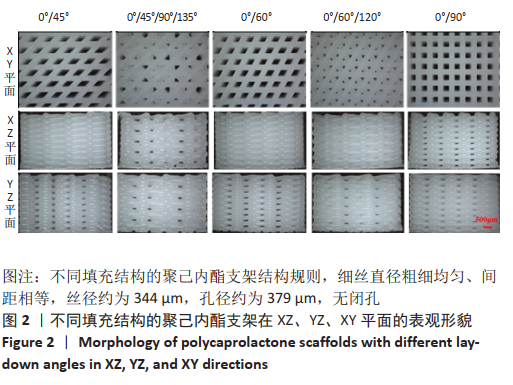
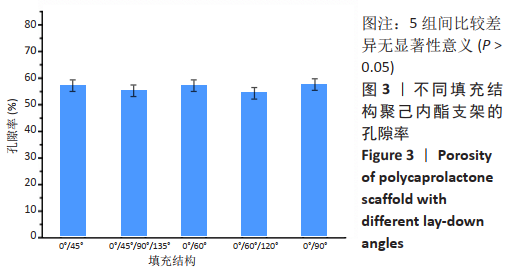
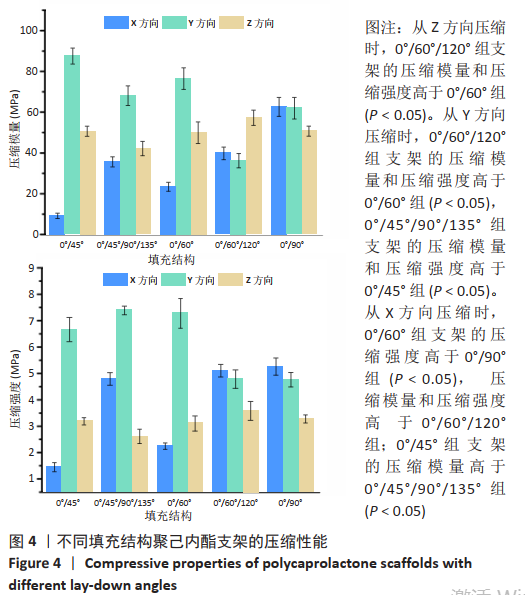
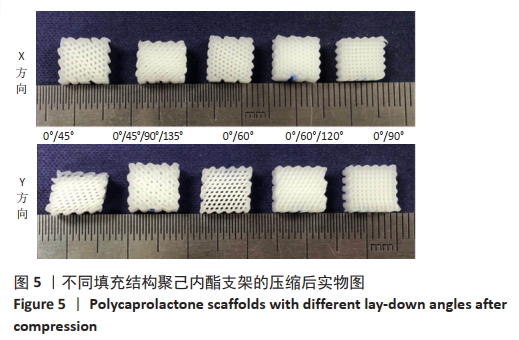
[1] JI WC, ZHANG XW, QIU YS. Selected suitable seed cell, scaffold and growth factor could maximize the repair effect using tissue engineering method in spinal cord injury. World J Exp Med. 2016;6(3): 58-62.
[2] O’KEEFE RJ, MAO J. Bone tissue engineering and regeneration: from discovery to the clinic-an overview introduction. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2011;17(6):389-392.
[3] 佘荣峰,张一,陈龙,等.丝素蛋白-壳聚糖支架复合骨髓间充质干细胞体内构建组织工程化软骨的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(1):27-32.
[4] SUH JK, MATTHEW HW. Application of chitosan-based polysaccharide biomaterials in cartilage tissue engineering: a review. Biomaterials. 2000;21(24):2589-2598.
[5] NG AMH, BIN SAIM A, TAN KK, et al. Comparison of bioengineered human bone construct from four sources of osteogenic cells. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10(2):192-199.
[6] HSIEH CY, HSIEH HJ, LIU HC, et al. Fabrication and release behavior of a novel freeze-gelled chitosan/gamma-PGA scaffold as a carrier for rhBMP-2. Dent Mater. 2006;22(7):622-629.
