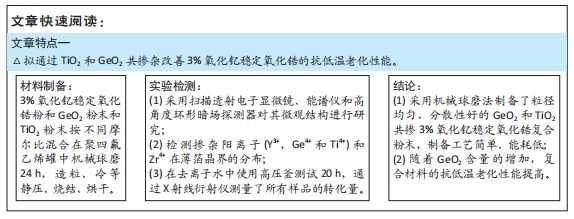
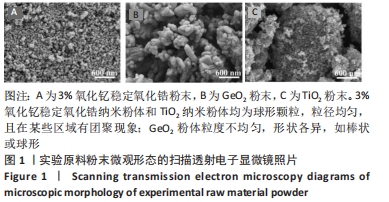
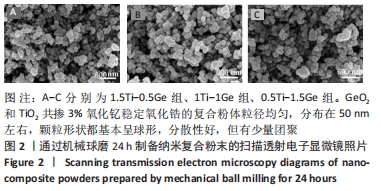
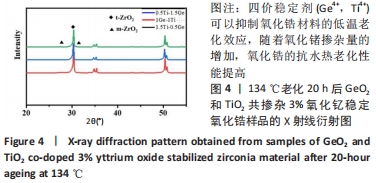
[1] HEATHER JC, WOOK JS, IGOR JP. Current ceramic materials and systems with clinical recommendations: A systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2007;98(5):389-404.
[2] TAKASHI M, TAKASHI M, HIDEO M, et al. Current status of zirconia restoration. J Prosthodont Res. 2013;57(4):236-261.
[3] 陈春霞,张亚东.氧化锆修复体光学性能的研究进展[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2021,19(4):247-251+232.
[4] SPIES BC, NOLD J, VACH K, et al. Two-piece zirconia oral implants withstand masticatory loads: An investigation in the artificial mouth. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2016;53:1-10.
[5] VANNI L, VALTER S. Low temperature degradation -aging- of zirconia: A critical review of the relevant aspects in dentistry. Dent Mater. 2010; 26(8):807-820.
[6] CALES B, STEFANI Y, LILLEY E. Long-term in vivo and in vitro aging of a zirconia ceramic used in orthopaedy. J Biomed Mater Res. 1994;28(5): 619-624.
[7] GUAZZATO M, ALBAKRY M, RINGER S, et al. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part II. Zirconia-based dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004;20(5):449-56.
[8] SATYAJIT S, SUDIPTA S. Thermodynamic Tetragonal Phase Stability in Sol−Gel Derived Nanodomains of Pure Zirconia. J Phys Chem. 2016; 108(11):3395-3399.
[9] 周珊羽,王琳琳,胡琛,等.齿科氧化锆陶瓷的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2012,6(19):5789-5791.
[10] CHEVALIER J, GREMILLARD L, DEVILLE S. Low-Temperature Degradation of Zirconia and Implications for Biomedical Implants. Annu Rev Mater Res. 2007;37:1-32.
[11] CHEVALIER J, GREMILLARD L. The tetragonal-monoclinic transformation in zirconia: lessons learned and future trends. J Am Ceram Soc. 2009; 92:1901-1920.
[12] 祖宇飞. TiO2掺杂Al2O3-ZrO2复相陶瓷烧结及超塑变形研究[D].大连:大连理工大学,2015.
[13] CHEVALIER J, GREMILLARD L, VIRKAR AV, et al. The tetragonal-monoclinic transformation in zirconia: lessons learned and future trends. J Am Ceram Soc. 2009;92:1901-1920.
[14] CHEVALIER J, CALES B, DROUIN JM. Low-temperature aging of Y -TZP ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc. 1999;82:2150-2154.
[15] CHEVALIER J, GREMILLARD L, DEVILLE S. Low-temperature degradation of zirconia and implications for biomedical implants. Annu Rev Mater Res. 2007;37:1-32.
[16] CHEVALIER J, GREMILLARD L. Ceramics for medical applications: a picture for the next 20 years. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2009;29:1245-1255.
[17] LI JF, WATANABE R. Phase transformation in Y2O3-partially-stabilized ZrO2polycrystals of various grain sizes during low-temperature aging in water. J Am Ceram Soc. 1998;81:2687-2691.
[18] COTIC J, JEVNIKAR P, KOCJAN A, et al. Complexity of the relationships between the sintering-temperature-dependent grain size, airborne-particle abrasion, ageing and strength of 3Y -TZP ceramics. Dent Mater. 2016;32:510-518.
[19] HALLMANN L, MEHL A, ULMER P, et al. The influence of grain size on low-temperature degradation of dental zirconia. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100b:447-456.
[20] TSUBAKINO H, SONODA K, NOZATO R. Martensite-transformation behavior during isothermal aging in partially-stabilized zirconia with and without alumina addition. J Mater Sci Lett. 1993;12:196-198.
[21] PALMERO P, FORNABAIO M, MONTANARO L, et al. Towards long lasting zirconia-based composites for dental implants. Part I: innovative synthesis, microstructural characterization and in vitro stability. Biomaterials. 2015;50:38-46.
[22] ZHANG F, VANMEENSEL K, INOKOSHI M, et al. 3Y -TZP ceramics with improved hydrothermal degradation resistance and fracture toughness. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2014;34:2453-2463.
[23] HALLMANN L, ULMER P, REUSSER E, et al. Effect of dopants and sintering temperature on microstructure and low temperature degradation of dental Y -TZP-zirconia. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2012;32:4091-4104.
[24] CHEVALIER J, GREMILLARD L, VIRKAR AV, et al. The tetragonal-monoclinic transformation in zirconia: lessons learned and future trends. J Am Ceram Soc. 2009;92:1901-1920.
[25] MIRANDA RB, MIRANDA WG, LAZAR DRR, et al. Effect of titania content and biomimetic coating on the mechanical properties of the Y -TZP/TiO2composite. Dent Mater. 2018;34:238-245.
[26] MARCHI J, AMORIM EM, LAZAR DRR, et al. Physico-chemical characterization of zirconia-titania composites coated with an apatite layer for dental implants. Dent Mater. 2013;29:954-962.
[27] HODGSON SNB, CAWLEY J. The effect of titanium oxide additions on the properties and behaviour of Y -TZP. J Mater Process Technol. 2001; 119:112-116.
[28] MIAO X, SUN D, HOO PW, et al. Effect of titania addition on yttria-stabilised tetragonal zirconia ceramics sintered at high temperatures. Ceram Int. 2004;30:1041-1047.
[29] MIYAZAKI T, NAKAMURA T, MATSUMURA H, et al. Current status of zirconia restoration. J Prosthodont Res. 2013;57(4):236-261.
[30] WENG MH, LIN CX, HUANG CS, et al. Improved microstructure and hardness properties of low-temperature microwave-dintered Y2O3 stabilized ZrO2 ceramics with additions of nano TiO2 powders. Mater. 2020;13(7):1546.
[31] PAULA M, RANULFO B, LEITE TP, et al. Effect of titania addition and sintering temperature on the microstructure, optical, mechanical and biological properties of the Y-TZP/TiO2 composite. Dent Mater. 2020;36(11):1418-1429.
[32] DEVILLE S, GREMILLARD L, CHEVALIER J, et al. A critical comparison of methods for the determination of the aging sensitivity in biomedical grade yttria-stabilized zirconia. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2005;72(2):239-245.
[33] CAMPOSILVAN E, MARRO FG, MESTRA A, et al. Enhanced reliability of yttria-stabilized zirconia for dental applications. Acta Biomater. 2015; 17:36-46.
[34] MATSUI K, YOSHIDA H, IKUHARA Y. Nanocrystalline, ultra-degradation-resistant zirconia: its grain boundary nanostructure and nanochemistry. Sci Rep. 2014;4(1):703-704.
[35] Malkin S, Anderson RB. Thermal Aspects of Grinding: Part 1-Energy Partition. J Eng Ind. 1974;96(4):1177.
[36] COSTA HL, PANDOLFELLI VC, MELLO JBD. On the abrasive wear of zirconias. Wear. 1997;203:626-636.
[37] SWAIN MV, HANNINK RHJ. Metastability of the Martensitic Transformation in a 12 mol% Ceria‐Zirconia Alloy: II, Grinding Studies. J Am Ceram Soc. 1989;72(8):1358-1364.
|