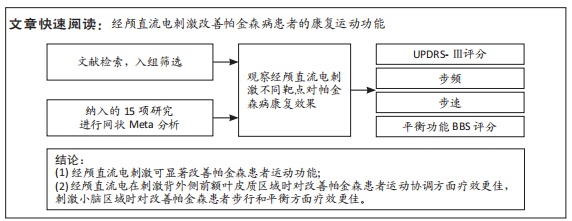
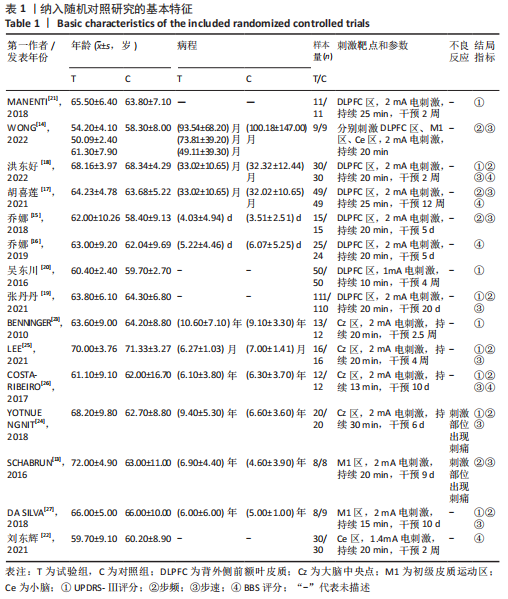
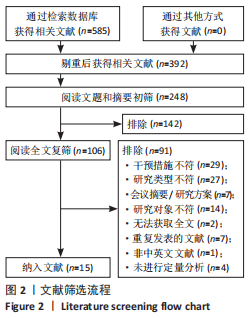
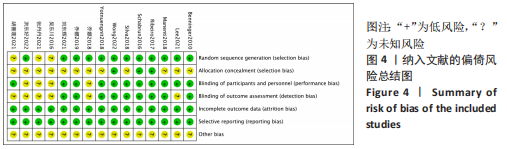
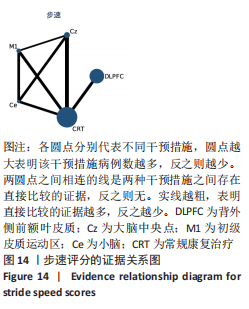
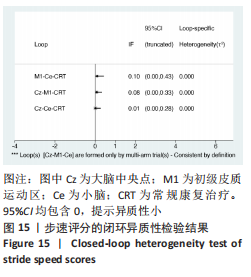
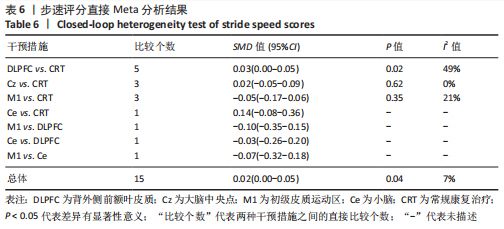
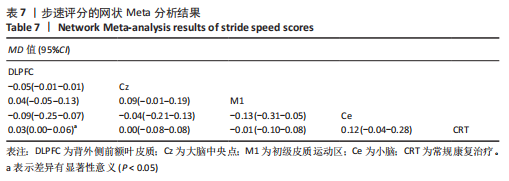
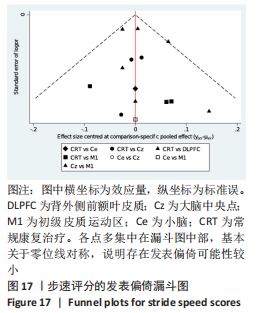
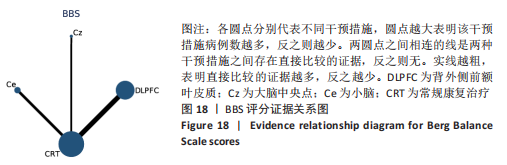
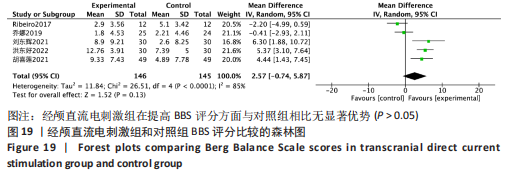
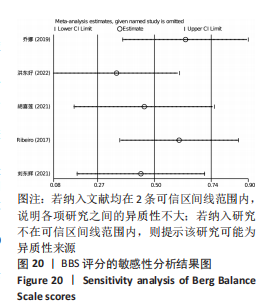
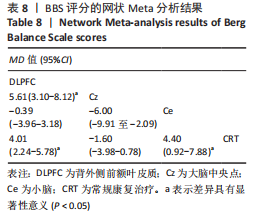
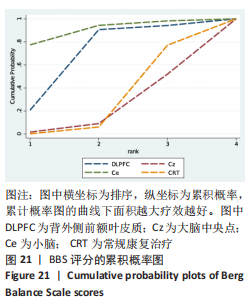
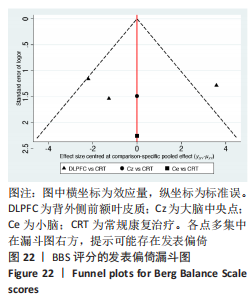
[1] 刘疏影,陈彪.帕金森病流行现状[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2016,16(2):98-101.
