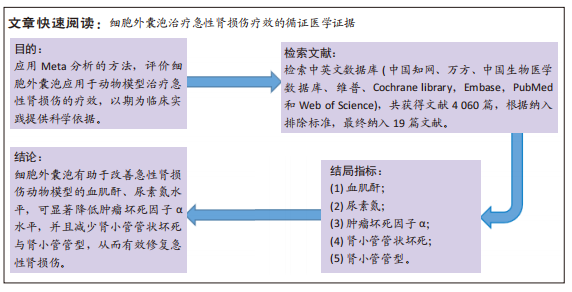
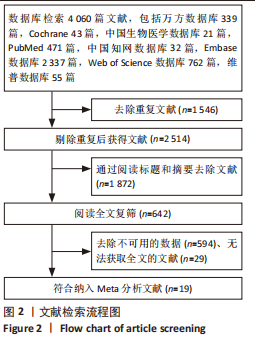
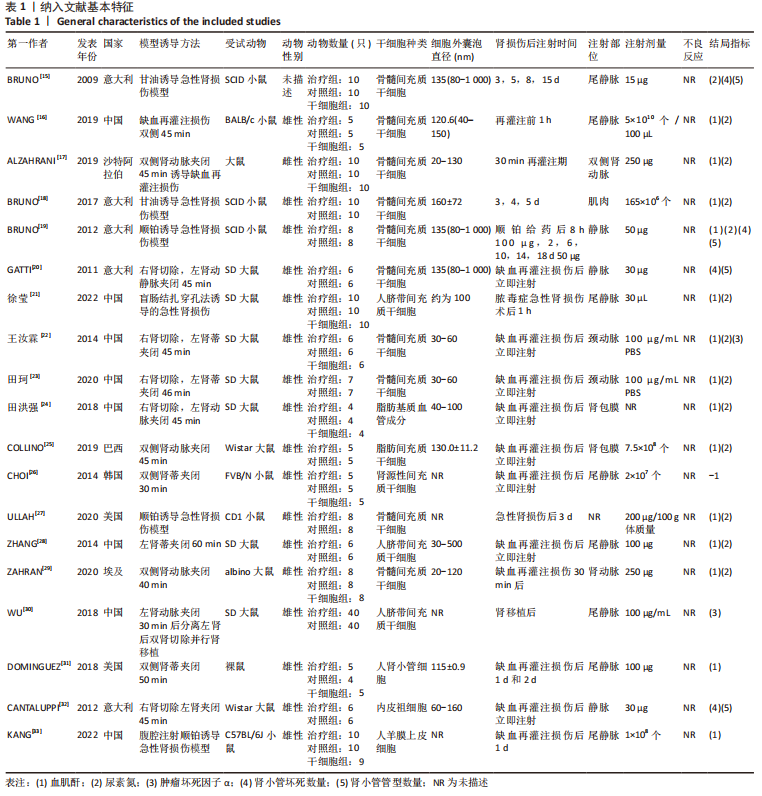
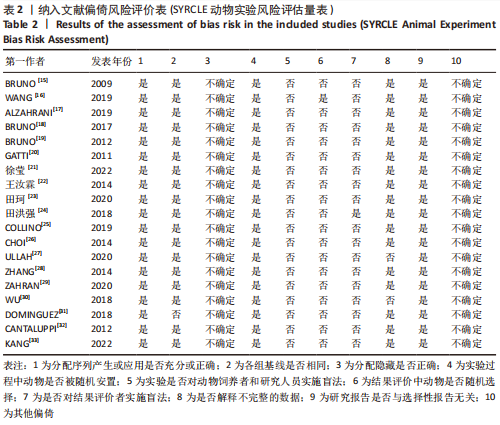
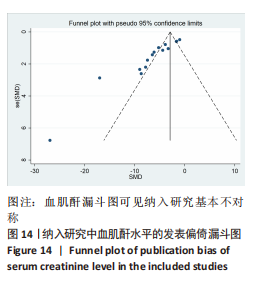
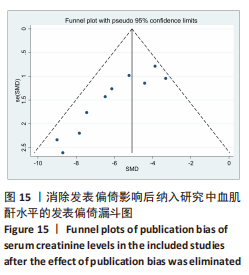
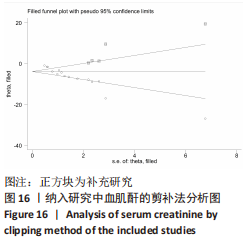
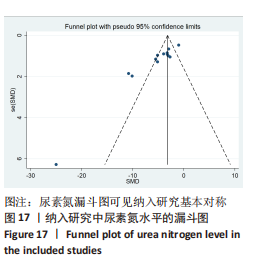
[1] HAN SJ, LEE HT. Mechanisms and therapeutic targets of ischemic acute kidney injury. Res Clin Pract. 2019;38(4):427-440.
