中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (34): 5569-5576.doi: 10.12307/2022.470
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇
仿生水凝胶在软骨组织工程应用中的优势与潜力
侯钰熙1,张 然1,武秀萍1,张清梅2,李 冰1
- 1山西医科大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,口腔疾病防治与新材料山西省重点实验室,山西省太原市 030001;2太原科技大学,山西省太原市 030024
-
收稿日期:2021-05-10接受日期:2021-06-28出版日期:2022-12-08发布日期:2022-04-16 -
通讯作者:李冰,男,博士,主任医师,博士生导师,山西医科大学口腔医学院·口腔医院,山西省太原市 030001 -
作者简介:侯钰熙,女,1995年生,山西省太原市人,山西医科大学在读硕士,主要从事口腔材料学的研究。 -
基金资助:山西省回国留学人员科研资助项目(HGKY2019-055),项目负责人:李冰;山西省教育厅研究生教育创新计划项目(2019SY280),项目负责人:武秀萍;山西省科技攻关项目(201803D31065),项目负责人:武秀萍
Advantages and potential of bionic hydrogels in cartilage tissue engineering
Hou Yuxi1, Zhang Ran1, Wu Xiuping1, Zhang Qingmei2, Li Bing1
- 1School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Oral Diseases and New Materials, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Taiyuan University of Science and Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-05-10Accepted:2021-06-28Online:2022-12-08Published:2022-04-16 -
Contact:Li Bing, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Oral Diseases and New Materials, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Hou Yuxi, Master candidate, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Oral Diseases and New Materials, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of Shanxi Province Returned Overseas Students, No. HGKY2019-055 (to LB); Graduate Education Innovation Project of Shanxi Provincial Department of Education, No. 2019SY280 (to WXP); Science and Technology Research Project of Shanxi Province, No. 201803D31065 (to WXP)
摘要:
文题释义:
交联:即多种聚合物链通过交联多维延伸形成稳定的网络结构。根据交联的类型可分为化学交联和物理交联。化学交联的凝胶可永久连接,其中不同的聚合物链之间形成共价键,从而产生优异的机械性能,但化学交联形成的水凝胶常具有毒性;而在物理交联中,物理相互作用(如离子键、氢键或疏水相互作用)抑制了凝胶的溶解,物理交联法形成的水凝胶不具有毒性。
整合能力:将修复材料植入缺损部位时,整合能力可用来反映组织的修复情况。材料与缺损部位组织的结合程度越高,再生细胞与原细胞越相似,其整合能力越强。如果新生组织不能与修复材料很好地整合,则组织再生修复失败。
背景:水凝胶是一类有弹性的生物材料,表面光滑,含水量高,有望成为软骨再生的候选材料。
目的:文章综述了仿生水凝胶在软骨组织工程中的最新研究成果和进展。
方法:由第一作者检索Web of Science和PubMed数据库1986-2021年发表的文献,英文检索词为“hydrogel,cartilage regeneration,cartilage defect,cartilage tissue engineering”。初检文献3 665篇,筛选后对86篇文献进行分析总结。
结果与结论:①用于合成仿生水凝胶的天然聚合物包括蛋白质基材料(如明胶、胶原蛋白和丝素蛋白等)和多糖材料(如透明质酸、壳聚糖和藻酸盐等),合成聚合物包括聚乙烯醇、聚乙二醇、聚乳酸、聚丙交酯-乙交酯共聚物等,这些材料具有各自的优缺点,通过交联这一方式可以使合成仿生水凝胶在具备更多的优势同时规避一些原材料的不足。②当前阶段已研究的仿生水凝胶材料各有优劣,例如通过紫外光交联的硫酸软骨素-聚乙二醇材料具有一定的抗炎特性,也可促进软骨组织再生,然而其促进软骨细胞的增殖和成熟能力有待加强;通过紫外光交联合成的明胶-羟基磷灰石材料细胞接种效率高,生物相容性较好,但是尚未有实验将人骨髓间充质干细胞接种于其上并进行实验观察,实验环境复杂性不足且观测周期较短,仍需进一步验证;酶促交联合成的聚乙二醇-二甲基丙烯酸能促进软骨基质形成,压缩模量变化范围大,然而其在改善软骨基质形成过程中也存在相应副反应。③因此,仿生水凝胶是软骨组织工程中具有较大优越性及应用潜力的新材料,目前仍然未出现较为完美的可应用于临床治疗软骨缺损的仿生水凝胶材料,未来还需进一步研究出性能更加完备的仿生水凝胶材料。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9410-733X (李冰)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
侯钰熙, 张 然, 武秀萍, 张清梅, 李 冰. 仿生水凝胶在软骨组织工程应用中的优势与潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(34): 5569-5576.
Hou Yuxi, Zhang Ran, Wu Xiuping, Zhang Qingmei, Li Bing. Advantages and potential of bionic hydrogels in cartilage tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5569-5576.
