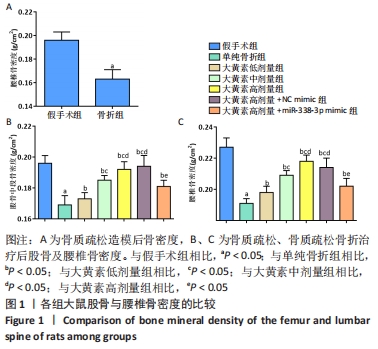
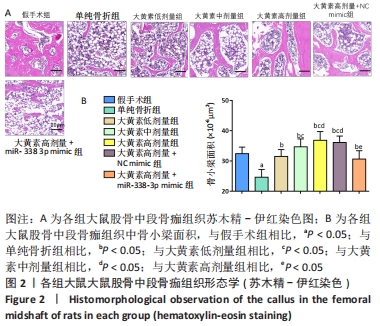
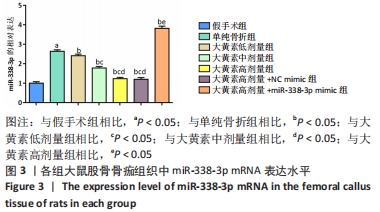
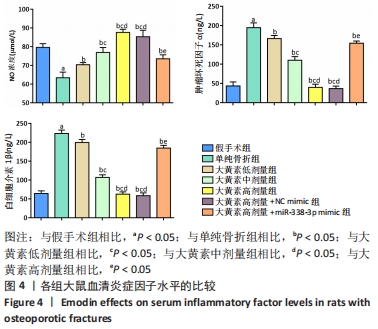
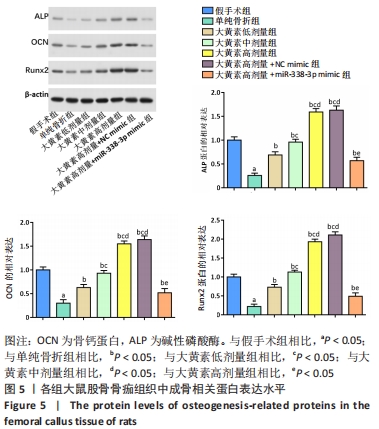
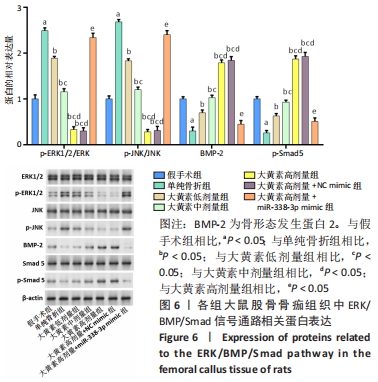
[1] QU XL, ZHENG B, CHEN TY, et al. Bone Turnover Markers and Bone Mineral Density to Predict Osteoporotic Fractures in Older Women: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):116-123.
[2] PAIK J, SCOTT LJ. Romosozumab: A Review in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Drugs Aging. 2020;37(11):845-855.
[3] JOHNSTON CB, DAGAR M. Osteoporosis in Older Adults. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(5):873-884.
[4] KAUSCHKE V, SCHNEIDER M, JAUCH A, et al. Effects of a Pasty Bone Cement Containing Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Functionalized Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Particles on Metaphyseal Healing in a New Murine Osteoporotic Fracture Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3531.
[5] LIN X, XIONG D, PENG YQ, et al. Epidemiology and management of osteoporosis in the People’s Republic of China: current perspectives. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;25(10):1017-1033.
[6] MARSELL R, EINHORN TA. The biology of fracture healing. Injury. 2011; 42(6):551-555.
[7] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutics for Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):76323.
[8] CHENG C, SHOBACK D. Mechanisms Underlying Normal Fracture Healing and Risk Factors for Delayed Healing. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(1): 36-47.
[9] WANG T, ZHANG X, BIKLE DD. Osteogenic Differentiation of Periosteal Cells During Fracture Healing. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(5):913-921.
[10] BAHNEY CS, ZONDERVAN RL, ALLISON P, et al. Cellular biology of fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(1):35-50.
[11] WON DY, BYUN SJ, JEONG JS, et al. Association Between Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Osteoporotic Fractures in Older Persons With Alzheimer’s Disease. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(8): 1128-1133.e1121.
[12] KIM YG, PARK YH, YANG EY, et al. Inhibition of tamoxifen’s therapeutic effects by emodin in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019;97(5):230-238.
[13] DONG X, FU J, YIN X, et al. Emodin: A Review of its Pharmacology, Toxicity and Pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res. 2016;30(8):1207-1218.
[14] LEE EH, BAEK SY, PARK JY, et al. Emodin in Rheum undulatum inhibits oxidative stress in the liver via AMPK with Hippo/Yap signalling pathway. Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):333-341.
[15] YANG Y, JIANG Z, ZHUGE D. Emodin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Injury via Down-Regulation of miR-223 in H9c2 Cells. Int Heart J. 2019;60(2):436-443.
[16] LI N, WANG C, ZHANG P, et al. Emodin inhibits pancreatic cancer EMT and invasion by up‑regulating microRNA‑1271. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 18(3):3366-3374.
[17] MADHYASTHA R, MADHYASTHA H, PENGJAM Y, et al. The pivotal role of microRNA-21 in osteoclastogenesis inhibition by anthracycline glycoside aloin. J Nat Med. 2019;73(1):59-66.