[2] AL-JEFRI M, LEE J, JAMES M. Predicting acute kidney injury after surgery. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2020;2020:5606-5609.
[3] LEWINGTON AJ, CERDÁ J, MEHTA RL. Raising awareness of acute kidney injury: a global perspective of a silent killer. Kidney Int. 2013; 84(3):457-467.
[4] HOSTE EAJ, KELLUM JA, SELBY NM, et al. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018; 14(10):607-625.
[5] RICCI Z, CRUZ DN, RONCO C. Classification and staging of acute kidney injury: beyond the RIFLE and AKIN criteria. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7(4):201-208.
[6] JANG HR, RABB H. The innate immune response in ischemic acute kidney injury. Clin Immunol. 2009;130(1):41-50.
[7] LI JS, LI B. Renal injury repair: how about the role of stem cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1165:661-670.
[8] BLAU HM, DALEY GQ. Stem cells in the treatment of disease. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380(18):1748-1760.
[9] YUN CW, LEE SH. Potential and therapeutic efficacy of cell-based therapy using mesenchymal stem cells for acute/chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1619.
[10] CALDAS HC, LOJUDICE FH, DIAS C,et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells reduce progression of experimental chronic kidney disease but develop Wilms’ tumors. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:7428316.
[11] XUNIAN Z, KALLURI R. Biology and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Cancer Sci. 2020; 111(9):3100-3110.
[12] CAO JY, WANG B, TANG TT, et al. Exosomal miR-125b-5p deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury. Theranostics. 2021;11(11):5248-5266.
[13] EIRIN A, ZHU XY, PURANIK AS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate kidney inflammation. Kidney Int. 2016;92(1):114-124.
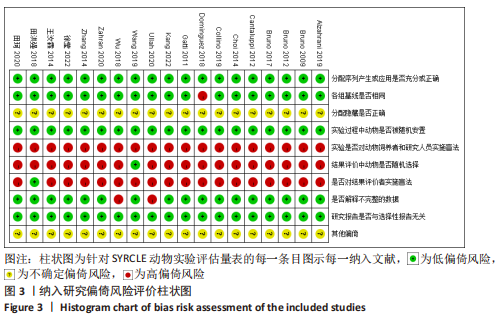
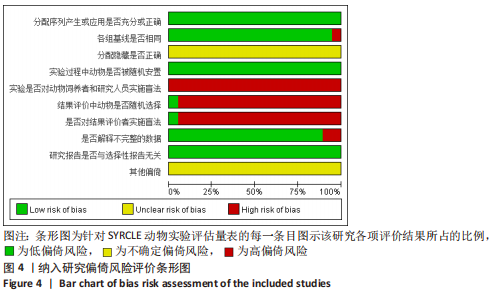
[14] HOOIJMANS CR, ROVERS MM, DE VRIES RB, et al. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;26;14:43.
