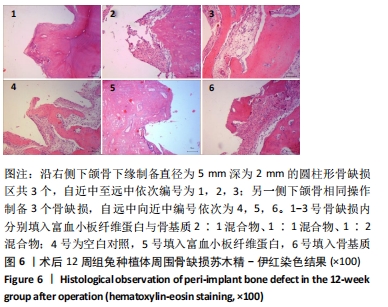
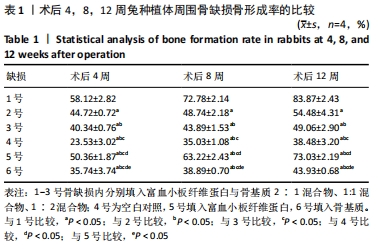
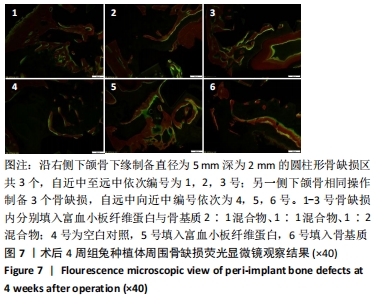
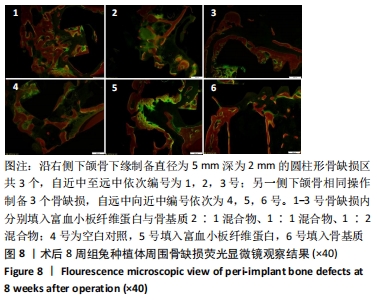
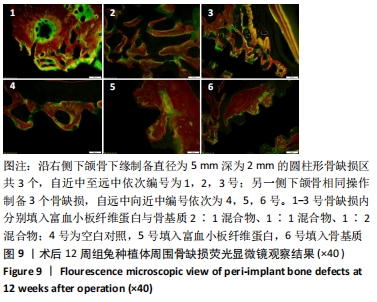
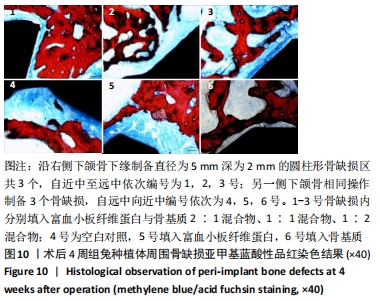
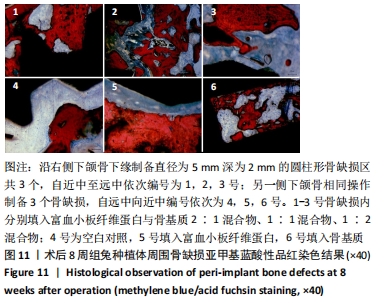
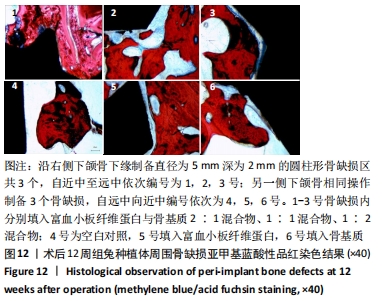
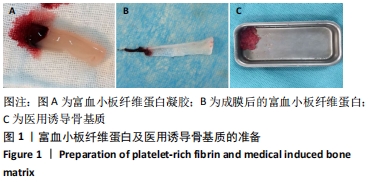
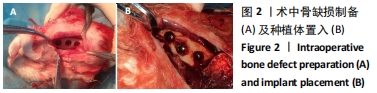
[1] 刘宝林, 林野, 李德华. 口腔种植学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2011.
[2] BORIE E, OLIVÍ DG, ORSI IA, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin application in dentistry: a literature review. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(5):7922-7929.
[3] CHOUKROUN J, ADDA F, SCHOEFFLER C, et al. Une opportunite´ en paro-implantologie: Le PRF. Implantodontie. 2000;42:55-62.
[4] VIDHALE G, JAIN D, JAIN S, et al. Management of Radicular Cyst Using Platelet-Rich Fibrin & Iliac Bone Graft - A Case Report. Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(6):ZD34-ZD36.
[5] BANSAL C, BHARTI V. Evaluation of efficacy of autologous platelet-rich fibrin with demineralized-freeze dried bone allograft in the treatment of periodontal intrabony defects. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2013;17(3): 361-366.
[6] RIEDEL K, RIEDEL F, GOESSLER UR, et al. Current status of genetic modulation of growth factors in wound repair. Int J Mol Med. 2006; 17(2):183-193.
[7] LI Q, PAN S, DANGARIA SJ, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Promotes Periodontal Regeneration and Enhances Alveolar Bone Augmentation. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:638043.
[8] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DISS A, ODIN G, et al. In vitro effects of Choukroun’s PRF (platelet-richfibrin)on human gingival fibroblasts,dermal prekeratinocytes, preadipocytes, and maxillofacial osteoblasts in primary cultures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108(3):341-352.
[9] LI Q, GENG Y, LU L. Platelet-rich fibrin-induced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblast-like cells and neural cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(31):2419-2423.
[10] 常晓峰, 杜良智, 刘少丽. 上颌窦底提升及人工骨粉植入的动物实验研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2010,26(4):441-444.
[11] 高飞, 衡立君, 贾栋. 神经内镜下经鼻蝶垂体腺瘤切除术中鞍底重建[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志,2014,19(7):403-405.
[12] ORTEGA-MEJIA H, ESTRUGO-DEVESA A, SAKA-HERRÁN C, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Maxillary SinusAugmentation: Systematic Review. Materials. 2020;13:622.
[13] JAYALAKSHMI KB, AGARWAL S, SINGH MP, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin with β-Tricalcium Phosphate—A Noval Approach for Bone Augmentation in Chronic Periapical Lesion: A Case Report. Case Rep Dent. 2012;2012: 902858.