水凝胶因其优异的特性,相关学者在过去的十年中对其在软骨再生中的应用研究不断增加。例如,在2021-04-24使用“Scaffold”“Cartilage”“Hydrogel”与“Regeneration”检索词组合后在PubMed数据库上进行检索,见图4。
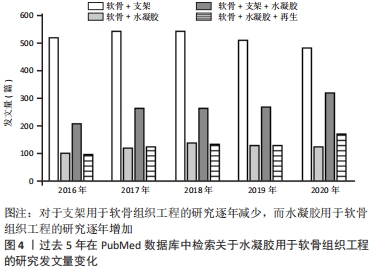
图4发现过去软骨支架的研究文献几乎是软骨水凝胶研究的3倍,但在2016-2020年,用于软骨组织工程学的水凝胶研究一直稳步增长,达到1.5倍。
近5年来,对用于软骨组织工程的仿生水凝胶研究兴起,例如受贻贝启发将聚多巴胺掺入水凝胶以促进细胞黏附和组织整合[14];掺入糖基添加剂如麦卢卡蜂蜜,以提高抗菌性能和机械性能,并模仿软骨天然结构网络[15]。
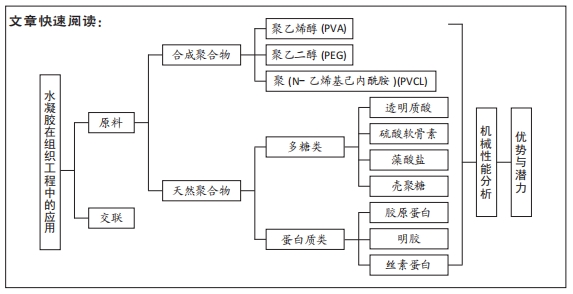
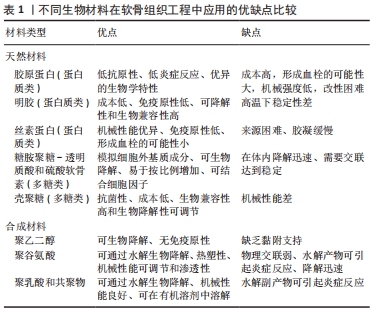
2.2 用于合成仿生水凝胶的原料 水凝胶可简单地根据材料成分的性质分为天然水凝胶和合成水凝胶。用于制备水凝胶的天然聚合物包括蛋白质基材料(如明胶、胶原蛋白和丝素蛋白等)和多糖材料(如透明质酸、壳聚糖和藻酸盐等),此外,天然水凝胶不会引起免疫和毒性反应,降解产物无毒无免疫性,但因其稳定性差、降解速率快和机械性能低,很大程度上限制了其应用。合成水凝胶包括聚乙烯醇、聚乙二醇、聚乳酸、聚丙交酯-乙交酯共聚物、聚乙交脂、聚己内酯和聚丙烯酰胺等,这些聚合物的掺入可用于增强机械性能或作为药物输送的载体。然而,某些聚合物结合时,会存在免疫反应和毒性。用于软骨组织工程的不同生物材料及其优缺点和潜在应用,见表1。
2.2.1 合成聚合物
聚乙烯醇:是一种可靠的高性能载体,具有优越的成膜、乳化和成膜性能。据报道,通过铸造干燥法得到的聚乙烯醇水凝胶具有和天然软骨相似的机械性能,表明这种水凝胶可以用为修复软骨缺损的替代材料[16]。另外,含有间充质细胞的聚乙烯醇-壳聚糖水凝胶在体外研究中显示出对于软骨形成分化和糖胺聚糖沉积的促进作用[17]。
聚乙二醇:是美国食品药品监督管理局批准用于药物及个人护理产品的一种聚合物,甚至被认为是口服安全的[18]。这种聚合物易于改性,在形成水凝胶后具有良好的机械性能。Skaalure等[19]合成了一种酶敏感型聚乙二醇水凝胶,该水凝胶由聚合聚糖中聚合蛋白酶可裂解位点衍生肽交联。这种水凝胶系统能够促进透明样软骨再生,同时避免肥大软骨的形成。
聚N-乙烯基己内酰胺:是一种细胞兼容性热敏聚合物,可用于合成软骨组织工程的可注射水凝胶。Sala等[20]的研究表明,软骨细胞和间充质干细胞在该水凝胶中表现出高活力。体内和体外实验中都证明,软骨特异性细胞外基质是在聚N-乙烯基己内酰胺水凝胶中生成的。随着时间的推移,软骨中的特异性成分包括糖胺聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原的含量增加。
2.2.2 天然聚合物
(1)多糖类
透明质酸:是一种线性生物大分子,在许多细胞功能中发挥重要作用[21]。它是软骨细胞外基质的主要成分,具有生物活性,通常用于制造与细胞相互作用的水凝胶支架[22]。与1.5%的透明质酸相比,封装在5%的透明质酸水凝胶中的软骨细胞的软骨标记基因表达增加,如聚集蛋白聚糖和Sox9的表达增加了10倍以上[23]。就植入材料的生物安全性而言,材料的可降解性在组织工程中越来越受到重视。有研究将人工合成的多糖聚合物和天然多糖聚合物结合起来,制备了一种可完全生物降解的水凝胶[24]。通过巯基化反应将混合的聚磷酸盐共聚物聚(丁炔基磷硅烷)-聚(乙基乙烯磷酸酯)与巯基化的透明质酸混合,制备所得的透明质酸水凝胶能够支持人骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附和生长,促进细胞之间的相互作用,具有酶促生物降解性,扩大了组织工程生物可降解材料的范围。然而,由于透明质酸酶、氮和活性氧可降解透明质酸,影响其细胞黏附能力,因此在体内使用透明质酸仍是一个挑战[25]。
硫酸软骨素:是一种多糖分子,是人体中含量最丰富的一种糖胺聚糖,占成人关节软骨中糖胺聚糖的80%[26]。硫酸软骨素是一种线性硫酸化糖胺聚糖,由D-葡萄糖醛酸与N-乙酰半乳糖胺的1-3键形成,它具有组织整合的能力,并有抗炎作用[27]。随着年龄的增长,软骨中的硫酸软骨素退行性减少[28]。由于其具有高电荷密度、高含水量,导致其机械强度较弱。因此硫酸软骨素常与其他材料结合并交联,以提高机械性能[29]。以往研究表明,硫酸软骨素结合普鲁兰多糖水凝胶包封的软骨细胞具有良好的生存能力,在自交联和酶交联的水凝胶中均显示出软骨形成能力增强[30]。与透明质酸-Ⅰ型胶原基水凝胶相比,硫酸软骨素基水凝胶在软骨区表现出最高的基因表达和基质累积。
藻酸盐:是一种阴离子多糖,在褐藻细胞壁中大量存在。由于藻酸盐可与Ca2+等二价阳离子简单凝胶化,故常用于软骨修复的非侵入性方法,用作可注射水凝胶[31]。此外,藻酸盐因其快速交联能力常用于3D打印技术[32]。然而,藻酸盐应用于软骨组织工程中仍存在一些缺陷:首先,物理交联的藻酸盐水凝胶的稳定性差,即使组织生理环境下,也会在短时间内失去其机械强度,但可以通过后续的交联来增加其机械性能;其次,由于藻酸盐在哺乳动物中的细胞低黏附性,常引入细胞黏附肽以支持细胞功能。为了克服这些缺陷,通常在藻酸盐水凝胶中加入其他生物活性物质。
壳聚糖:是从虾和其他甲壳类动物的壳中提取的多糖,它具有抗菌特性,并且有很高的生物黏附性[33]。LIANG等[34]合成了两性壳聚糖/卡拉胶杂化水凝胶,可在体外诱导小鼠成软骨细胞成软骨分化,展现出良好的软骨组织工程应用潜力。另外,为了构建修复不同形状软骨缺损的水凝胶支架,MENG等[35]将壳聚糖与相位显示延生肽E7修饰的脱矿骨基质颗粒混合,并证明混合水凝胶支架提高了骨髓间充质干细胞的存活率、基质生成量,促进了软骨的形成分化。
(2)蛋白质类
胶原蛋白:是一种存在于天然软骨中的细胞外基质蛋白,能够支持软骨细胞的生长,因此,它被广泛应用于软骨组织工程。胶原水凝胶通过刺激细胞外基质的形成来降低免疫排斥的风险,降低接种在工程水凝胶构建体中的外源性细胞的免疫原性,并促进软骨再生[36]。此外,WONG等[37]发现,通过单层传代,Ⅱ型胶原能在去分化后将耳软骨细胞转化为关节软骨细胞。JIANG等[38]研究发现,用间充质干细胞包裹的胶原基水凝胶可介导Sox9(一种调节软骨形成的细胞因子)的表达,这表明经设计的水凝胶支架在无生长因子的情况下也可以发挥作用。另外,胶原蛋白还可与其他材料结合形成混合水凝胶支架,与单个组分相比,该支架性能增强。例如,利用胶原蛋白与壳聚糖和透明质酸构建仿生水凝胶[39]。
明胶:是一种变性胶原蛋白,具有生物兼容性、可降解性、良好的细胞黏附性等优点[40]。然而,明胶用于软骨修复的主要缺点是机械性能差和热稳定性低。为克服其缺点,WANG等[41]合成了一种由明胶和羟苯丙酸组成的杂化水凝胶。其中,用过氧化氢和辣根过氧化物酶催化羟苯丙酸氧化偶联形成水凝胶,这种水凝胶可以通过改变过氧化氢和明胶-羟苯丙酸的浓度来调节其机械性能。另一项研究表明,五嵌段共聚物与明胶形成的杂化水凝胶支架为细胞生长提供亲水性环境[42],同时材料强度有所提高。另外,LI等[43]合成了明胶降冰片烯,可用于封装人骨髓间充质干细胞。这项工作为研究人员和临床医生提供了另一种关节软骨组织再生的明胶改性选择。
丝素蛋白:是蚕丝的主要成分,具有优异的生物兼容性和可降解性。丝素蛋白能模仿天然软骨的胶原结构,在软骨组织工程学中有巨大潜力。RIBEIRO等[44]通过光交联法合成了甲基丙烯酸甲酯化的丝素蛋白,所形成的水凝胶与小鼠关节软骨细胞的生物兼容性高,有利于细胞黏附。在生理条件下,辣根过氧化物酶介导的交联下产生坚固且相互连接的多孔丝素蛋白支架。SINGH等[45]合成了一种由丝素蛋白和琼脂糖组成的水凝胶用于软骨组织工程,该水凝胶表现出良好的细胞兼容性。为了进一步提高其机械性能,YODMUANG等[46]合成了微纤维-丝素蛋白水凝胶,该水凝胶也表现出良好的软骨细胞反应。
2.3 交联在水凝胶中的作用 多种聚合物链通过多维延伸形成稳定网络结构的方式称为交联。交联度的大小可以影响材料的降解速率和孔隙率,进而影响水凝胶的溶胀性能,同时增加其材料稳定性[47]。这些特性对于软骨再生十分重要,影响细胞功能,并为新组织形成提供支持。水凝胶聚合物链可通过化学或物理反应形成共价或非共价键交联(如离子键)[48]。化学交联剂通常在聚合物链之间建立共价键,而物理交联剂促进链之间的物理相互作用或引发化学聚合。亲水单体与多功能交联剂反应通过自由基聚合或共聚产生交联和物理相互作用力。缩合反应通常存在于蛋白质和多糖中的羧酸与羟基或胺类进行交联,例如,N,N-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)-N-乙基碳二亚胺试剂与具有酰胺键的水溶性聚合物交联即碳二亚胺反应。O-酰基异脲中间体——碳二亚胺活化酸很快失活,从而阻碍胺反应的发生。与O-酰基异脲中间体相比,n -羟基琥珀酰亚胺的添加使得酯类稳定性增强,对胺类的反应性更强[49]。
原位交联可以实现可注射水凝胶的微创手术、细胞封装和移植,并且能与不规则的缺损匹配[50]。可注射水凝胶可采用物理或化学交联法制备,合成如光交联水凝胶、酶交联水凝胶、离子或pH敏感水凝胶等。酶促交联法合成的水凝胶在生理条件下能够快速凝胶化,具有高度特异性和低细胞毒性[51]。但最适酶的选择仍需进一步研究,以保证细胞在封装期的生物活性[52]。最近一些酶交联法合成胶原-透明质酸水凝胶的研究显示,可注射负载骨髓间充质干细胞水凝胶用于软骨再生具有良好的效果[53]。其中,在体内和体外实验中将水凝胶植入大鼠的软骨缺损处,支持骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化,促进透明软骨修复。同样地,基于利用酶交联法合成的富含细胞外基质的明胶仿生水凝胶研究,证明了其在兔膝关节模型中对于透明软骨的形成和糖胺聚糖含量方面有正向作用[54]。
