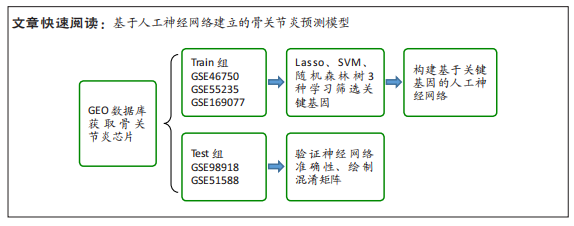
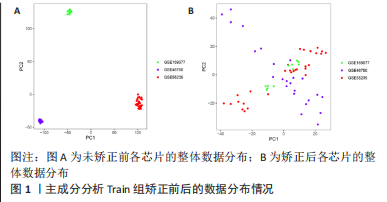
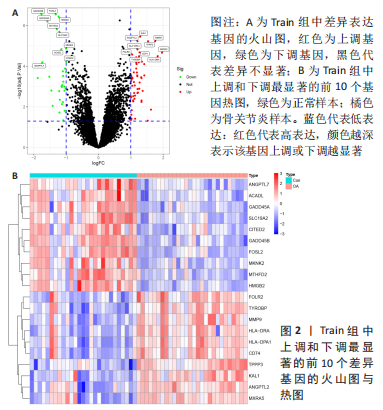
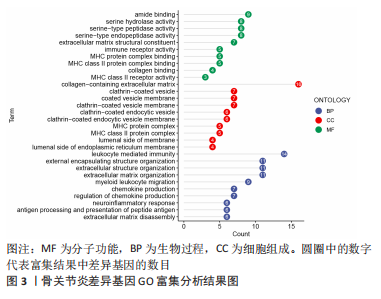
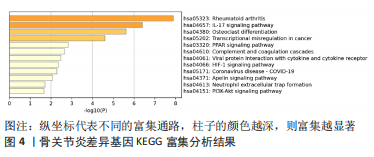
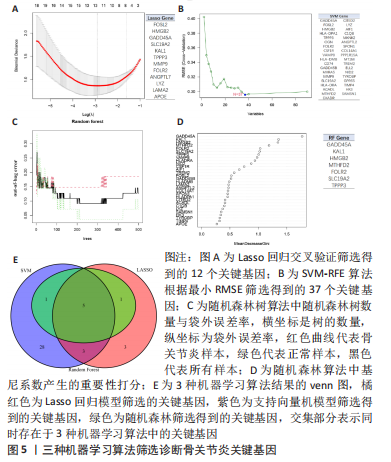
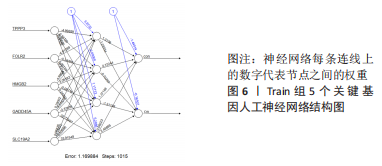
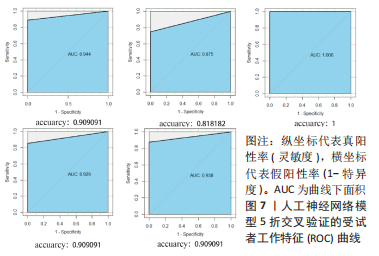
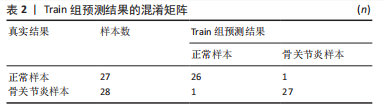
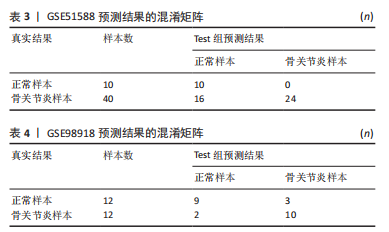
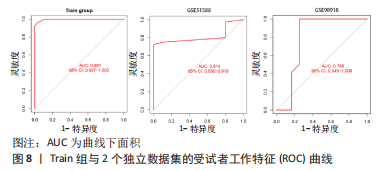
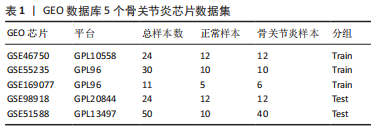
[1] JANG S, LEE K, JU J H. Recent updates of diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment on osteoarthritis of the knee. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2619.
[2] WANG J, SUN Y, LIU J, et al. Roles of long non‑coding RNA in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(1):133.
[3] LIANG Y, LIN F, HUANG Y. Identification of Biomarkers Associated with Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis Patients Based on Bioinformatics and Machine Learning. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:5600190.
[4] XIE NN, WANG FF, ZHOU J, et al. Establishment and analysis of a combined diagnostic model of polycystic ovary syndrome with random forest and artificial neural network. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2613091.
[5] MAMOSHINA P, VIEIRA A, PUTIN E, et al. Applications of deep learning in biomedicine. Mol Pharm. 2016;13(5):1445-1454.
[6] WEI Q, FANG W, CHEN X, et al. Establishment and validation of a mathematical diagnosis model to distinguish benign pulmonary nodules from early non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese people. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020;9(5):1843-1852.
