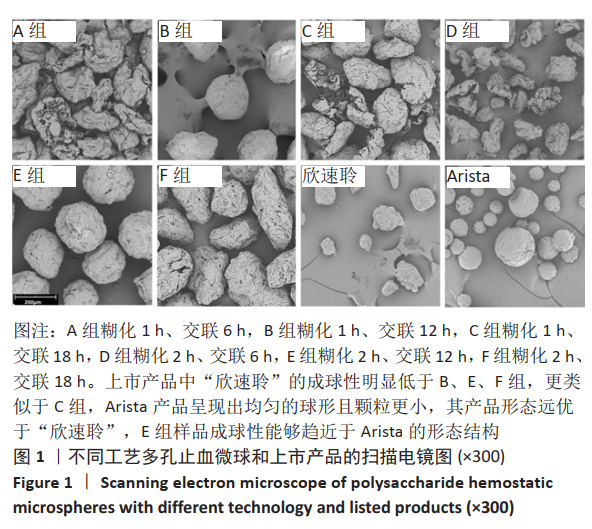
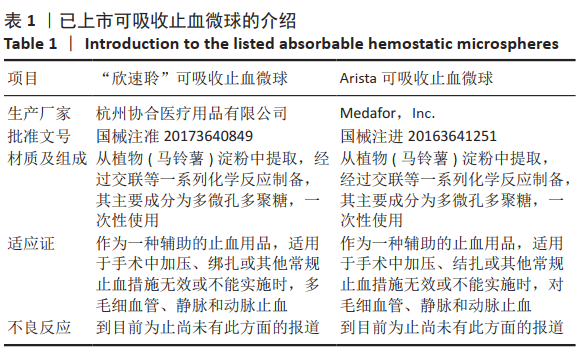
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2487-2491.doi: 10.12307/2022.245
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
可生物降解植物多糖止血微球的制备及性能
杨 雪1,王宝群1,姜晓文1,邹圣灿1,明津法2,林莎莎1
- 1青岛琛蓝海洋生物工程有限公司,山东省青岛市 266100;2青岛大学纺织服装学院,山东省青岛市 266000
Preparation and properties of biodegradable plant polysaccharide hemostatic microspheres
Yang Xue1, Wang Baoqun1, Jiang Xiaowen1, Zou Shengcan1, Ming Jinfa2, Lin Shasha1
- 1Qingdao Chenland Marine Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Qingdao 266100, Shandong Province, China; 2College of Textiles and Clothing, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
微孔多糖止血微球:为一种新型止血材料,具有良好的生物兼容性,无毒副作用,能直接作用于手术创面迅速止血。淀粉糊化:是将淀粉混合于水中并加热,达到一定温度后淀粉粒溶胀、崩溃,形成黏稠均匀的透明糊溶液。
背景:止血是临床治疗的重要部分,快速有效的止血是手术患者生命安全的必要保障。
目的:制备一种具有多孔结构的植物多糖止血微球,评价其性能。
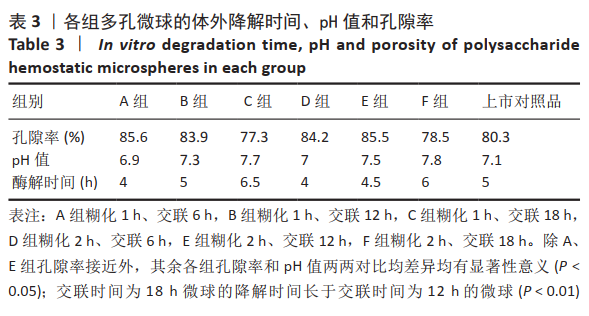
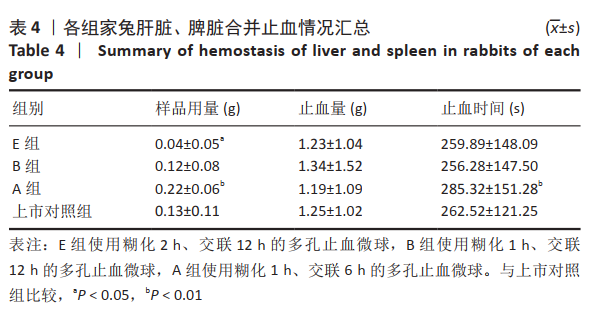
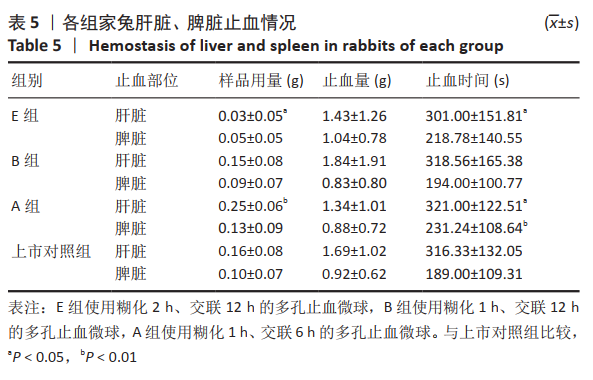
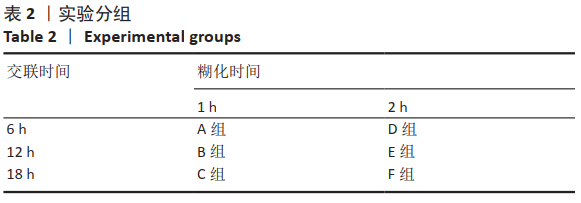
方法:以马铃薯淀粉为原料,通过糊化、乳化交联、清洗、干燥技术制备多孔止血微球,其中通过改进淀粉的糊化和交联工艺,以提高止血微球的止血性能,设置分组:A组糊化1 h、交联6 h,B组糊化1 h、交联12 h,C组糊化1 h、交联18 h,D组糊化2 h、交联6 h,E组糊化2 h、交联12 h,F组糊化2 h、交联18 h,以上市的可吸收止血微球为对照,检测各组微球的微观形貌、pH值、孔隙率与体外降解情况。根据上述实验结果,选择适宜的微球用于新西兰兔肝脏与脾脏的止血,对比样品用量、止血量与止血时间。
结果与结论:①扫描电镜显示,B组与E组形成了直径为50-200 μm结构稳定的多孔微球,成球形态及孔隙率优于对照组;除C组和E组外,其他样品的pH值均在6.5-7.5之间,符合pH值要求;相同质量的样品,交联时间增长降解时间明显增长(P < 0.01)。根据前期形态结构、孔隙率、pH值和体外降解的检测,选择A、B、E组和对照组进行止血实验。②在相同的止血效果下,与对照组比较,E组微球的止血时间更短、用量更少,B组止血效果与对照组比较无明显差异。③结果表明,在60 ℃下、糊化2 h、乳化45 min、交联12 h后制备的多孔淀粉微球,止血效果最佳且其降解时间也相对较短,其性能优于上市对照品。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6294-3368 (杨雪)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: