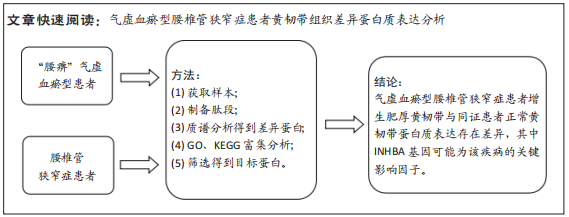
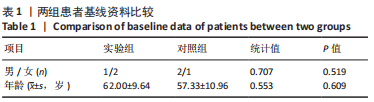
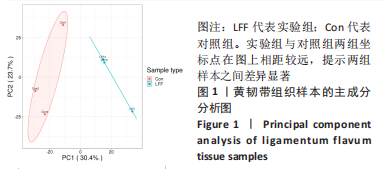
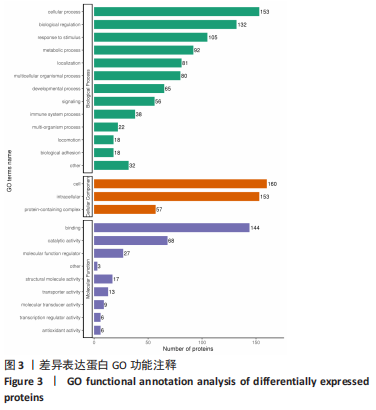
[1] LURIE J, TOMKINS-LANE C. Management of lumbar spinal stenosis. BMJ. 2016;352:h6234.
[2] SAKAI Y, ITO S, HIDA T, et al. Clinical outcome of lumbar spinal stenosis based on new classification according to hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(1):27-33.
[3] MUNNS JJ, LEE JY, ESPINOZA ORÍAS AA, et al. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy in asymptomatic and chronic low back pain subjects. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0128321.
[4] SUN C, ZHANG H, WANG X, et al. Ligamentum flavum fibrosis and hypertrophy: Molecular pathways, cellular mechanisms, and future directions. FASEB J. 2020;34(8):9854-9868.
[5] ANDERSON DB, LUCA K, JENSEN RK, et al. A critical appraisal of clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine J. 2021;21(3):455-464.
[6] 祝乾清,曾曼杰.国际中医临床实践指南:退变性腰椎管狭窄症[J].世界中医药,2021,17(34):21.
[7] 周宾宾,李玉文,蔡乐乐,等.腰椎管狭窄症中医证型规范化的探讨[J].时珍国医国药,2009,20(12):3176-3177.
[8] 鲁齐林.高糖伴腰椎管狭窄黄韧带肥厚的炎性机制及姜黄素的干预效应研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2020.
[9] 中华医学会.临床诊疗指南·骨科分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009.
[10] PIECHOTA M, KRÓL R, ELIAS DA, et al. The nerve root sedimentation sign in diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Radiol. 2019;60(5): 634-642.
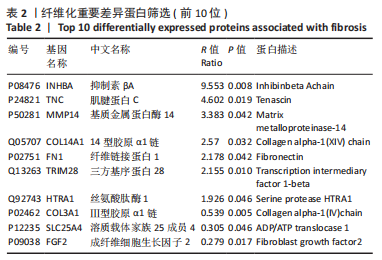
[11] NAMWANJE M, BROWN CW. Activins and inhibins: Roles in development, physiology,and disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8(7):a021881.
[12] YI Y, CHENG JC, KLAUSEN C, et al. Activin A promotes ovarian cancer cell migration by suppressing E-cadherin expression. Exp Cell Res. 2019;382(2):111471.
[13] KALLI M, MPEKRIS F, WONG CK, et al. Activin A Signaling Regulates IL13Rα2 Expression to Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis. Front Oncol. 2019;9:32.
[14] QIANG L, CAO H, CHEN J, et al. Pancreatic tumor cell metastasis is restricted by MT1-MMP binding protein MTCBP-1. J Cell Biol. 2019; 218(1):317-332.
