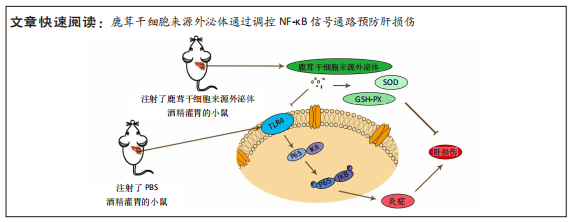
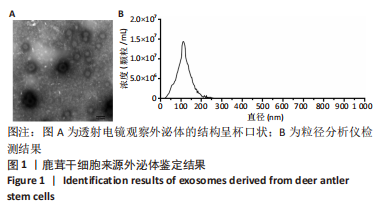
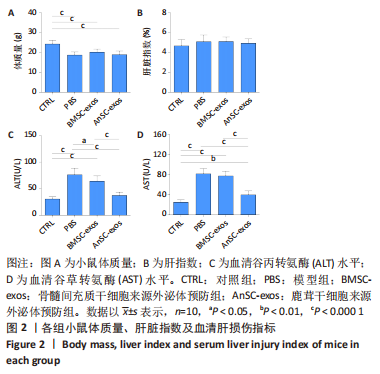
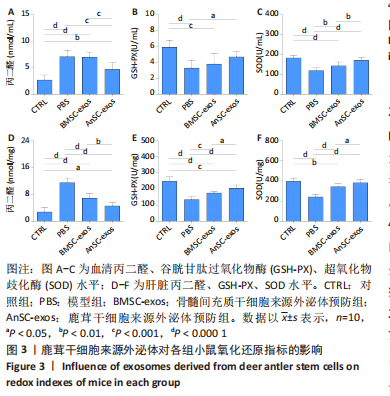
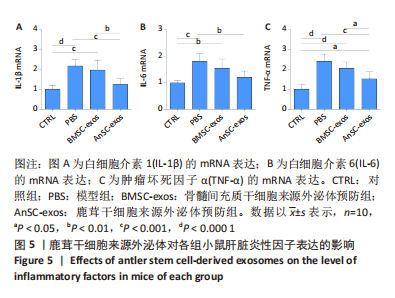
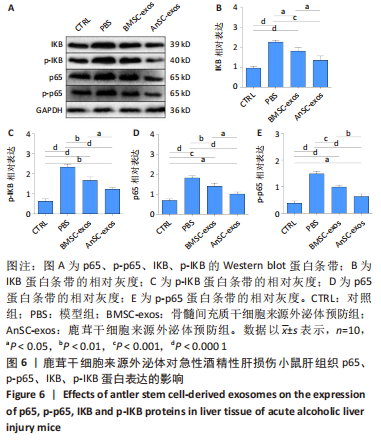
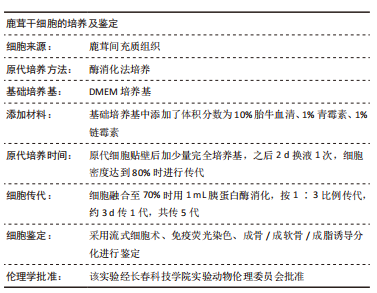
[1] 赵云霞.鸡枞菌多糖对小鼠急性酒精肝损伤保护作用的研究[D].南京:南京师范大学,2014.
[2] 刘庆普,陈燕,谢彩侠,等.桑叶生物碱对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J].现代食品科技,2022,38(6):1-8.
[3] 刘岩,苏琳.酒精性肝病基层诊疗指南[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2021, 37(1):36-40.
[4] 厉铭.二烯丙基一硫拮抗小鼠急性肝脏损伤的作用效果及机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2019.
[5] 韵海霞,黄以哲,穆志龙,等.藏药帕珠丸对慢性酒精性肝损伤大鼠肝组织IL-1,IL-6,TNF-α,TGF-β1含量及TGF-β1 mRNA表达的影响[J].青海医学院学报,2014,35(2):119-122.
[6] LUEDDE T, SCHWABE RF. NF-κB in the liver--linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8(2): 108-118.