另一种方法是互穿网络合成水凝胶,其中网络中两种或多种聚合物在分子级别上部分交织;聚合物之间不是通过共价键键合的,并且在不破坏其基质的化学键情况下,多种聚合物不能被分离[55]。就其机械性能和溶胀能力而言,多个网络(如互穿网络)优于单个网络[56]。一般而言,高含水量会降低单个网络水凝胶的机械性能。因此,目前有很多研究致力于开发双网络水凝胶来改善其机械性能。互穿网络水凝胶首先通过密集交联形成聚电解质网络,再通过松散交联形成[57],这种方法在模拟天然软骨方面取得了进展,提高了材料的硬度、耐磨性和压缩性能[58]。
2.4 仿生水凝胶的机械性能和生物特性 仿生水凝胶可以模拟软骨细胞外基质的组成和结构,具有和天然组织相似的机械性能和生物特性。天然材料如明胶和硫酸软骨素是无毒性的,具有可调节的生物降解性;然而,它们的机械性能很差,这限制了它们在组织工程中的应用[59]。基于此,研究人员将天然材料和合成材料相结合来改善水凝胶的机械性能和生物特性。据报道,关节软骨在浅层的压缩模量为0.02-1.60 MPa[60],在深层为6.44-7.75 MPa,然而在骨关节炎软骨中,其压缩模量在2-20 MPa。
从不同期刊数据库收集的大量有关机械性能(如压缩模量)和生物特性(如细胞活力、糖胺聚糖/脱氧核糖核酸含量)数据显示,大多数水凝胶的压缩模量为10-1 000 kPa,即合成水凝胶的压缩模量比天然软骨低至少10倍。值得注意的是,基于聚乙二醇-透明质酸的无细胞水凝胶的压缩模量最大(217-1 227 kPa)[61]。然而,基于硫酸软骨素-聚乙二醇的水凝胶表现出非常低的压缩性能(0.73 kPa)[62],但这可以通过交联改善[63],水凝胶的强度随着聚乙二醇的浓度增大而增大。
就机械性能而言,水凝胶应为细胞生长提供合适的微环境,促进细胞外基质生成和新组织形成。硬度过高的水凝胶会影响机体的生物行为,例如改变细胞表型或激化骨髓间充质干细胞分化为骨细胞[64]。此外,增加基质提高水凝胶硬度后,软骨细胞细胞外基质的生成下调,抑制细胞与水凝胶的黏附,应力纤维产生减少[65]。然而,如果水凝胶硬度在早期不足,软骨细胞将产生大量细胞外基质,随着时间推移,细胞外基质可增强水凝胶硬度,并承受高应力[66]。
就生物特性而言,水凝胶用于软骨组织工程表现出良好的细胞活力。从相关生存率数据(活/死细胞染色)可得,基于硫酸软骨素-聚乙二醇、聚乙二醇-透明质酸的水凝胶细胞活力高(>90%)[4,67],然而凝胶-甲基丙烯酸甲酯表现出低细胞活力(<80%)[68]。这可能是源于甲基丙烯酸甲酯过程中产生了细胞毒性,甲基丙烯酸甲酯加合物形成引起的氧化应激增加导致细胞毒性。就细胞外基质而言,明胶基水凝胶能刺激糖胺聚糖的分泌,并且表现出最高的糖胺聚糖/脱氧核糖核酸含量,特别是凝胶-透明质酸水凝胶[69]。已有研究证明透明质酸的加入可以增强细胞外基质重塑为更有序的胶原排列,并增强软骨特异性基因的表达[70]。
相反,细胞在含有聚乙二醇的水凝胶上生长时,其糖胺聚糖/脱氧核糖核酸的含量最低[61]。但可以通过加入其它聚合物的方法来改善。VARGHESE等[71]的研究表明,与单纯的聚乙二醇相比,硫酸软骨素的掺入可导致软骨形成的基因表达,促进软骨基质的产生。另外,凝胶-甲基丙烯酸甲酯和聚乙二醇结合后有利于细胞外基质的产生,并促进骨髓间充质干细胞的软骨分化[72]。BRYANT等[73]研究表明,添加可降解交联剂可促进凝胶中糖胺聚糖的扩散,而不影响其机械性能。此外,在未来的研究中可以考虑加入信号分子,如人转化生长因子β1,以改善细胞增殖和细胞外基质分泌等功能[74]。
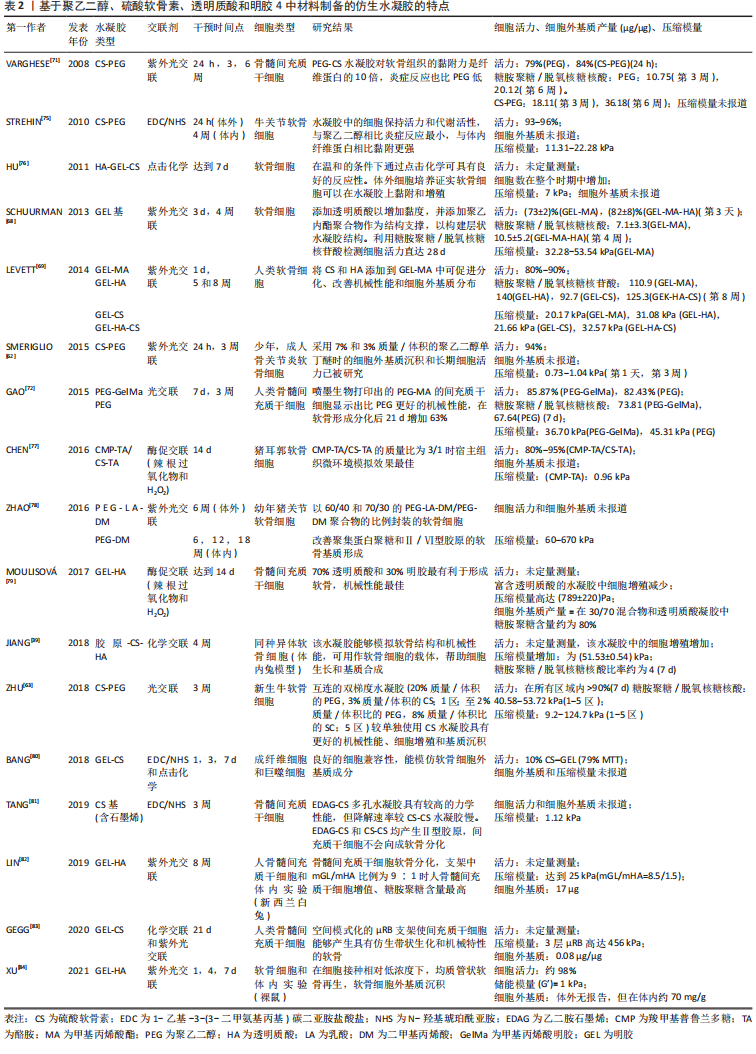
在过去几年的研究中,基于硫酸软骨素、透明质酸及明胶等天然聚合物水凝胶已被大量研制。经过物理或化学交联改进后,例如光交联、酶促交联及互穿网络等,已经实现了机械性能和生物特性的改善。基于细胞外基质衍生物的仿生水凝胶已具有与天然软骨相似的机械性能[39]。一般来说,天然来源的生物材料(如硫酸软骨素、透明质酸和明胶)是软骨组织工程的理想仿生来源。然而,由于一些关系因素如机械性能、降解速率等,限制了其临床应用。在该综述中已阐明,在近些年的研究中,对于天然来源的水凝胶材料进行化学或物理修饰后,可改善其机械性能及生物特性,并且与单一或生物合成制剂相比,表现出更优异的性能[75-84]。表2中总结了部分天然材料和合成材料相结合后形成的仿生水凝胶的相关特性。
| [1] GAN D, WANG Z, XIE C, et al. Mussel-inspired tough hydrogel with in situ nanohydroxyapatite mineralization for osteochondral defect repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(22):e1901103. [2] SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(11):625-635. [3] LIAO J, TIAN T, SHI S, et al. The fabrication of biomimetic biphasic CAN-PAC hydrogel with a seamless interfacial layer applied in osteochondral defect repair. Bone Res. 2017;5:17018. [4] ZHANG W, CHEN J, TAO J, et al. The use of type 1 collagen scaffold containing stromal cell-derived factor-1 to create a matrix environment conducive to partial-thickness cartilage defects repair. Biomaterials. 2013;34(3):713-713. [5] CHEN SS, FALCOVITZ YH, SCHNEIDERMAN R, et al. Depth-dependent compressive properties of normal aged human femoral head articular cartilage: relationship to fixed charge density. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9(6):561-569. [6] LEE HP, GU L, MOONEY DJ, et al. Mechanical confinement regulates cartilage matrix formation by chondrocytes. Nat Mater. 2017;16(12):1243-1251. [7] YANG J, ZHANG YS, YUE K, et al. Cell-laden hydrogels for osteochondral and cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017;57:1-25. [8] MORGESE G, BENETTI EM, ZENOBI-WONG M. Molecularly engineered biolubricants for articular cartilage. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(16):e1701463. [9] CHAI Q, JIAO Y, YU X. Hydrogels for biomedical applications: their characteristics and the mechanisms behind them. Gels. 2017;3(1):1-15. [10] SOPHIA FOX AJ, BEDI A, RODEO SA. The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 2009;1(6):461-468. [11] WILLIAMS DF. Biocompatibility pathways: biomaterials-induced sterile inflammation, mechanotransduction, and principles of biocompatibility control. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017;3(1):2-35. [12] HUANG L, HU J, LANG L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of electroactive and biodegradable ABA block copolymer of polylactide and aniline pentamer. Biomaterials. 