[18] LI Z, ZHANG W, HUANG Y. MiRNA-133a is involved in the regulation of postmenopausal osteoporosis through promoting osteoclast differentiation. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2018;50(3):273-280.
[19] TONG J, ZHANG M, LI X, et al. MicroRNA-338-3p regulates age‑associated osteoporosis via targeting PCSK5. Mol Med Rep. 2021; 23(2):136.
[20] ZHANG XH, GENG GL, SU B, et al. MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoid-induced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(3). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15037674.
[21] LIU H, SUN Q, WAN C, et al. MicroRNA-338-3p regulates osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow stromal stem cells by targeting Runx2 and Fgfr2. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(10):1494-1502.
[22] SUN Q, ZHANG B, ZHU W, et al. A potential therapeutic target for regulating osteoporosis via suppression of osteoclast differentiation. J Dent. 2019;82:91-97.
[23] XIAO L, ZHONG M, HUANG Y, et al. Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(21):21706-21729.
[24] HUANG K, WU G, ZOU J, et al. Combination therapy with BMP-2 and psoralen enhances fracture healing in ovariectomized mice. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):1655-1662.
[25] LU X, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. The miRNA-15b/USP7/KDM6B axis engages in the initiation of osteoporosis by modulating osteoblast differentiation and autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):2069-2081.
[26] RUTTEN S, NOLTE PA, KORSTJENS CM, et al. Low- intensitypulsed ultrasound affects RUNX2 immunopositive osteogenic cells in delayed clinical fracture healing. Bone. 2009;(1):862-869.
[27] 陈玲,杨云洲,陈继革.接骨七厘片促进大鼠骨折愈合的实验研究[J].湖北中医杂志,2005,27(1):50-52.
[28] 张杰,刘广宇,张晓峰,等.香丹注射液促进骨痂生长的生物力学研究[J].中医药信息,2006,23(6):50-51.
[29] KLOEN P, DOTY SB, GORDON E, et al. Expression and activation of the BMP-signaling components in human fracture nonunions. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84 (11):1909-1918.
[30] 潘月兴.壮筋续骨汤对骨折大鼠血清 bFGF和IGF-1含量的影响和意义[D].青岛:青岛大学,2013.
[31] MARITATO KC, BARNHART MD. Minimally Invasive Fracture Repair. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2020;50(1): xiii-xiv.doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2019.10.001.
[32] BAECKER H, FRIELER S, SCHILDHAUER TA, et al. Fracture-related infections in traumatology : Current standards and new developments in diagnostics and treatment. Orthopade. 2020;49(8):702-709.
[33] VAN DER KLIFT M, DE LAET CD, POLS HA. Assessment of fracture risk: who should be treated for osteoporosis? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2005;19(6):937-950.
[34] KAVEH S, HOSSEINIFARD H, GHADIMI N, et al. Efficacy and safety of Romosozumab in treatment for low bone mineral density: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(11):3261-3276.
[35] CHEN X, REN S, ZHU G, et al. Emodin suppresses cadmium-induced osteoporosis by inhibiting osteoclast formation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;54:162-168.
[36] YANG F, YUAN PW, HAO YQ, et al. Emodin enhances osteogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:74.
[37] LEE SU, SHIN HK, MIN YK, et al. Emodin accelerates osteoblast differentiation through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation and bone morphogenetic protein-2 gene expression. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008;8(5):741-747.
[38] JIA R, YI Y, LIU J, et al. Cyclic compression emerged dual effects on the osteogenic and osteoclastic status of LPS-induced inflammatory human periodontal ligament cells according to loading force. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):7.
[39] ZHENG J, ZHU X, HE Y, et al. CircCDK8 regulates osteogenic differentiation and apoptosis of PDLSCs by inducing ER stress/autophagy during hypoxia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021;1485(1):56-70.
[40] KOMORI T. Runx2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):313-323.
[41] 曾宪良,黄军铭.股骨重建髓内钉结合有限切开重建股骨外侧壁治疗不稳定型粗隆下骨折的疗效分析[J].当代医学,2021,27(9):158-160.
[42] DONG Y, ZHANG L, JIANG Y, et al. Emodin reactivated autophagy and alleviated inflammatory lung injury in mice with lethal endotoxemia. Exp Anim. 2019;68(4):559-568.
[43] REDLICH K, SMOLEN JS. Inflammatory bone loss: pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11(3):234-250.
[44] YANG Y, YUJIAO W, FANG W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):40.
[45] LV PY, GAO PF, TIAN GJ, et al. Osteocyte-derived exosomes induced by mechanical strain promote human periodontal ligament stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation via the miR-181b-5p/PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):295.
[46] SUN Z, WANG H, WANG Y, et al. MiR-103-3p targets the m(6) A methyltransferase METTL14 to inhibit osteoblastic bone formation. Aging Cell. 2021;20(2):e13298.
[47] LI Z, OH H, CUNG M, et al. TAOK3 is a MAP3K contributing to osteoblast differentiation and skeletal mineralization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(4):497-502.
[48] CHEON YH, LEE CH, KIM S, et al. Pitavastatin prevents ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by regulating osteoclastic resorption and osteoblastic formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;139:111697.
[49] XU Y, GU Y, JI W, et al. Activation of the extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signal pathway and osteogenic factors in subchondral bone of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(8):663.
[50] HUANG D, HOU X, ZHANG D, et al. Two novel polysaccharides from rhizomes of Cibotium barometz promote bone formation via activating the BMP2/SMAD1 signaling pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;231:115732.
|