[14] NASIRZADE J, KARGARPOUR Z, HASANNIA S, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin elicits an anti-inflammatory response in macrophages in vitro. J Periodontol. 2020;91:244-252.
[15] 郭洪亮, 郑纪伟, 韩建国. 转化生长因子β1对种植体表面成骨细胞Ⅰ性胶原蛋白基因表达研究[J]. 交通医学,2013,27(5):449-453.
[16] 杨全全, 何家才. 富血小板纤维蛋白在口腔种植中应用的研究进展[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2011,46(10):1066-1067.
[17] LYNCH SE, BUSER D, HERNANDEZ RA, et al. Effects of the plate-let-derived growth factor insulin-like growth factor-I combinationon bone regeneration aroundtitanium dental implants. Results of apilot study in beagle dogs. J Periodontol. 1991;62(11):710-716.
[18] 胡雅丽, 焦艳军, 高莺. 罗格列酮对2型糖尿病大鼠种植体周围血小板衍生生长因子-B 影响的实验研究[J]. 中国口腔种植学杂志, 2013,18(3):125-128.
[19] 郭玲, 王敏, 郝亮. 胰岛素样生长因子1对小鼠成骨细胞增殖和碱性磷酸酶活性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(33):6095-6098.
[20] SHAH M, PATEL J, DAVE D, et al. Comparative evaluation of platelet-rich fibrin with demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft in periodontal infrabony defects:A randomized controlled clinical study. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2015;19(1):56-60.
[21] LIU R, YAN M, CHEN S, et al. Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Fibrin as an Adjunctive Material to Bone Graft in Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trails. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:7267062.
[22] PANG L, HAO W, JIANG M, et al. Bony defect repair in rabbitusinghybrid rapidprototypingpolylactic-co-glycolic acid/β-tricalciumphosphate collagen I/apatite scaffold and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Indian J Orthop. 2013;47(4):388-394.
[23] JAMES R, LAURENCIN CT. Regenerative engineering and advanced materials science. MRS Bulletin. 2017;42(8):600-607.
[24] ANBU RT, SURESH V, GOUNDER R, et al. Comparison of the Efficacy of Three Different Bone Regeneration Materials: An Animal Study. Eur J Dent. 2019;13:22-28.
[25] MOURÃO CF, VALIENSE H, MELO ER, et al. Obtention ofinjectable platelets rich-fibrin (i-PRF) and its polymerization with bone graft: technical note. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2015;42(6):421-423.
[26] AMARAL VALLADÃO CA JR, FREITAS MONTEIRO M, JOLY JC. Guided bone regeneration in stagedvertical and horizontal bone augmentation using platelet-rich fibrin associated with bone grafts: a retrospective clinical study. Int J Implant Dent. 2020;6(1):72.
[27] MIRON RJ, PINTO NR, QUIRYNEN M, et al. Standardization of relative centrifugal forces in studiesrelated to platelet-rich fibrin. J Periodontol. 2019;90(8):817-820.
[28] ARUNACHALAM M, PULIKKOTIL SJ, SONIA N. Platelet richfibrin in periodontal regeneration. Open Dent J. 2016;10:174-181.
[29] YAJAMANYA SR, CHATTERJEE A, BABU CN, et al. Fibrin network pattern changes of platelet-rich fibrin in young versus old age group of individuals:a cell block cytology study. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2016; 20(2):151-156 .
[30] LIU Y, SUN X, YU J, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin as a Bone Graft Material in Oral and Maxillofacial Bone Regeneration: Classification and Summary for Better Application. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:3295756.
[31] SINGH S, SINGH A, SINGH S, et al. Application of PRF in surgical management of periapical lesions. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2013;4(1): 94-99.
[32] 李超,王天祥,邹高峰. CGF技术在口腔种植中的应用[J]. 中外健康文摘,2012,9(17):446-447.
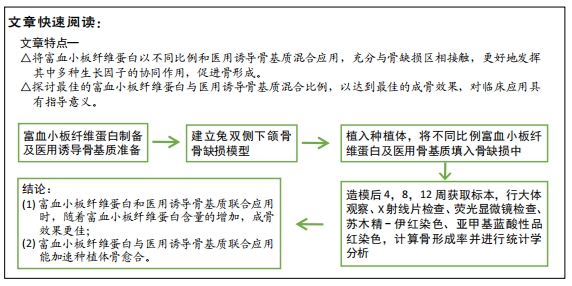
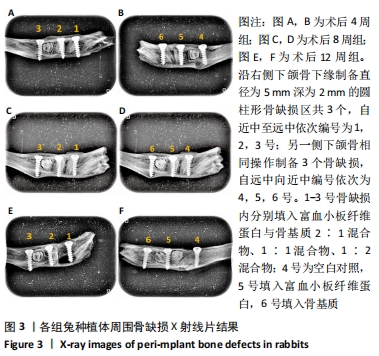
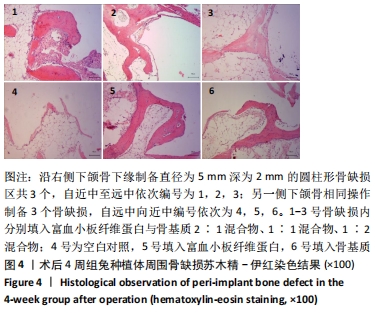
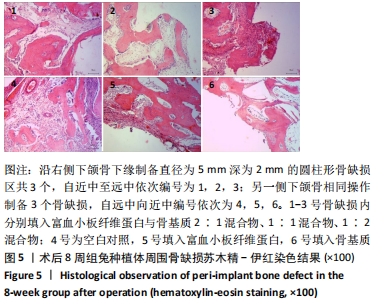
|