2007;28(10):1741-1751. [13] AKIZUKI S, MOW VC, MULLER F, et al. Tensile properties of human knee joint cartilage: I. influence of ionic conditions, weight bearing, and fibrillation on the tensile modulus. J Orthop Res. 1986;4(4):379-392. [14] SCALZONE A, BONIFACIO MA, COMETA S, et al. pH-triggered adhesiveness and cohesiveness of chondroitin sulfate-catechol biopolymer for biomedical applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:712. [15] HE W, REAUME M, HENNENFENT M, et al. Biomimetic hydrogels with spatial- and temporal-controlled chemical cues for tissue engineering. Biomater Sci. 2020; 8(12):3248-3269. [16] OLIVEIRA AS, SEIDI O, RIBEIRO N, et al. Tribomechanical comparison between pva hydrogels obtained using different processing conditions and human cartilage. Materials. 2019;12(20):1-21. [17] DASHTDAR H, MURALI MR, ABBAS AA, et al. PVA-chitosan composite hydrogel versus alginate beads as a potential mesenchymal stem cell carrier for the treatment of focal cartilage defects. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23(5):1368-1377. [18] CHIN SY, POH YC, KOHLER AC, et al. An additive manufacturing technique for the facile and rapid fabrication of hydrogel-based micromachines with magnetically responsive components. J Vis Exp. 2018;137(e56727):1-12. [19] SKAALURE SC, CHU S, BRYANT SJ. An enzyme-sensitive PEG hydrogel based on aggrecan catabolism for cartilage tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015; 4(3):420-431. [20] SALA RL, KWON MY, KIM M, et al. Thermosensitive Poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) injectable hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23: 935-945. [21] YANG Y, ZHANG J, LIU Z, et al. Tissue-integratable and biocompatible photogelation by the imine crosslinking reaction. Adv Mater. 2016;28(14):2724-2730. [22] LAM J, TRUONG NF, SEGURA T. Design of cell-matrix interactions in hyaluronic acid hydrogel scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(4):1571-1580. [23] ZHU D, WANG H, TRINH P, et al. Elastin-like protein-hyaluronic acid (ELP-HA) hydrogels with decoupled mechanical and biochemical cues for cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2017;127:132-140. [24] HAO Y, HE J, MA X, et al. A fully degradable and photocrosslinked polysaccharide-polyphosphate hydrogel for tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;225:115257. [25] COWMAN MK, SHORTT C, ARORA S, et al. Role of Hyaluronan in Inflammatory Effects on Human Articular Chondrocytes. Inflammation. 2019;42(5):1808-1820. [26] ALINEJAD Y, ADOUNGOTCHODO A, HUI E, et al. An injectable chitosan/chondroitin sulfate hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties for cell therapy/tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;113:132-141. [27] WANG DA, VARGHESE S, SHARMA B, et al. Multifunctional chondroitin sulphate for cartilage tissue-biomaterial integration. Nat Mater. 2007; 6(5):385-392. [28] COLLIN EC, CARROLL O, KILCOYNE M, et al. Ageing affects chondroitin sulfates and their synthetic enzymes in the intervertebral disc. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017;2:e17049. [29] ZHOU L, FAN L, ZHANG FM, et al. Hybrid gelatin/oxidized chondroitin sulfate hydrogels incorporating bioactive glass nanoparticles with enhanced mechanical properties, mineralization, and osteogenic differentiation. Bioact Mater. 2021; 6(3):890-904. [30] CHEN F, YU S, LIU B, et al. An injectable enzymatically crosslinked carboxymethylated pullulan/chondroitin sulfate hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20014. [31] YAN S, WANG T, FENG L, et al. Injectable in situ self-cross-linking hydrogels based on poly(L-glutamic acid) and alginate for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(12):4495-4508. [32] MULLER M, OZTURK E, AELOV Ø, et al. Alginate sulfate-nanocellulose bioinks for cartilage bioprinting applications. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(1):210-223. [33] KASHI M, BLAGHBAN F, MOZTARZADEH F, et al. Green synthesis of degradable conductive thermosensitive oligopyrrole/chitosan hydrogel intended for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;107:1567-1575. [34] LIANG X, WANG X, XU Q, et al. Rubbery chitosan/carrageenan hydrogels constructed through an electroneutrality system and their potential application as cartilage scaffolds. