. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2527.
[13] LU Y, MA ZX, DENG R, et al. The SIRT1 activator SRT2104 promotes BMP9-induced osteogenic and angiogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Mech Ageing Dev. 2022;207:111724.
[14] ZHANG Q, CAO L, ZOU S, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Carrying MicroRNA-181c-5p Promote BMP2-Induced Repair of Cartilage Injury through Inhibition of SMAD7 Expression. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:1157498.
[15] ZENG Y, DU C, XIAO P, et al. Sox9-Increased miR-322-5p Facilitates BMP2-Induced Chondrogenic Differentiation by Targeting Smad7 in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:9778207.
[16] XIAO P, ZHU Z, DU C, et al. Silencing Smad7 potentiates BMP2-induced chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits endochondral ossification in human synovial-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):132.
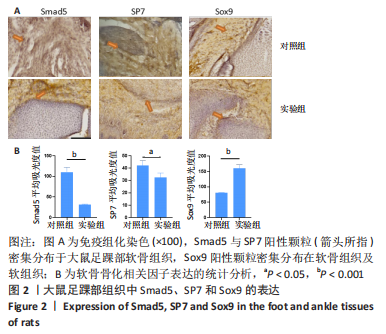
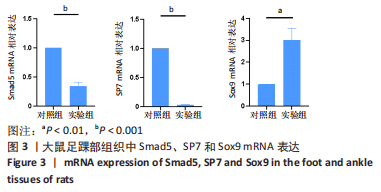
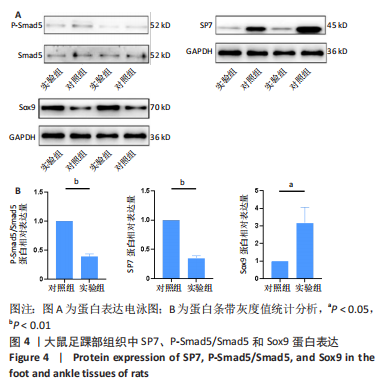
[17] 王正东,颜南,王效杰,等.Sox9基因在马蹄内翻足大鼠模型足踝软骨组织表达的实验研究[J].沈阳医学院学报,2012,14(4):199-201.
[18] BASIT S, KHOSHHAL KI. Genetics of clubfoot; recent progress and future perspectives.Eur J Med Genet. 2018;61(2):107-113.
[19] CANAVESE F, DIMEGLIO A. Clinical examination and classification systems of congenital clubfoot: a narrative review. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(13):1097.
[20] HEMO Y, GIGI R, WIENTROUB S. Delayed ossification and abnormal development of tarsal bones in idiopathic clubfoot: should it affect bracing protocol when using the Ponseti method? J Child Orthop. 2019;13(3):265-270.
[21] HASEEB A, KC R, ANGELOZZI M, et al. SOX9 keeps growth plates and articular cartilage healthy by inhibiting chondrocyte dedifferentiation/osteoblastic redifferentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(8):e2019152118.
[22] SONG H, PARK KH. Regulation and function of SOX9 during cartilage development and regeneration. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;67(Pt 1):12-23.
[23] SHI C, ZHENG W, WANG J. lncRNA-CRNDE regulates BMSC chondrogenic differentiation and promotes cartilage repair in osteoarthritis through SIRT1/SOX9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(4):1881-1890.
[24] LEFEBVRE V, ANGELOZZI M, HASEEB A. SOX9 in cartilage development and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019;61:39-47.
[25] JIAO F, TANG W, WANG J, et al. Icariin promotes the repair of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rabbit knee cartilage defects via the BMP/Smad pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(12):691.
[26] LOH HY, NORMAN BP, LAI KS, et al. Post-Transcriptional Regulatory Crosstalk between MicroRNAs and Canonical TGF-β/BMP Signalling Cascades on Osteoblast Lineage: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6423.
[27] LUO C, XU W, TANG X, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling works downstream of iron overload to prevent ferroptosis from damaging osteoblast differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;188:337-350.
[28] XUE Y, HU S, CHEN C, et al. Myokine Irisin promotes osteogenesis by activating BMP/SMAD signaling via αV integrin and regulates bone mass in mice. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(2):572-584.
[29] ZOU ML, CHEN ZH, TENG YY, et al. The Smad Dependent TGF-β and BMP Signaling Pathway in Bone Remodeling and Therapies. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:593310.
[30] KUSHIOKA J, KAITO T, OKADA R, et al. A novel negative regulatory mechanism of Smurf2 in BMP/Smad signaling in bone. Bone Res. 2020;8(1):41.
[31] LU Z, DU L, LIU R, et al. MiR-378 and BMP-Smad can influence the proliferation of sheep myoblast. Gene. 2018;674:143-150.
[32] SETIAWAN AM, KAMARUDIN TA, ABD GHAFAR N. The role of BMP4 in adipose-derived stem cell differentiation: A minireview. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1045103.
[33] LADEMANNF, WEIDNER H, TSOURDI E,et al.Disruption of BMP Signaling Prevents Hyperthyroidism-Induced Bone Loss in Male Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(10):2058-2069.
[34] THIELEN NGM, VAN DER KRAAN PM, VAN CAAM APM. TGFβ/BMP Signaling Pathway in Cartilage Homeostasis. Cells. 2019;8(9):969.
[35] WU M,CHEN G,LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016;26(4):16-19.
[36] LIU DD, ZHANG CY, LIU Y,et al. RUNX2 Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation via the BMP4 Signaling Pathway. J Dent Res. 2022;101(10):1227-1237.
[37] KOMORI T. Molecular Mechanism of Runx2-Dependent Bone Development. Mol Cells. 2020;43(2):168-175.
[38] LIANG N, ZHANG Q, HE B. Depth Vision-Based Assessment of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation Capacity in Patients with Congenital Scoliosis. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:4890008.
[39] NAVEN MA, ZEEF LAH, LI S, et al. Development of human cartilage circadian rhythm in a stem cell-chondrogenesis model. Theranostics. 2022;12(8):3963-3976.
[40] 赵翔.Pitx1和维甲酸通路在马蹄内翻足相关机制的研究并临床观察[D].上海:上海交通大学,2019.
|