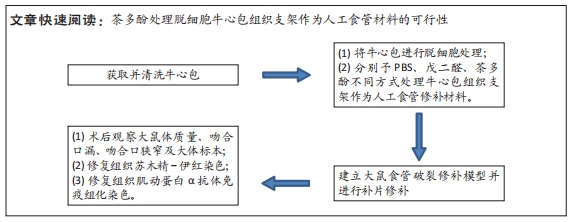
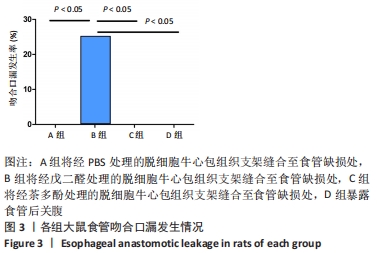
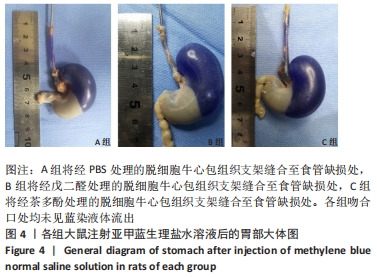
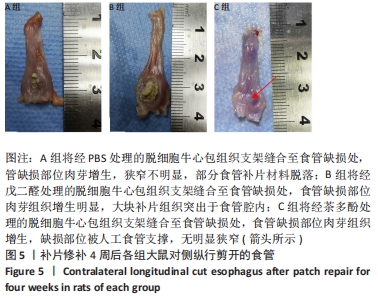
[1] NATIONAL HEALTH COMMISSION OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF C. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of esophageal carcinoma 2018 (English version). Chin J Cancer Res. 2019;31(2):223-258.
[2] GUINAN EM, BENNETT AE, DOYLE SL, et al. Measuring the impact of oesophagectomy on physical functioning and physical activity participation: a prospective study. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):682.
[3] MENDIBIL U, RUIZ-HERNANDEZ R. Tissue-Specific Decellularization Methods: Rationale and Strategies to Achieve Regenerative Compounds. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5447.
[4] FELGENDREFF P, SCHINDLER C, MUSSBACH F, et al. Identification of tissue sections from decellularized liver scaffolds for repopulation experiments. Heliyon. 2021;7(2):e06129.
[5] GAFAROVA ER, GREBENIK EA. Evaluation of Supercritical CO(2)-Assisted Protocols in a Model of Ovine Aortic Root Decellularization. Molecules. 2020;25(17):3923.
[6] TEIXEIRA MA, ANTUNES JC, AMORIM MTP, et al. Green Optimization of Glutaraldehyde Vapor-Based Crosslinking on Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Cellulose Acetate Electrospun Mats for Applications as Chronic Wound Dressings. Proceedings. 2021;69(1):30.
[7] YU T, CHEN X, ZHUANG W, et al. Nonglutaraldehyde treated porcine pericardium with good biocompatibility, reduced calcification and improved Anti-coagulation for bioprosthetic heart valve applications. Chem EngJ. 2021;414:128900.
[8] KHAN N, MUKHTAR H. Tea Polyphenols in Promotion of Human Health. Nutrients. 2018; 11(1):39.
[9] PERAZZO KK, CONCEI OAC, DOS SANTOS JC, et al. Properties and antioxidant action of actives cassava starch films incorporated with green tea and palm oil extracts. PLoS One. 2014;9(9): e105199.
[10] OZ HS. Chronic Inflammatory Diseases and Green Tea Polyphenols. Nutrients. 2017;9(6): 561.
[11] LIU X, WU H, LU F, et al. Fabrication of porous bovine pericardium scaffolds incorporated with bFGF for tissue engineering applications. Xenotransplantation. 2020;27(1):e12568.
[12] 谭何易,赖应龙.食管癌术后并发肺部感染的相关因素[J].中华实验和临床感染病杂志(电子版),2016,10(4):467-472.
[13] SAMUEL M, BURGE DM, MOORE IE. Gastric tube graft interposition as an oesophageal substitute. ANZ J Surg. 2001;71(1):56-61.
[14] KIM SH, KIM HK, KIM K, et al. Outcome of free jejunal transfer using the end-to-side arterial anastomosis technique as a pharyngo-oesophageal substitute: a 15-year experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013;44(3):520-524.
[15] POGHOSYAN T, SFEIR R, MICHAUD L, et al. P-31: Esophageal Replacement by a Tissue Engineered Substitute in a Porcine Model. Dis Esophagus. 2016;29(3):298-298.
[16] 雷洋,胡雪丰,张婕妤,等.组织工程方法在人工心脏瓣膜领域中的应用[J].生命科学,2020(3):288-298.
[17] VOGT CD, PANOSKALTSIS-MORTARI A. Tissue engineering of the gastroesophageal junction. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(6):855-868.
[18] HEATH DE. A Review of Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Biomaterials for Regenerative Engineering Applications. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2019;5(2):155-166.
[19] RASHTBAR M, HADJATI J, AI J, et al. Characterization of decellularized ovine small intestine submucosal layer as extracellular matrix-based scaffold for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(3):933-944.
[20] GILPIN A, YANG Y. Decellularization Strategies for Regenerative Medicine: From Processing Techniques to Applications. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9831534.
[21] LUC G, CHARLES G, GRONNIER C, et al. Decellularized and matured esophageal scaffold for circumferential esophagus replacement: Proof of concept in a pig model. Biomaterials. 2018;175:1-18.
[22] SHANG F, HOU Q. Effects of allogenic acellular dermal matrix combined with autologous razor-thin graft on hand appearance and function of patients with extensive burn combined with deep hand burn. Int Wound J. 2021;18(3):279-286.
[23] LI MH. Application of natural acellular matrix graft in bladder reconstruction. J Clin Rehabil. 2006;10(29):146-148.
[24] XIAO S, WANG P. Bi-layer silk fibroin skeleton and bladder acellular matrix hydrogel encapsulating adipose-derived stem cells for bladder reconstruction. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(18):6169-6182.
[25] NOWAK-SLIWINSKA P, ALITALO K, ALLEN E, et al. Consensus guidelines for the use and interpretation of angiogenesis assays. Angiogenesis. 2018;21(3):425-532.
[26] YUAN X, SMITH RJ JR, GUAN H, et al. Hybrid Biomaterial with Conjugated Growth Factors and Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Ectopic Bone Formation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(13-14):928-939.
[27] FAN X, XIAO X, MAO X. Tea bioactive components prevent carcinogenesis via anti-pathogen, anti-inflammation, and cell survival pathways. IUBMB Life. 2021;73(2):328-340.
[28] DONG R, YU Q, LIAO W, et al. Composition of bound polyphenols from carrot dietary fiber and its in vivo and in vitro antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2021;339:127879.
[29] HONG M, ZHANG R. The interaction effect between tea polyphenols and intestinal microbiota: Role in ameliorating neurological diseases. 2021:e13870.
[30] REN Y, WEI X, WEI ST, et al. High Oxidation Stability of Tea Polyphenol-stabilized Highly Crosslinked UHMWPE Under an in Vitro Aggressive Oxidative Condition. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(8):1947-1955.
|