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(2):340-352. [35] MENG Q, MAN Z, DAI L, et al. A composite scaffold of MSC affinity peptide-modified demineralized bone matrix particles and chitosan hydrogel for cartilage regeneration. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17802. [36] YUAN T, ZHANG L, LI K, et al. Collagen hydrogel as an immunomodulatory scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(2):337-344. [37] WONG CC, CHEN CH, CHIU LH, et al. Facilitating in vivo articular cartilage repair by tissue-engineered cartilage grafts produced from auricular chondrocytes. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(3):713-727. [38] JIANG X, HUANG X, JIANG T, et al. The role of Sox9 in collagen hydrogel-mediated chondrogenic differentiation of adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Biomater Sci. 2018;7(9):1556-1568. [39] JIANG X, LIU J, LIU Q, et al. Therapy for cartilage defects: functional ectopic cartilage constructed by cartilage-simulating collagen, chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid (CCH) hybrid hydrogel with allogeneic chondrocytes. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(6):1616-1626. [40] HAN L, XU J, LU X, et al. Biohybrid methacrylated gelatin/polyacrylamide hydrogels for cartilage repair. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(4):731-741. [41] WANG LS, DU C, TOH WS, et al. Modulation of chondrocyte functions and stiffness-dependent cartilage repair using an injectable enzymatically crosslinked hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2207-2217. [42] SAGHEBASL S, DAVARAN S, RAHBARGHAZI R, et al. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of thermosensitive hydrogel scaffolds based on (PNIPAAm-PCL-PEG-PCL-PNIPAAm)/Gelatin and (PCL-PEG-PCL)/Gelatin for use in cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(10):1185-1206. [43] LI F, TRUONG VX, THISSEN H, et al. Microfluidic encapsulation of human mesenchymal stem cells for articular cartilage tissue regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(10):8589-8601. [44] RIBEIRO VP, DA SILVA MORSIA A, MAIA FR, et al. Combinatory approach for developing silk fibroin scaffolds for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018; 72:167-181. [45] SINGH YP, BHARDWAJ N, MANDAL BB. Potential of Agarose/Silk Fibroin Blended Hydrogel for in Vitro Cartilage Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(33):21236-21249. [46] YODMUANG S, MCNAMARA SL, NOVER AB, et al. Silk microfiber-reinforced silk hydrogel composites for functional cartilage tissue repair. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:27-36. [47] BUWALDA SJ, BETHRY A, HUNGER S, et al. Ultrafast in situ forming poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(amido amine) hydrogels with tunable drug release properties via controllable degradation rates. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019;139:232-239. [48] HU W, WANG Z, XIAO Y, et al. Advances in crosslinking strategies of biomedical hydrogels. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(3):843-855. [49] TAN YH, SCHALLOM JR, GANESH NV, et al. Characterization of protein immobilization on nanoporous gold using atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Nanoscale. 2011;3(8):3395-3407. [50] LIU M, ZENG X, MA C, et al. Injectable hydrogels for cartilage and bone tissue engineering. Bone Res. 2017;5:17014. [51] NEZHAD-MOKHTARI P, GHORBANI M, ROSHANGAR L, et al. Chemical gelling of hydrogels-based biological macromolecules for tissue engineering: photo- and enzymatic-crosslinking methods. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;139:760-772. [52] VALOT L, MAUMUS M, MONTHEIL T, et al. Biocompatible glycine-assisted catalysis of the sol-gel process: development of cell-embedded hydrogels. Chempluschem. 2019;84(11):1720-1729. [53] ZHANG Y, CAO Y, ZHAO H, et al. An injectable BMSC-laden enzyme-catalyzed crosslinking collagen-hyaluronic acid hydrogel for cartilage repair and regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(19):4237-4244. [54] TSAI CC, KUO SH, LU TY, et al. Enzyme-cross-linked gelatin hydrogel enriched with an articular cartilage extracellular matrix and human adipose-derived stem cells for hyaline cartilage regeneration of rabbits. