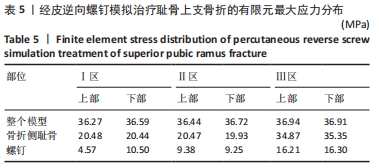
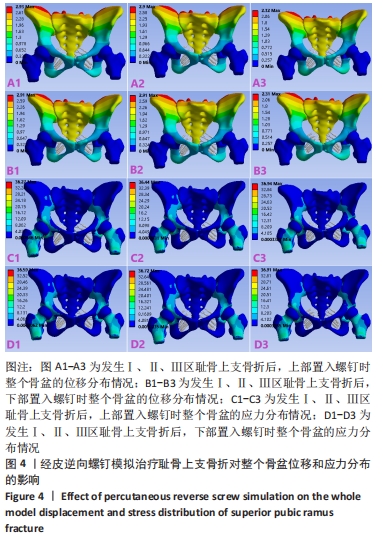
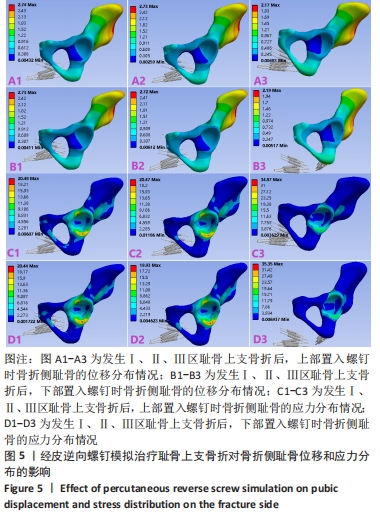
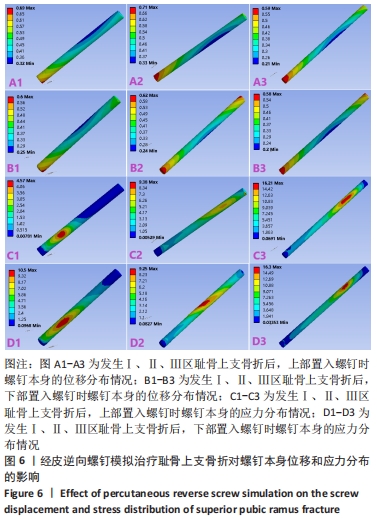
[1] HUNG CC, WU JL, LI YT, et al. Minimally invasive treatment for anterior pelvic ring injuries with modified pedicle screw-rod fixation: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):238.
[2] LI L, LU J, YANG L, et al. Stability evaluation of anterior external fixation in patient with unstable pelvic ring fracture: a finite element analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(14):303.
[3] MARECEK GS, SCOLARO JA. Anterior Pelvic Ring: Introduction to Evaluation and Management. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32 Suppl 6:S1-S3.
[4] LEI J, ZHANG Y, WU G, et al. The Influence of Pelvic Ramus Fracture on the Stability of Fixed Pelvic Complex Fracture. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015;2015:790575.
[5] STEVENSON AJ, SWARTMAN B, BUCKNILL AT. Percutaneous internal fixation of pelvic fractures. German version. Unfallchirurg. 2016;119:825-834.
[6] QUERCETTI N, HORNE B, DIPAOLO Z, et al. Gun barrel view of the anterior pelvic ring for percutaneous anterior column or superior pubic ramus screw placement. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27:695-704.
[7] LIU HS, DUAN SJ, LIU SD, et al. Robot-assisted percutaneous screw placement combined with pelvic internal fixator for minimally invasive treatment of unstable pelvic ring fractures. Int J Med Robot. 2018;14:e1927.
[8] BANASZEK D, STARR AJ, LEFAIVRE KA. Technical Considerations and Fluoroscopy in Percutaneous Fixation of the Pelvis and Acetabulum. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27:899-908.
[9] ROUTT ML, SIMONIAN PT, GRUJIC L. The retrograde medullary superior pubic ramus screw for the treatment of anterior pelvic ring disruptions: a new technique. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9:35-44.
[10] FRANK M, DEDEK T, TRLICA J, et al. Percutaneous fixation of anterior column acetabular fractures--first experience. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010;77(2):99-104.
[11] 王叙进,方诗元,徐磊,等. 有限元法分析不同内固定方法治疗复杂性骨盆骨折的力学稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(27):4354-4358.
[12] 鲁辉,吴启梅,刘融. 单侧与双侧入路植入骨填充网袋治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的有限元分析与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(3):391-397.
[13] LU H, JIANG D, WU Q, et al. A combination of digital design and three-dimensional printing to assist treatment of thoracolumbar compression fractures using percutaneous kyphoplasty. Global Health J. 2021;ISSN 2414-6447.