[7] HE G, KARIN M. NF-κB and STAT3 - key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011;21(1):159-168.
[8] LANDETE-CASTILLEJOS T, KIERDORF H, GOMEZ S, et al. Antlers - Evolution, development, structure, composition, and biomechanics of an outstanding type of bone. Bone. 2019;128:115046.
[9] 李勋胜,赵海平,李春义,等.鹿茸神经再生的研究进展[J].生命科学,2021,33(8):955-961.
[10] LI C, YANG F, SHEPPARD A. Adult stem cells and mammalian epimorphic regeneration-insights from studying annual renewal of deer antlers. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009;4(3):237-251.
[11] RONG X, YANG Y, ZHANG G, et al. Antler stem cells as a novel stem cell source for reducing liver fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;379(1):195-206.
[12] CAO Y, JI C, LU L. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(8):562.
[13] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346.
[14] LI C, SUTTIE JM. Tissue collection methods for antler research. Eur J Morphol. 2003;41(1):23-30.
[15] WANG D, BERG D, BA H, et al. Deer antler stem cells are a novel type of cells that sustain full regeneration of a mammalian organ-deer antler. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(6):443.
[16] ZHANG Y, PAN Y, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells stimulate regenerative wound healing via transforming growth factor-β receptor inhibition. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):434.
[17] DUAN M, ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Epidermal stem cell-derived exosomes promote skin regeneration by downregulating transforming growth factor-β1 in wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):452.
[18] 胡戈,曹建民,周海涛,等.黑果枸杞汁对大鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2022,38(3):241-246.
[19] 桑文华,曾美纯,陈莎,等.自噬抑制剂氯喹对急性酒精诱导小鼠肝损伤的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2018,34(2):102-105.
[20] OHASHI K, PIMIENTA M, SEKI E. Alcoholic liver disease: A current molecular and clinical perspective. Liver Res. 2018;2(4):161-172.
[21] WANG M, MA LJ, YANG Y, et al. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129.
[22] CHO SS, LEE JH, KIM KM, et al. REDD1 attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis via inhibiting of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;176:246-256.
[23] 黄颖,谭书明,陈萍,等.蜂蜜多酚提取物对大鼠急性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J].食品科学,2020,41(21):154-159.
[24] UCHIDA T, KAO H, QUISPE-SJOGREN M, et al. Alcoholic foamy degeneration--a pattern of acute alcoholic injury of the liver. Gastroenterology. 1983;84(4):683-692.
[25] HALL PD. The pathological spectrum of alcoholic liver disease. Pathology. 1985;17(2):209-218.
[26] XU QW, SCOTT RB, TAN DT, et al. Slow intestinal transit: a motor disorder contributing to cholesterol gallstone formation in the ground squirrel. Hepatology. 1996;23(6):1664-1672.
[27] 王宏志,刘俊,侯晓华.乌司他丁与川芎嗪合用对急性胰腺炎大鼠氧自由基影响的研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2007,16(3):271-273.
[28] 王英丽.银杏叶提取物抗辐射作用的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2006.
[29] 刘姝.急性酒精性肝损伤中槲皮素抗氧化应激及抗炎作用交互影响的机制研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2019.
[30] GAO B, AHMAD MF, NAGY LE, et al. Inflammatory pathways in alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2019;70(2):249-259.
[31] BRENNER C, GALLUZZI L, KEPP O, et al. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J Hepatol. 2013;59(3):583-594.
[32] TIAN Y, JOCHUM W, GEORGIEV P, et al. Kupffer cell-dependent TNF-alpha signaling mediates injury in the arterialized small-for-size liver transplantation in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103(12):4598-4603.
[33] HE Y, HWANG S, AHMED YA, et al. Immunopathobiology and therapeutic targets related to cytokines in liver diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(1):18-37.
[34] SCHMIDT-ARRAS D, ROSE-JOHN S. IL-6 pathway in the liver: From physiopathology to therapy. J Hepatol. 2016;64(6):1403-1415.
|