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020; 6(9):5110-5119. [55] PARHI R. Cross-linked hydrogel for pharmaceutical applications: a review. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017;7(4):515-530. [56] INGAVLE GC, DORMER NH, GEHRKE SH, et al. Using chondroitin sulfate to improve the viability and biosynthesis of chondrocytes encapsulated in interpenetrating network (IPN) hydrogels of agarose and poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(1):157-170. [57] HUANG KT, ISHIHARA K, HUANG CJ. Huang. Polyelectrolyte and antipolyelectrolyte effects for dual salt-responsive interpenetrating network hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2019;20(9):3524-3534. [58] NONOYAMA T, GONG JP. Double-network hydrogel and its potential biomedical application: a review. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2015;229(12):853-863. [59] TAGHIPOUR YD, HOKMABAD VR, DEL BAKHSHAYESH AR, et al. The application of hydrogels based on natural polymers for tissue engineering. Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(16):2658-2680. [60] KERIN AJ, WISNOM MR, ADAMS MA. The compressive strength of articular cartilage. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 1998;212(4):273-280. [61] NGUYEN LH, KUDVA AK, SAXENA NS, et al. Engineering articular cartilage with spatially-varying matrix composition and mechanical properties from a single stem cell population using a multi-layered hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2011;32(29): 6946-6952. [62] SMERIGLIO P, LAI JH, YANG F, et al. 3D Hydrogel scaffolds for articular chondrocyte culture and cartilage generation. J Vis Exp. 2015;(104):e53085. [63] ZHU D, TRINH P, LIU E, et al. Biochemical and mechanical gradients synergize to enhance cartilage zonal organization in 3D. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(10): 3561-3569. [64] VEDADGHAVAMI A, MINOOEI F, MOHAMMADI MH, et al. Manufacturing of hydrogel biomaterials with controlled mechanical properties for tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:42-63. [65] KIM JH, LEE G, WON Y, et al. Matrix cross-linking-mediated mechanotransduction promotes posttraumatic osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(30): 9424-9429. [66] SRIDHAR BV, BROCK JL, SILVER JS, et al. Development of a cellularly degradable PEG hydrogel to promote articular cartilage extracellular matrix deposition. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(5):702-713. [67] YU F, CAO X, ZENG L, et al. An interpenetrating HA/G/CS biomimic hydrogel via Diels-Alder click chemistry for cartilage tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;97(1):188-195. [68] SCHUURMAN W, LEVETT PA, POT MW, et al. Gelatin-methacrylamide hydrogels as potential biomaterials for fabrication of tissue-engineered cartilage constructs. Macromol Biosci. 2013;13(5):551-561. [69] LEVETT PA, MELCHELS FP, SCHROBBACK K, et al. A biomimetic extracellular matrix for cartilage tissue engineering centered on photocurable gelatin, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):214-223. [70] KO CS, HUANG JP, HUANG CW, et al. Type II collagen-chondroitin sulfate-hyaluronan scaffold cross-linked by genipin for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009;107(2):177-182. [71] VARGHESE S, HWANG NS, CANVER AC, et al. Chondroitin sulfate based niches for chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Matrix Biol. 2008; 27(1):12-21. [72] GAO G, SCHILLING AF, HUBBELL K, et al. Improved properties of bone and cartilage tissue from 3D inkjet-bioprinted human mesenchymal stem cells by simultaneous deposition and photocrosslinking in PEG-GelMA. Biotechnol Lett. 2015;37(11):2349-2355. [73] BRYANT SJ, ANSETH KS, LEE DA, et al. Crosslinking density influences the morphology of chondrocytes photoencapsulated in PEG hydrogels during the application of compressive strain. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(5):1143-1149. [74] LEE SH, SHIN H. Matrices and scaffolds for delivery of bioactive molecules in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:339-359. [75] STREHIN I, NAHAS Z, ARORA K, et al. A versatile pH sensitive chondroitin sulfate-PEG tissue adhesive and hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2010;31(10):2788-2797. [76] HU X, LI D, ZHOU F, et al. Biological hydrogel synthesized from hyaluronic acid, gelatin and chondroitin sulfate by click chemistry. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(4):1618-1626. [77] CHEN F, YU S, LIU B, et al. An injectable enzymatically crosslinked carboxymethylated pullulan/chondroitin sulfate hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20014. [78] ZHAO X, PAPADOPOULOS A, IBUSUKI S, et al. Articular cartilage generation applying PEG-LA-DM/PEGDM copolymer hydrogels. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:245. [79] MOULISOVA V, POVEDA-REYES S, SANMARTIN-MASIA E, et al. Hybrid protein-glycosaminoglycan hydrogels promote chondrogenic stem cell differentiation. ACS Omega. 2017;2(11):7609-7620. [80] BANG S, JUNG UW, NOH I. Synthesis and biocompatibility characterizations of in situ chondroitin sulfate-gelatin hydrogel for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;15(1):25-35. [81] TANG C, HOLT BD, WRIGHT ZM, et al. Injectable amine functionalized graphene and chondroitin sulfate hydrogel with potential for cartilage regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(15):2442-2453. [82] LIN H, BECK AM, SHIMOMURA K, et al. Optimization of photocrosslinked gelatin/hyaluronic acid hybrid scaffold for the repair of cartilage defect. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(8):1418-1429. [83] GEGG C, YANG F. Spatially patterned microribbon-based hydrogels induce zonally-organized cartilage regeneration by stem cells in 3D. Acta Biomater. 2020;101: 196-205. [84] XU Y, WANG Z, HUA Y, et al. Photocrosslinked natural hydrogel composed of hyaluronic acid and gelatin enhances cartilage regeneration of decellularized trachea matrix. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;120:111628. [85] SUN JY, ZHAO X, ILLEPERUMA WR, et al. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature. 2012;489(7414):133-136. [86] ZHOU F, HONG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Tough hydrogel with enhanced tissue integration and in situ forming capability for osteochondral defect repair. Applied Materials Today. 2018;13:32-44. |
| [1] | 姚晓玲, 彭建城, 许岳荣, 杨志东, 张顺聪. 可变角度零切迹前路椎间融合内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病:30个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | 安维政, 何 萧, 任 帅, 刘建宇. 肌源干细胞在周围神经再生中的潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [3] | 张璟琳, 冷 敏, 朱博恒, 汪 虹. 干细胞源外泌体促进糖尿病创面愈合的机制及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [4] | 陈晓旭, 罗雅馨, 毕浩然, 杨 琨. 脱细胞支架制备及其在组织工程和再生医学中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [5] | 康坤龙, 王新涛. 生物支架材料促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究热点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [6] | 沈佳华, 付 勇. 基于石墨烯的纳米材料可否在干细胞领域应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [7] | 张 通, 蔡金池, 袁志发, 赵海燕, 韩兴文, 王文己. 基于透明质酸的复合水凝胶修复骨关节炎软骨损伤:应用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [8] | 李 辉, 陈良龙. 植骨材料在脊柱结核治疗中的应用与特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [9] | 高仓健, 杨 振, 刘舒云, 李 浩, 付力伟, 赵天元, 陈 威, 廖志垚, 李品学, 眭 翔, 郭全义. 静电纺丝技术在肩袖损伤修复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [10] | 黄传俊, 邹 煜, 周晓婷, 朱扬清, 钱 伟, 张 卫, 刘 星. 携带脐带间充质干细胞的RADA16-BDNF水凝胶支架定向移植促进脑出血大鼠神经功能恢复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [11] | 何云影, 李玲婕, 张舒淇, 李雨舟, 杨 生, 季 平. 聚丙烯酸/琼脂糖三维培养构建细胞球的方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [12] | 何冠宇, 徐宝山, 杜立龙, 张同星, 霍振鑫, 申 力. 天然丝素蛋白构建仿生取向微通道纤维环支架[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [13] | 龙智生, 熊 龙, 龚飞鹏, 李经堂, 曾建华, 邓 颖, 兰 敏, 孔维豪, 陈 钢. 多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构人工骨对兔骨缺损修复及成血管的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(34): 5436-5441. |
| [14] | 路冬冬, 朱天峰, 张一健, 赵志坚, 刘 洋, 沈 序, 朱雪松. 3D生物打印甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶支架促进软骨下骨缺损的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(34): 5454-5460. |
| [15] | 刘 沛, 张冠英, 余泉峰, 李泽宇, 韩广业, 吴春磊. 复合碱性成纤维细胞生长因子聚乳酸/胶原支架修复兔尿道缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(34): 5468-5474. |
颞下颌关节形成于颞骨关节窝和下颌骨髁突之间,是日常功能(如语言和咀嚼)所必须的关节。颞下颌关节疾病是累及颞下颌关节及其相关组织的多种功能性和器质性疾病,其主要特征之一是髁突软骨的损伤。软骨的存在可以减少关节中骨骼之间的磨擦,故软骨的损伤会导致关节功能下降[1]。另外骨性关节炎和软骨缺损的发展是一个恶性循环:骨性关节炎中分解代谢产生的促炎介质导致蛋白水解酶过量产生并破坏软骨,软骨的缺损反过来会加剧关节的炎症[2]。