[7] WANG C, ZHAO Y, JIN B, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for coronary artery disease using machine learning. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021; 8:614204.
[8] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436-444.
[9] TIAN Y, YANG J, LAN M, et al. Construction and analysis of a joint diagnosis model of random forest and artificial neural network for heart failure. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):26221-26235.
[10] SUN D, PENG H, WU Z. Establishment and analysis of a combined diagnostic model of alzheimer’s disease with random forest and artificial neural network. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:921906.
[11] SHE J, SU D, DIAO R, et al. A Joint Model of Random Forest and Artificial Neural Network for the Diagnosis of Endometriosis. Front Genet. 2022;13:848116.
[12] LAMBERT C, DUBUC JE, MONTELL E, et al. Gene expression pattern of cells from inflamed and normal areas of osteoarthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):960-968.
[13] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84.
[14] BROPHY RH, ZHANG B, CAI L, et al. Transcriptome comparison of meniscus from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3): 422-432.
[15] CHOU CH, WU CC, SONG IW, et al. Genome-wide expression profiles of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6):R190.
[16] LIU W, ZENG S, WU G, et al. Rice seed purity identification technology using hyperspectral image with LASSO logistic regression model. Sensors (Basel). 2021;21(13):4384.
[17] HUANG ML, HUNG YH, LEE WM, et al. SVM-RFE based feature selection and Taguchi parameters optimization for multiclass SVM classifier. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:795624.
[18] ACHARJEE A, LARKMAN J, XU Y, et al. A random forest based biomarker discovery and power analysis framework for diagnostics research. BMC Med Genomics. 2020;13(1):178.
[19] XIANG J, HUANG W, HE Y, et al. Construction of artificial neural network diagnostic model and analysis of immune infiltration for periodontitis. Front Genet. 2022; 13:1041524.
[20] WU Y, CHEN H, LI L, et al. Construction of novel gene signature-based predictive model for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction by combining random forest with artificial neural network. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:876543.
[21] YE T, HAOYUAN Z, BEI Z, et al. Exploration of biomarkers in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(31):e26730.
[22] 陈宗锐,孙洁,姜萍.骨关节炎软骨代谢相关生物标志物的研究进展[J].医学综述,2022,28(12):2351-2356
[23] KUO YY, HUANG ST, CHIU HW. Applying artificial neural network for early detection of sepsis with intentionally preserved highly missing real-world data for simulating clinical situation. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021;21(1):290.
[24] BAXT WG. Application of artificial neural networks to clinical medicine. The lancet. 1995;346(8983):1135-1138.
[25] TANIGUCHI N, CARAMÉS B, RONFANI L, et al. Aging-related loss of the chromatin protein HMGB2 in articular cartilage is linked to reduced cellularity and osteoarthritis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(4):1181-1186.
[26] 谢春意,刘晓辉,谢获,等.膝骨关节炎患者滑液和血清中HMGB2的研究[J].放射免疫学杂志,2012,25(6):675-677
[27] WARMINK K, SIEBELT M, LOW PS, et al. Folate Receptor Expression by Human Monocyte–Derived Macrophage Subtypes and Effects of Corticosteroids. Cartilage. 2022;13(1):19476035221081469.
[28] YI YS. Folate receptor-targeted diagnostics and therapeutics for inflammatory diseases. Immune Netw. 2016;16(6):337-343.
[29] BLOM AB, VAN LENT PL, HOLTHUYSEN AE, et al. Synovial lining macrophages mediate osteophyte formation during experimental osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(8):627-635.
[30] LI RN, LIN YZ, PAN YC, et al. GADD45a and GADD45b genes in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus patients. J Clin Med. 2019;8(6):801.
[31] ZHAN Q. Gadd45a, a p53-and BRCA1-regulated stress protein, in cellular response to DNA damage. Mutat Res. 2005;569(1-2):133-143.
[32] HASHIMOTO S, NISHIYAMA T, HAYASHI S, et al. Role of p53 in human chondrocyte apoptosis in response to shear strain. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(8):2340-2349.
[33] JANG HJ, YANG JH, HONG E, et al. Chelidonine induces apoptosis via GADD45a-p53 regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells. Integr Cancer Ther. 2021;20:15347354211006191.
[34] JIN S, MAZZACURATI L, ZHU X, et al. Gadd45a contributes to p53 stabilization in response to DNA damage. Oncogene. 2003;22(52):8536-8540.
[35] AMR K, PAWLIKOWSKA P, AOUFOUCHI S, et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies a new mutation in the SLC19A2 gene leading to thiamine‐responsive megaloblastic anemia in an Egyptian family. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019; 7(7):e00777.
[36] LO PK, CHEN JY, TANG PP, et al. Identification of a mouse thiamine transporter gene as a direct transcriptional target for p53. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(40):37186-37193.
[37] STAVEROSKY JA, PRYCE BA, WATSON SS, et al. Tubulin polymerization‐promoting protein family member 3, Tppp3, is a specific marker of the differentiating tendon sheath and synovial joints. Dev Dyn. 2009;238(3):685-692. |