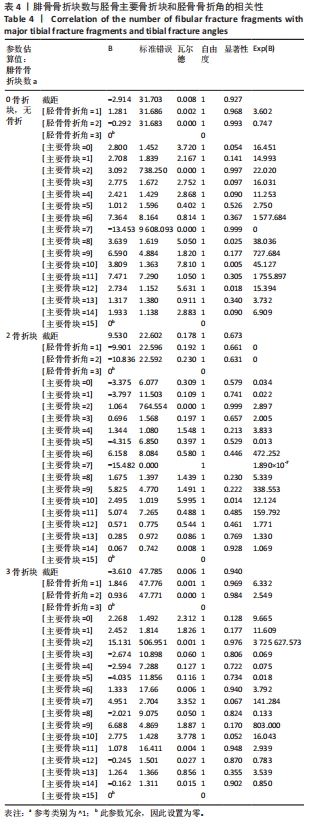
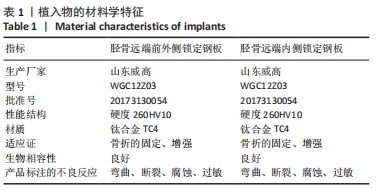
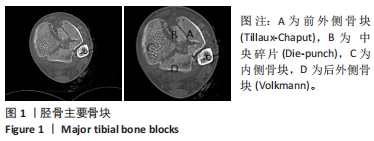
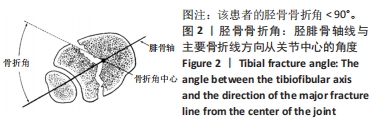
[1] 王智祥, 魏世隽, 蔡贤华. 胫骨Pilon骨折分型现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(6):533-557.
[2] HEIM U. Morphological Features for Evaluation and Classification of Pilon Tibial Fractures. Major Fractures of the Pilon, the Talus, and the Calcaneus, 1993.
[3] CHEN DW, LI B, AUBEELUCK A, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of posterior pilon fractures with buttress plate. Acta Ortopedica Brasileira. 2014;22(1):48.
[4] ZELLE BA, DANG KH, ORNELL SS. High-energy tibial pilon fractures: an instructional review. Int Orthop. 2019;43(8):1939-1950.
[5] SHU W, HU X, YANG X. Comparison Between the Modified External Fixation and Calcaneal Traction in Ruedi-Allgower Type II/III Pilon Fractures. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e933385.
[6] HADEED MM, EVANS CL, WERNER BC, et al. Does external fixator pin site distance from definitive implant affect infection rate in pilon fractures? Injury. 2019;50(2):503-507.
[7] JIANG GQ, JIAO FD, YING WC, et al. [Staged operation for complex closed Pilon fracture] . Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022;35(9):878-882.
[8] KEILER A, RIECHELMANN F, THÖNI M, et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography reconstruction improves the reliability of tibial pilon fracture classification and preoperative surgical planning . Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(2):187-195.
[9] LUO T D, PILSON H. Pilon Fracture. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL); StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC. 2023.
[10] BAREI DP, NORK SE, BELLABARBA C, et al. Is the absence of an ipsilateral fibular fracture predictive of increased radiographic tibial pilon fracture severity? J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(1):6-10.
[11] MAUFFREY C, VASARIO G, BATTISTON B, et al. Tibial pilon fractures: a review of incidence, diagnosis, treatment, and complications . Acta Orthop Belg. 2011;77(4):432-440.
[12] RUEDI TP, ALLGOWER M. The operative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the lower end of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;(138):105-110.
[13] LEE YS, CHEN SW, CHEN SH, et al. Stabilisation of the fractured fibula plays an important role in the treatment of pilon fractures: a retrospective comparison of fibular fixation methods. Int Orthop. 2009;33(3):695-699.
[14] TORINO D, MEHTA S. Fibular Fixation in Distal Tibia Fractures: Reduction Aid or Nonunion Generator? J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30 Suppl 4:S22-S25.
[15] HALLER JM, GITHENS M, ROTHBERG D, et al. Syndesmosis and Syndesmotic Equivalent Injuries in Tibial Plafond Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;3:e74-e78.
[16] BASTIAS C, LAGOS L. New Principles in Pilon Fracture Management: Revisiting Rüedi and Allgöwer Concepts. Foot Ankle Clin. 2020;25(4):505-521.
[17] MAIR O, PFLUGER P, HOFFELD K, et al. Management of Pilon Fractures-Current Concepts. Front Surg. 2021;8:764232.
[18] TOULOUPAKIS G, MESSORI M, GILLI A, et al.Distal Tibia Fractures: is the Tibia First Technique a Rational Approach? Malays Orthop J. 2023; 1:172-179.
[19] EGOL KA, WEISZ R, HIEBERT R, et al. Does fibular plating improve alignment after intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibia fractures? J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(2):94-103.
[20] BEAR J, ROLLICK N, HELFET D. Evolution in Management of Tibial Pilon Fractures. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(4):537-545.
[21] PARK YU, KIM SJ, KIM HN. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using the oblong hole of a locking plate for comminuted distal fibular fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):281.
[22] JUNG GH, CHUNG H, BAEK SH, et al. Percutaneous bridge plating of extra-articular distal fibular fracture for the management of distal tibia type III open fracture. Asian J Surg. 2021;44(1):363-368.
[23] KURYLO JC, DATTA N, ISKANDER KN, et al. Does the Fibula Need to be Fixed in Complex Pilon Fractures? J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(9):424-427.
[24] TORINO D, MEHTA S. Fibular Fixation in Distal Tibia Fractures: Reduction Aid or Nonunion Generator? J Orthop Trauma. 2016;4:S22-S25.
[25] HOHENBERGER GM, SCHWARZ AM, GRECHENIG C, et al. Dorsal minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of the distal tibia with regard to adjacent anatomical characteristics. Injury. 2021;5:S11-S16.
[26] VIDOVIC D, MATEJCIC A, IVICA M, et al. Minimally-invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibial fractures: Results and complications. Injury. 2015;6:S96-S99.
[27] HENDRYCH J, PESL T, HAVRANEK P. [Triplane Fractures of the Distal Tibial Epiphysis - Contributions of CT Scans to Indication and Planning of Osteosynthesis. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2018;85(5):336-342.
[28] WANG C, CHEN C, ZHOU Y, et al. Morphological study of CT image of posterior pilon variant fracture and its possible clinical significance. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;3:1203-1215.
[29] BUSEL GA, WATSON JT, ISRAEL H. Evaluation of Fibular Fracture Type vs Location of Tibial Fixation of Pilon Fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;6:650-655.
[30] LUK PC, CHARLTON TP, LEE J, et al. Ipsilateral intact fibula as a predictor of tibial plafond fracture pattern and severity. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;10:1421-1426.
[31] KELLAM JF, WADDELL JP. Fractures of the distal tibial metaphysis with intra-articular extension--the distal tibial explosion fracture. J Trauma. 1979;19(8):593-601.
[32] TORNETTA P 3RD, GORUP J. Axial computed tomography of pilon fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;323:273-276.
[33] 黄彬. 移位Pilon骨折的分型与手术治疗[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学, 2010.
[34] LABRONICI P, JUNIOR AFM, DA SILVA AAM, et al. CT mapping for complex tibial pilon fractures: Understanding the injury pattern and its relation to the approach choice. Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 3:s70-s76.
|