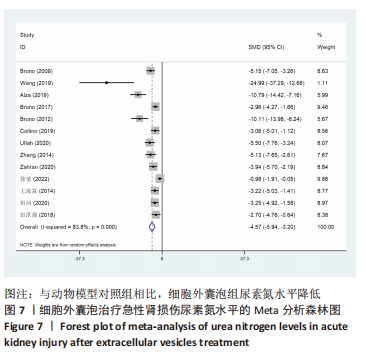
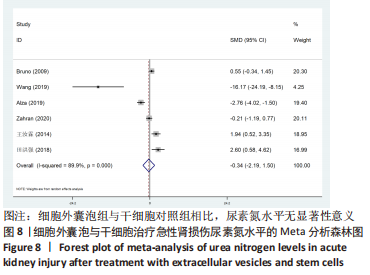
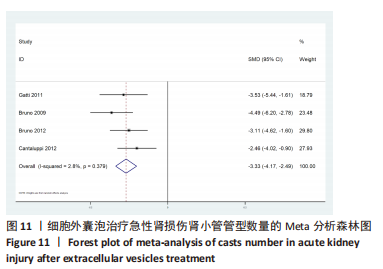
[15] BRUNO S, GRANGE C, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:1053-1067.
[16] WANG C, ZHU G, HE W, et al. BMSCs protect against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by secreting exosomes loaded with miR-199a-5p that target BIP to inhibit endoplasmic reticulum stress at the very early reperfusion stages. FASEB J. 2019;33: 5440-5456.
[17] ALZAHRANI FA. Melatonin improves therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:2887-2907.
[18] BRUNO S, TAPPARO M, COLLINO F, et al. Renal regenerative potential of different extracellular vesicle populations derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23:1262-1273.
[19] BRUNO S, GRANGE C, COLLINO F, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33115.
[20] GATTI S, BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26:1474-1483.
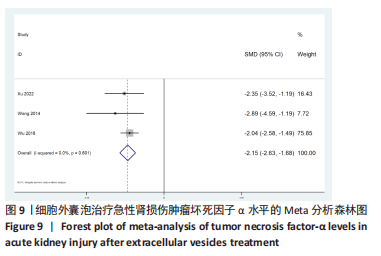
[21] 徐莹,周茹,张欣洲,等.间充质干细胞外泌体对CLP大鼠急性肾损伤作用研究[J].湖北医药学院学报,2022,41(2):116-120.
[22] 王汝霖,林淼,黎力平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源exosome对大鼠肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中华医学杂志, 2014,94(42):3298-3303.
[23] 田珂.骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体对大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤保护作用研究[J]. 医药前沿,2020,10(18):99-100.
[24] 田洪强. Ad-SVF来源的外泌体对大鼠肾脏缺血再灌注损伤的影响及机制[D].南京:南京医科大学,2018.
[25] COLLINO F, LOPES JA, CORRÊA S, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells under hypoxia: changes in extracellular vesicles secretion and improvement of renal recovery after ischemic injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52:1463-1483.
[26] CHOI HY, MOON SJ, RATLIFF BB, et al. Microparticles from kidney-derived mesenchymal stem cells act as carriers of proangiogenic signals and contribute to recovery from acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e87853.
[27] ULLAH M, LIU DD, RAI S, et al. HSP70-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome suppression underlies reversal of acute kidney injury following extracellular vesicle and focused ultrasound combination therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):4085.
[28] ZHANG G, ZOU X, MIAO S, et al. The anti-oxidative role of micro-vesicles derived from human Wharton-Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells through NOX2/gp91(phox) suppression in alleviating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e92129.
[29] ZAHRAN R, GHOZY A, ELKHOLY SS, et al. Combination therapy with melatonin, stem cells and extracellular vesicles is effective in limiting renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model. Int J Urol. 2020;27(11):1039-1049.
[30] WU X, YAN T, WANG Z, et al. Micro-vesicles derived from human Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells mitigate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats after cardiac death renal transplantation. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(2):1879-1888.
[31] DOMINGUEZ JM 2ND, DOMINGUEZ JH, XIE D, et al. Human extracellular microvesicles from renal tubules reverse kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0202550.
[32] CANTALUPPI V, GATTI S, MEDICA D, et al. Microvesicles derived from endothelial progenitor cells protect the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury by microRNA-dependent reprogramming of resident renal cells. Kidney Int. 2012;82(4):412-427.
[33] KANG X, CHEN Y, XIN X, et al. Human amniotic epithelial cells and their derived exosomes protect against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury without compromising its antitumor activity in mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:752053.