基于精密医学修复,软骨修复需根据软骨缺损的不同类型而确定。根据缺损的区域,软骨缺损可分为3类:软骨部分缺损、软骨全层缺损以及骨软骨缺损[3],见图1。
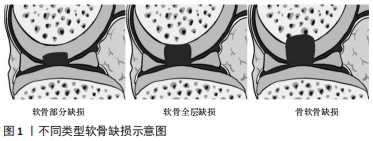
软骨部分缺损是软骨表层的缺损,不累及软骨中硬化与非硬化部分的分界线(潮痕);而骨软骨缺损穿透到骨髓。此3类软骨缺损的微环境有所差异,骨髓间充质干细胞可以修复软骨全层和骨软骨缺损,而由于软骨的阻挡,在软骨表面不存在骨髓基质细胞[4],单依靠骨髓间充质干细胞不能修复所有类型的软骨缺损,所以研究设计软骨替代材料是非常有必要的。但是,天然软骨结构复杂,如压缩模量随着软骨深度的增加而增加[5],因此,在设计软骨替代材料时应考虑天然软骨每个区域的组成及特点,赋予每个区域不同的性能。
在临床上,自体软骨移植、微软骨手术、自体软骨细胞植入和基质诱导自体软骨细胞植入是修复软骨小缺损的最常用策略,但这些策略会促进纤维软骨的形成,从而影响关节功能[6]。YANG等[7]在最近的一篇综述中总结了这些策略的其他局限性,如软骨细胞来源的缺乏和有效率低,尤其在老年患者中表现明显。
组织工程学是一个结合材料学和细胞生物学的跨学科领域,用于修复难以再生的生物组织。软骨一旦出现缺损,由于其结构复杂,缺乏血管、神经及淋巴管,组织自限性差,尤其软骨全层缺损难以修复再生[8]。因此,组织工程学已成为修复软骨缺损(尤其是软骨全层缺损)的有效方法:开发人造材料以模拟天然骨软骨的机械性能和生物特性,用于植入缺损处以替代其生物功能。软骨再生中使用的支架可以分为海绵、膜、非织造、非注射和可注射水凝胶等,这些支架材料各有其用途与特点,海绵支架有利于细胞接种,但其结构单一;膜状支架适用于精细修复,但其对于工艺要求高且成本高,不方便运输和储存;非织造支架韧性高,适用于软骨表层缺损。然而水凝胶是一种亲水聚合物[9],其具有优异的机械性能(如弹性模量)和生物特性(如细胞活力和糖胺聚糖含量),这些特性对于模拟高含水量(80%)的软骨至关重要[10]。此外,水凝胶便于储存和携带,应用效益和前景广阔,故文章着重对仿生水凝胶在软骨组织工程领域的研究和应用进展作综述。
文章总结以往大量相关研究成果及结论,以合成仿生水凝胶的不同原材料(天然原材料和合成原材料)为综述切入点,介绍、总结了交联这一方式在仿生水凝胶合成中的作用原理及重要意义,对得到的不同仿生水凝胶的性能和优缺点进行了较为完备的分析和总结,并从其机械性能和生物特性等角度进行详细的对比。仿生水凝胶具备的相关优越性能使其在软骨组织工程领域应用较为广泛,并且由于口腔医学中颞下颌关节的特殊性,仿生水凝胶在口腔医学软骨再生领域的应用前景较好,对于未来颞下颌关节软骨缺损的相关治疗将有革命性的推动作用。然而,在软骨组织工程中,具有改善细胞功能以再生软骨并具备恰当支持承重能力的支架或水凝胶尚未完全成功。
该综述通过总结不同仿生合成水凝胶的性能及优缺点,以期未来获得性能完备可广泛用于临床治疗的仿生水凝胶材料。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2021年4月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 1986-2021年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 Web of Science和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词:“hydrogel,cartilage regeneration,cartilage defect,cartilage tissue engineering”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评、经验交流和病例报告。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图2。

1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索到英文文献3 665篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 仿生水凝胶应用于软骨组织工程的一次文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 文章内容与该综述相关性不强、发表时间过早、参考价值不高及内容重复的同类研究。
1.3 数据提取及质量评估 共检索到3 665篇文献,在进行文献排除后得到131篇,对131篇文献进行大致的粗略阅读及质量评估,最终纳入86篇符合标准的英文文献进行综 述,文献筛选流程,见图3。
基于水凝胶材料在软骨组织工程中的巨大潜力,近年来关于该材料的相关研究已成为热点,该综述总结了既往其他学者在仿生水凝胶原材料、交联方式及其机械性能和生物特性等角度的相关研究成果,对现阶段实验研究得到的部分合成仿生水凝胶的性能和优缺点进行了较为完备的分析和总结,并从其机械性能和生物特性等角度进行详细的对比。然而,将软骨完全恢复到与其原始组成、结构、力学和生物功能相同仍然是一项重大挑战。基于软骨缺损设计仿生水凝胶,首先需考虑其材料来源,例如聚丙烯酰胺及其衍生物的双重网络制成的水凝胶机械强度很高[85],而有关报道表明,聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶在隆胸中引起炎症反应,并于2006年被中国、美国食品药品监督管理局禁止使用,因此,将其用于软骨修复的植入材料更需慎重考虑。除材料类型外,基质弹性、基质刚度、机械约束等参数也会改变细胞活性[6],由于组织的复杂性,基于机械和生物学的考虑,尚无最佳的软骨修复仿生水凝胶材料。软骨组织工程中的另一个问题是如何将仿生材料结合到软骨上,如果没有有效的结合,即使在引入的水凝胶支架周围有新形成的软骨组织,也无法和宿主组织很好地结合[86]。以上问题仍是该领域研究的困难之处,在以往相关实验和综述中也表明这些问题仍客观存在,且是未来仍需攻克的。
作者所研究专业为口腔医学领域,口腔颌面部颞下颌关节结构较为复杂,具有关节软骨等相关组织结构。以往关于仿生水凝胶应用于口腔领域的软骨组织工程中研究较少,多用于膝关节、髋关节等软骨再生组织工程。仿生水凝胶应用于颞下颌关节软骨组织再生具有巨大发展潜力,因此该综述通过仿生水凝胶相关领域总结论述,以期将其与口腔医学领域相结合,这是文章不同于以往同领域综述的一点。此外,文章通过总结以往大量相关研究成果及结论,以合成仿生水凝胶的不同原材料(天然原材料和合成原材料)为综述主线,以交联这一重要结合手段为桥梁,对得到的不同合成仿生水凝胶的机械性能、生物特性和优缺点等角度进行了比较充分的对比、分析和总结,该论述思路也是文章区别于该方向其余综述及科研文章的相对创新之处。
文章所总结论述的合成仿生水凝胶在软骨组织工程领域的应用进展是当前比较热点的研究方向。基于该文阐述进行总结来看,一种理想的用于软骨组织工程的仿生水凝胶应同时具备以下特征:①生物活性和仿生性能;②优越的机械性能;③软骨与骨组织的整合能力;④药物和生长因子的转运功能。由此可以看出,软骨组织工程对于仿生水凝胶材料的性能要求较高,目前尚无完美的合成仿生水凝胶材料问世。因此,该综述将现阶段研究成果进行论述总结:在近些年的研究中发现,利用天然或合成聚合物交联后形成的仿生水凝胶材料具备更优越的机械性能及生物特性,但是仍然存在一些不足,例如通过紫外光交联的硫酸软骨素-聚乙二醇材料具有一定的抗炎特性,也可促进软骨组织再生,然而其促进软骨细胞的增殖和成熟能力有待加强。因此,尚无法在当前阶段断言性能最佳的水凝胶材料,仅可将现有研究成果进行较为完整全面的分析总结,以期为后续相关研究提供某一阶段性资料,这是该综述的相对局限性。但随着人工智能的兴起,未来有望利用新技术在未来开发出更优异的材料,这些技术也在加速试错的过程,以最终获得理想的软骨修复仿生水凝胶材料。
综上所述,仿生水凝胶在软骨组织工程领域未来应用拥有广阔前景,但是当前研究阶段仍然面临很多挑战。文章通过介绍合成仿生水凝胶的不同原材料以及通过交联使得材料之间取长补短,得到更优性能的仿生水凝胶,最后将现阶段研究成果中的一些仿生水凝胶材料进行了全面对比分析总结。通过前文叙述可以看出,为实现定制化的临床应用,需要制备具有复杂结构的仿生水凝胶支架,基于这种认识,未来的研究工作应着力于构建仿生水凝胶的二、三级和更高级结构,量化它们的组成、形态和功能,最后将它们转化为软骨组织工程的生物材料。并且目前在该领域的研究仍然突飞猛进,例如最近有研究开发具有强黏附力的潮湿水凝胶表面,这可能为构建软骨组织工程的生物材料开辟一条新道路[86]。因此,随着仿生水凝胶研究的不断深入和对其机械性能和生物特性的精细调整,不断优化其结构和功能,未来新型仿生水凝胶将会广泛应用于软骨组织工程领域。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程

文题释义:
交联:即多种聚合物链通过交联多维延伸形成稳定的网络结构。根据交联的类型可分为化学交联和物理交联。化学交联的凝胶可永久连接,其中不同的聚合物链之间形成共价键,从而产生优异的机械性能,但化学交联形成的水凝胶常具有毒性;而在物理交联中,物理相互作用(如离子键、氢键或疏水相互作用)抑制了凝胶的溶解,物理交联法形成的水凝胶不具有毒性。
整合能力:将修复材料植入缺损部位时,整合能力可用来反映组织的修复情况。材料与缺损部位组织的结合程度越高,再生细胞与原细胞越相似,其整合能力越强。如果新生组织不能与修复材料很好地整合,则组织再生修复失败。
水凝胶是一类有弹性的生物材料,表面光滑,含水量高,有望成为软骨再生的候选材料。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||