[2] DING C, WU Y, CHEN X, et al. Global, regional, and national burden and attributable risk factors of neurological disorders: the Global Burden of Disease study 1990-2019. Front Public Health. 2022;10:952161.
[3] GUADARRAMA-MOLINA E, BARRÓN-GÁMEZ CE, ESTRADA-BELLMANN I, et al. Comparison of the effect of whole-body vibration therapy versus conventional therapy on functional balance of patients with Parkinson’s disease: adding a mixed group. Acta Neurol Belg. 2021; 121(3):721-728.
[4] DELGADO-ALVARADO M, MARANO M, SANTURTúN A, et al. Nonpharmacological, nonsurgical treatments for freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. Mov Disord. 2020;35(2):204-214.
[5] FENG XJ, HUANG YT, HUANG YZ, et al. Early transcranial direct current stimulation treatment exerts neuroprotective effects on 6-OHDA-induced Parkinsonism in rats. Brain Stimul. 2020;13(3):655-663.
[6] PEREIRA JB, JUNQUé C, BARTRéS-FAZ D, et al. Modulation of verbal fluency networks by transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Stimul. 2013;6(1):16-24.
[7] FILMER HL, DUX PE, MATTINGLEY JB. Applications of transcranial direct current stimulation for understanding brain function. Trends Neurosci. 2014;37(12):742-753.
[8] 张嫣然,袁勇贵.经颅直流电刺激在抑郁症治疗中的应用[J].实用医院临床杂志,2015, 12(6):12-15.
[9] 李泓钰,宋鲁平.经颅直流电刺激在卒中后抑郁中的研究进展[J].中国老年保健医学, 2018,16(3):61-64.
[10] 郭慧敏,朱玉连.经颅直流电刺激改善帕金森病患者步态及平衡障碍的研究进展[J].上海医药,2021,42(12):3-6, 62.
[11] DE OLIVEIRA PCA, DE ARAúJO TAB, MACHADO D, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation on parkinson’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol. 2021;12:794784.
[12] 张振馨.帕金森病的诊断[J].中华神经科杂志,2006,39(6):408-409.
[13] SCHABRUN SM, LAMONT RM, BRAUER SG. Transcranial direct current stimulation to enhance dual-task gait training in parkinson’s disease: a pilot RCT. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0158497.
[14] WONG PL, YANG YR, HUANG SF, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation on different targets to modulate cortical activity and dual-task walking in individuals with parkinson’s disease: a double blinded randomized controlled trial. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:807151.
[15] 乔娜,燕铁斌,卢健军,等.经颅直流电刺激对帕金森病早期患者步行功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2018,40(7):509-512.
[16] 乔娜,卢健军,郭永亮,等.经颅直流电刺激对帕金森病患者平衡功能的影响[J].康复学报,2019,29(3):22-26.
[17] 胡喜莲,薛翠萍,刘自双.经颅直流电刺激辅助功能康复训练对帕金森病患者康复的效果[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(17):3724-3727.
[18] 洪东好,祝善尧,陈海燕,等.康复运动训练联合经颅直流电刺激对帕金森病患者步行功能、平衡功能和认知功能的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2022,22(13):2575-2578, 2563.
[19] 张丹丹,毛洁萍.重复经颅直流电刺激对于PD患者躯干肌电特征、步行功能及生存质量的影响[J].中华保健医学杂志,2021, 23(5):465-468.
[20] 吴东川,吴晓霞,王广君,等.多巴丝肼片口服联合经颅直流电刺激对帕金森病患者非运动症状的改善作用[J].山东医药,2016, 56(31):88-90.
[21] MANENTI R, COTELLI MS, COBELLI C, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation combined with cognitive training for the treatment of Parkinson Disease: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Brain Stimul. 2018; 11(6):1251-1262.