[15] 许静轩,杜少倩,曹源,等.MMP14在胰腺癌中的表达及其与肿瘤免疫微环境特征的相关性研究[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2022,42(3):312-322.
[16] 李刚,刘江豪,罗璟璐,等.MMP14通过调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响胃癌的发生、发展机制研究[J].医学研究杂志,2020,49(2): 92-98.
[17] 蔡隽,沈文远,王慧,等.重组人源TNC诱导胰腺癌细胞系PANC1的EMT及迁移和侵袭[J].基础医学与临床,2020,40(2):167-172.
[18] FISCHER D, TUCKER RP, CHIQUET-EHRISMANN R, et al. Cell-adhesive responses to tenascin-C splice variants involve formation of fascin microspikes. Mol Biol Cell. 1997;8(10):2055-2075.
[19] 王道,梁波罗.人HtrA1基因的生物信息学分析[J].湖南师范大学自然科学学报,2021,44(3):54-62.
[20] CLAUSEN T, SOUTHAN C, EHRMANN M. The HtrA family of proteases: implications for protein composition and cell fate. Mol Cell. 2002;10(3): 443-455.
[21] OKA C, TSUJIMOTO R, KAJIKAWA M, et al. HtrA1 serine protease inhibits signaling mediated by Tgfbeta family proteins. Development. 2004;131(5):1041-1053.
[22] LI XY, BAN GF, AL-SHAMERI B, et al. High-temperature Requirement Protein A1 Regulates Odontoblastic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Cells via the Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1/Smad Signaling Pathway. J Endod. 2018;44(5):765-772.
[23] YAMAWAKI S, NAITOH M, KUBOTA H, et al. HtrA1 Is Specifically Up-Regulated in Active Keloid Lesions and Stimulates Keloid Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1275.
[24] JIN SF, WANG YX, XU N, et al. High temperature requirement factor A1 (HTRA1) regulates the activation of latent TGF-β1 in keloid fibroblasts. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018;64(1):107-110.
[25] Guan X, Nie L, He T, et al. Klotho suppresses renal tubulo-interstitial fibrosis by controlling basic fibroblast growth factor-2 signalling. J Pathol. 2014;234(4):560-572.
[26] 陈立,袁军,詹理睿,等.FGF2/FGFR1/ERK信号通路在高糖诱导人肾小管上皮细胞转分化中的机制及肾元颗粒的干预作用[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2017,18(3):201-204.
[27] 刘梦昕,孙昌业,李铎,等.大鼠成纤维细胞生长因子对心肌成纤维细胞增殖和转分化的作用机制[J].解剖学报,2021,52(5):712-719.
[28] 张晗,孙超,刘新晖.腰椎黄韧带纤维化的研究进展[J].临床骨科杂志,2022,25(3):450-453.
[29] EMING SA, MARTIN P, TOMIC-CANIC M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(265):265sr6.
[30] STONE RC, PASTAR I, OJEH N, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;365(3):495-506.
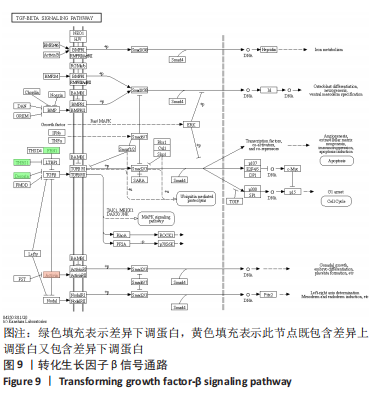
[31] 戚潇禹,刘璐佳,杨阳,等.基于TGF-β_1/Smads信号通路中医药抗纤维化研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2021,23(1):58-62.
[32] 杨信强,陈锋,闫乾,等.TGF-β_1/CTGF信号通路及其在黄韧带肥厚中作用机制的研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(17):3345-3350.
[33] HAWKE LG, MITCHELL BZ, ORMISTON ML. TGF-β and IL-15 Synergize through MAPK Pathways to Drive the Conversion of Human NK Cells to an Innate Lymphoid Cell 1-like Phenotype. J Immunol. 2020;204(12): 3171-3181.
|