[14] LU H, PENG H, PENG Z, et al. The Application of Digital Design Combined with 3D Printing Technology in Skin Flap Transplantation for Fingertip Defects during the COVID-19 Epidemic. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:5554500.
[15] ZHAO Y, ZHANG S, SUN T, et al. Mechanical comparison between lengthened and short sacroiliac screws in sacral fracture fixation: a finite element analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(5):601-606.
[16] DALSTRA M, HUISKES R. Load transfer across the pelvic bone.J Biomech. 1995;28(6):715-724.
[17] PHILLIPS AT, PANKAJ P, HOWIE CR, et al. Finite element modelling of the pelvis: inclusion of muscular and ligamentous boundary conditions. Med Eng Phys. 2007;29(2):739-748.
[18] 王琦. 张力带钢板治疗不稳定骨盆骨折的生物力学性能评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(11):1737-1741.
[19] ZHENG N, WATSON LG, YONG-HING K. Biomechanical modelling of the human sacroiliac joint.Med Biol Eng Comput. 1997;35(2):77-82.
[20] 钟子毅, 童凯, 谢献进, 等. 髋臼T形骨折不同内固定方式的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(6):515-522.
[21] 潘昌武, 刘曦明, 蔡贤华, 等. 微型联合重建接骨板内固定治疗髋臼后壁骨折坐位下的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(2): 160-164.
[22] STARR AJ, NAKATANI T, REINERT CM, et al. Superior pubic ramus fractures fixed with percutaneous screws: what predicts fixation failure? J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(2):81-87.
[23] MURPHY WS, YUN HH, HAYDEN B, et al. The Safe Zone Range for Cup Anteversion Is Narrower Than for Inclination in THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(2):325-335.
[24] OCHS BG, STUBY FM, STOECKLE U, et al. Virtual mapping of 260 three-dimensional hemipelvises to analyse gender-specific differences in minimally invasive retrograde lag screw placement in the posterior acetabular column using the anterior pelvic and midsagittal plane as reference. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:240.
[25] 王尧,张雪松,罗春材,等. 国人成人经第1及第2骶椎骶髂骨螺钉置钉钉道差异的CT测量[J]. 解放军医学院学报,2016,37(6):591-594,606.
[26] 王庆贤, 张英泽, 潘进社, 等. 耻骨上支逆行拉力螺钉内固定的应用解剖学研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2005,23(6):617-619.
[27] SUZUKI T, SOMA K, SHINDO M, et al. Anatomic study for pubic medullary screw insertion. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2008;16:321-325.
[28] 赵勇, 马玉鹏, 邹德鑫, 等. 三种微创内固定治疗骨盆前环双侧骨折的生物力学比较[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(11):2110-2113.
[29] 张永强,章莹,夏远军, 等. 髋臼部T形骨折四种不同内固定方式的生物力学有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2017,35(3):312-317.
[30] 柳超,王前,张杰峰, 等. 不同内固定手术方式治疗寰枢椎复合骨折稳定性的有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(10):904-911.
[31] MISKIMINS R, DECKER M, HOBBY B, et al. Complications of pelvic ring fixation in patients requiring laparotomy.J Surg Res. 2015;199:244-248.
[32] DALSTRA M, HUISKES R, VAN ERNING L. Development and validation of a three-dimensional finite element model of the pelvic bone. J Biomech Eng. 1995;117:272-278.
[33] ANDERSON AE, PETERS CL, TUTTLE BD, et al. Subject-specific finite element model of the pelvis: development, validation and sensitivity studies. J Biomech Eng. 2005;127:364-373.
[34] MASLOV L, BOROVKOV A, MASLOVA I, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Customized Acetabular Implant and Bone after Pelvic Tumour Resection throughout the Gait Cycle. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(22):7066.
[35] SALO Z, KREDER H, WHYNE CM. The Impact of an Open-Book Pelvic Ring Injury on Bone Strain: Validation of a Finite Element Model and Analysis Within the Gait Cycle. J Biomech Eng. 2021;143(7):071005.
[36] ZHANG BF, WANG J, ZHANG YM, et al. The morphological mapping of lateral compression type 1 pelvic fracture and pelvic ring stability classification: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):675.
[37] 贺宇,周东生,邱贵兴,等. 四种内固定方式治疗耻骨联合分离生物力学特性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(4):317-322.
[38] GUO HZ, TANG YC, GUO DQ, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of four different posterior instrumentation techniques for single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element analysis. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:6160-6169.
[39] LU H, ZHANG Q, DING F, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Unilateral versus Bipedicular Bone-Filling Mesh Container for the Management of Osteoporotic Compression Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:6850089.
|