[22] 刘东辉,张大华.经颅直流电刺激改善帕金森病患者平衡障碍的疗效观察[J].中国医刊,2021,56(7):765-768.
[23] BENNINGER DH, LOMAREV M, LOPEZ G, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010;81(10):1105-1111.
[24] YOTNUENGNIT P, BHIDAYASIRI R, DONKHAN R, et al. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation plus physical therapy on gait in patients with parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018; 97(1):7-15.
[25] LEE SA, KIM MK. The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation combined with visual cueing training on motor function, balance, and gait ability of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(11):1146.
[26] COSTA-RIBEIRO A, MAUX A, BOSFORD T, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation associated with gait training in Parkinson’s disease: a pilot randomized clinical trial. Dev Neurorehabil. 2017;20(3):121-128.
[27] DA SILVA DCL, LEMOS T, FERREIRA AD, et al. Effects of acute transcranial direct current stimulation on gait kinematics of individuals with Parkinson disease. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;34(4):262-268.
[28] FERRAZZOLI D, ORTELLI P, CUCCA A, et al. Motor-cognitive approach and aerobic training: a synergism for rehabilitative intervention in Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2020;10(1):41-55.
[29] ABBRUZZESE G, MARCHESE R, AVANZINO L, et al. Rehabilitation for Parkinson’s disease: current outlook and future challenges. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016;22 Suppl 1:S60-S64.
[30] GALNA B, LORD S, BURN DJ, et al. Progression of gait dysfunction in incident Parkinson’s disease: impact of medication and phenotype. Mov Disord. 2015;30(3):359-367.
[31] CURTZE C, NUTT JG, CARLSON-KUHTA P, et al. Levodopa is a double-edged sword for balance and gait in people with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2015;30(10):1361-1370.
[32] SáNCHEZ-KUHN A, PéREZ-FERNáNDEZ C, CáNOVAS R, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation as a motor neurorehabilitation tool: an empirical review. Biomed Eng Online. 2017;16(Suppl 1):76.
[33] POLANíA R, PAULUS W, NITSCHE MA. Modulating cortico-striatal and thalamo-cortical functional connectivity with transcranial direct current stimulation. Hum Brain Mapp. 2012;33(10):2499-2508.
[34] BROWN GL, BROWN MT. Transcranial electrical stimulation in neurological disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(10):2221-2222.
[35] NITSCHE MA, PAULUS W. Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol. 2000;527(Pt 3):633-639.
[36] SABATINI U, BOULANOUAR K, FABRE N, et al. Cortical motor reorganization in akinetic patients with Parkinson’s disease: a functional MRI study. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 2):394-403.
[37] LATTARI E, COSTA SS, CAMPOS C, et al. Can transcranial direct current stimulation on the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex improves balance and functional mobility in Parkinson’s disease? Neurosci Lett. 2017;636:165-169.
[38] WITT I, GANJAVI H, MACDONALD P. Relationship between freezing of gait and anxiety in parkinson’s disease patients: a systemic literature review. Parkinsons Dis. 2019;2019:6836082.
[39] MORI S, MATSUI T, KUZE B, et al. Stimulation of a restricted region in the midline cerebellar white matter evokes coordinated quadrupedal locomotion in the decerebrate cat. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82(1):290-300.
[40] JAYARAM G, GALEA JM, BASTIAN AJ, et al. Human locomotor adaptive learning is proportional to depression of cerebellar excitability. Cereb Cortex. 2011;21(8):1901-1909.
[41] MORTON SM, BASTIAN AJ. Cerebellar contributions to locomotor adaptations during splitbelt treadmill walking. J Neurosci. 2006;26(36):9107-9116.
[42] RICHARD A, VAN HAMME A, DREVELLE X, et al. Contribution of the supplementary motor area and the cerebellum to the anticipatory postural adjustments and execution phases of human gait initiation. Neuroscience. 2017; 358:181-189.
[43] 马东辉,王红.帕金森病与小脑相关的研究[J].医学信息,2021,34(7):44-46.
[44] GILAT M, DIJKSTRA BW, D’CRUZ N, et al. Functional MRI to study gait impairment in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and exploratory ALE meta-analysis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(8):49.
[45] HUANG Y, LIU AA, LAFON B, et al. Measurements and models of electric fields in the in vivo human brain during transcranial electric stimulation. Elife. 2017;6:e18834.
[46] DUNCAN ES, NAKKAWITA SG. Clinical feasibility of combining transcranial direct current stimulation with standard aphasia therapy. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2020;23(Suppl 2): S102-S108.
|