[7] LIU Y, NELSON T, CROMEENS B, et al. HB-EGF embedded in PGA/PLLA scaffolds via subcritical CO2 augments the production of tissue engineered intestine. Biomaterials.2016;103:150-159.
[8] RAFIEI M, JOOYBAR E, ABDEKHODAIE MJ, et al. Construction of 3D fibrous PCL scaffolds by coaxial electrospinning for protein delivery. Mater Sci Eng C-Biomimetic Supramol Syst. 2020;113:110913.
[9] 潘璐,程亭亭,徐岚.聚己内酯/聚乙二醇大孔径纳米纤维膜的制备及其在组织工程支架中的应用[J] . 纺织学报,2020,41(9): 167-173.
[10] OH SH, PARK IK, KIM JM, et al. In vitro and in vivo characteristics of PCL scaffolds with pore size gradient fabricated by a centrifugation method. Biomaterials. 2007;28(9):1664-1671.
[11] SIDDIQUI N, ASAWA S, BIRRU B, et al. PCL-Based composite scaffold matrices for tissue engineering applications. Mol Biotechnol. 2018; 60(7):506-532.
[12] HWANG S, TODO M. Characterization of compressive deformation behavior of multi-layer porous composite materials for articular tissue engineering. J Mech Sci Technol. 2012;26(7):1999-2004.
[13] DENG Y, JIANG C, LI C, et al. 3D printed scaffolds of calcium silicate-doped beta-TCP synergize with co-cultured endothelial and stromal cells to promote vascularization and bone formation. Sci Rep. 2017;7: 5588.
[14] DIAO J, OUYANG J, DENG T, et al. 3D-Plotted beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds with smaller pore sizes improve in vivo bone regeneration and biomechanical properties in a critical-sized calvarial defect rat model. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(17):1800441.
[15] ROOHANI-ESFAHANI SI, NEWMAN P, ZREIQAT H. Design and fabrication of 3D printed scaffolds with a mechanical strength comparable to cortical bone to repair large bone defects. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19468.
[16] SHAO H, YANG X, HE Y, et al. Bioactive glass-reinforced bioceramic ink writing scaffolds: sintering, microstructure and mechanical behavior. Biofabrication. 2015;7(3):035010.
[17] ANG KC, LEONG KF, CHUA CK, et al. Investigation of the mechanical properties and porosity relationships in fused deposition modelling-fabricated porous structures. Rapid Prototyping J. 2006;12(2):100-105.
[18] ZHANG B, GUO L, CHEN H, et al. Finite element evaluations of the mechanical properties of polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds by direct ink writing: Effects of pore geometry. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;104:103665.
[19] DOMINGOS M, INTRANUOVO F, RUSSO T, et al. The first systematic analysis of 3D rapid prototyped poly(epsilon-caprolactone) scaffolds manufactured through BioCell printing: the effect of pore size and geometry on compressive mechanical behaviour and in vitro hMSC viability. Biofabrication. 2013;5(4):045004.
[20] KORPELA J, KOKKARI A, KORHONEN H, et al. Biodegradable and bioactive porous scaffold structures prepared using fused deposition modeling. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101B(4): 610-619.