[34] GREENBERG JH, COCA S, PARIKH CR. Long-term risk of chronic kidney disease and mortality in children after acute kidney injury: a systematic review. BMC Nephrol. 2014;15:184.
[35] VANDENBERGHE W, GEVAERT S, KELLUM JA, et al. Acute kidney injury in cardiorenal syndrome type 1 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiorenal Med. 2016;6(2):116-128.
[36] ELEFTHERIADIS T, PISSAS G, CRESPO M, et al. A role for human renal tubular epithelial cells indirect allo-recognition by CD4+T-cells and the effect of ischemia-reperfusion. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1733.
[37] FAZEKAS B, GRIFFIN MD. Mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies for acute kidney injury: progress in the last decade. Kidney Int . 2020;97(6):1130-1140.
[38] SHEN B, LIU J, ZHANG F, et al. CCR2 positive exosome released by mesenchymal stem cells suppresses macrophage functions and alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:1240301.
[39] RAGNI E, BANFI F, BARILANI M, et al. Extracellular vesicle-shuttled mRNA in mesenchymal stem cell communication. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):1093-1105.
[40] ZHAO L, HU C, HAN F, et al. Regenerative abilities of mesenchymal stem cells via acting as an ideal vehicle for subcellular component delivery in acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):4882-4891.
[41] YUAN X, LI D, CHEN X, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (hiPSC-MSCs) protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via delivering specificity protein (SP1) and transcriptional activating of sphingosine kinase 1 and inhibiting necroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(12):3200.
[42] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750.
[43] REIS LA, BORGES FT, SIMÕES MJ, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells repaired but did not prevent gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury through paracrine effects in rats. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44092.
[44] 李清茹,张琳琪,陈旭,等.间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡治疗和修复急慢性肾损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(31): 5069-5075.
[45] SUN X, MENG H, WAN W, et al. Application potential of stem/progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles in renal diseases.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):8.
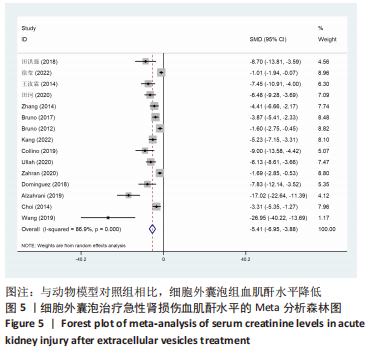
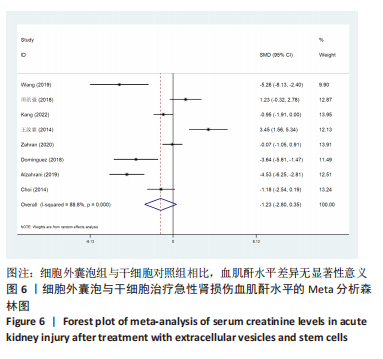
[46] LIU C, WANG J, HU J, et al. Extracellular vesicles for acute kidney injury in preclinical rodent models: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):11.
[47] CHEN TS, ARSLAN F, YIN Y, et al. Enabling a robust scalable manufacturing process for therapeutic exosomes through oncogenic immortalization of human ESC‐derived MSCs. J Transl Med. 2011;9:47.
[48] GREENING DW, GOPAL SK, XU R, et al. Exosomes and their roles in immune regulation and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:72-81.
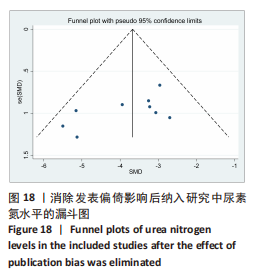
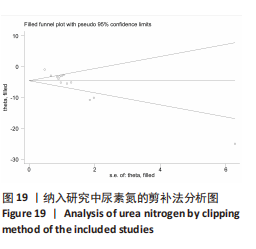
[49] 徐同成,李霞,王文亮,等.分类变量Meta分析中偏倚的检测—Egger法和Begg法[J].循证医学,2009,9(3):181-184. |