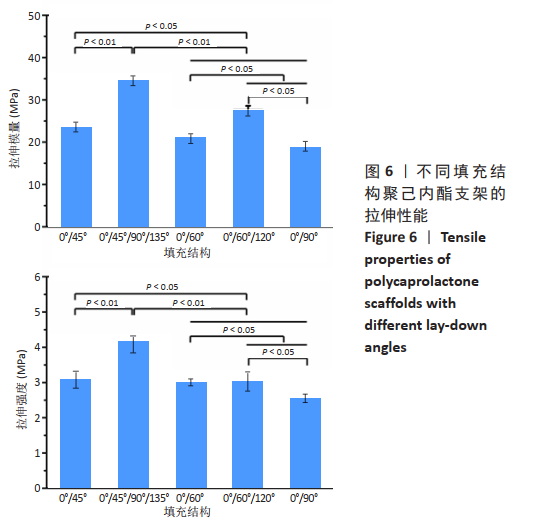
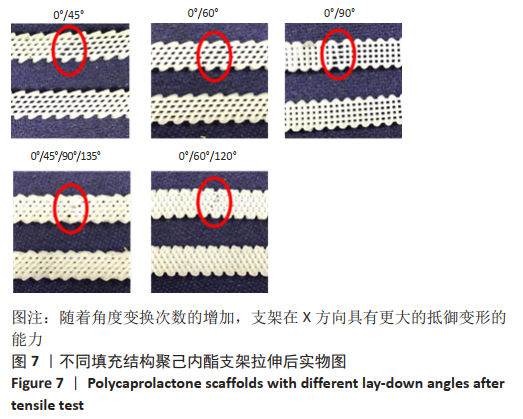
[21] 李相成,索海瑞,王玲,等.基于3D打印羟基磷灰石支架的填充结构与力学性能研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2020,39(1):91-96.
[22] LEVINGSTONE TJ, MATSIKO A, DICKSON GR, et al. A biomimetic multi-layered collagen-based scaffold for osteochondral repair. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):1996-2004.
[23] O’LEARY C, CAVANAGH B, UNGER RE, et al. The development of a tissue-engineered tracheobronchial epithelial model using a bilayered collagen-hyaluronate scaffold. Biomaterials. 2016;85:111-127.
[24] GLEADALL A, VISSCHER D, YANG J, et al. Review of additive manufactured tissue engineering scaffolds: relationship between geometry and performance. Burns Trauma. 2018;6:19.
[25] SHEPHERD DE, SEEDHOM BB. The ‘instantaneous’ compressive modulus of human articular cartilage in joints of the lower limb. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999;38(2):124-132.
[26] ATHANASIOU KA, AGARWAL A, DZIDA FJ. Comparative study of the intrinsic mechanical properties of the human acetabular and femoral head cartilage. J Orthop Res. 1994;12(3):340-349.
[27] CHEN SS, FALCOVITZ YH, SCHNEIDERMAN R, et al. Depth-dependent compressive properties of normal aged human femoral head articular cartilage: relationship to fixed charge density. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9(6):561-569.
[28] KAPLAN SJ, HAYES WC, STONE JL, et al. Tensile strength of bovine trabecular bone. J Biomech. 1985;18(9):723-727.
[29] WILLIAMS JL, LEWIS JL. Properties and an anisotropic model of cancellous bone from the proximal tibial epiphysis. J Biomech Eng. 1982;104(1):50-56.
[30] WONG BL, SAH RL. Mechanical asymmetry during articulation of tibial and femoral cartilages: Local and overall compressive and shear deformation and properties. J Biomech Eng. 2010;43(9): 1689-1695.
[31] AKIZUKI S, MOW VC, MULLER F, et al. Tensile properties of human knee joint cartilage: I. Influence of ionic conditions, weight bearing, and fibrillation on the tensile modulus. J Orthop Res. 1986;4(4): 379-392.
[32] TELLIS BC, SZIVEK JA, BLISS CL, et al. Trabecular scaffolds created using micro CT guided fused deposition modeling. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Biomimetic Supramol. Syst. 2008;28(1):171-178.
[33] HUTMACHER DW, SCHANTZ T, ZEIN I, et al. Mechanical properties and cell cultural response of polycaprolactone scaffolds designed and fabricated via fused deposition modeling. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;55(2):203-216.
[34] ZHANG B, GUO L, CHEN H, et al. Finite element evaluations of the mechanical properties of polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds by direct ink writing: Effects of pore geometry. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;104:103665. |
 文题释义:
文题释义: