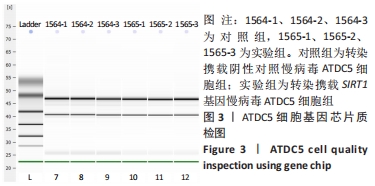
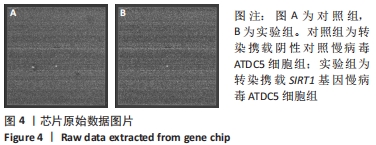
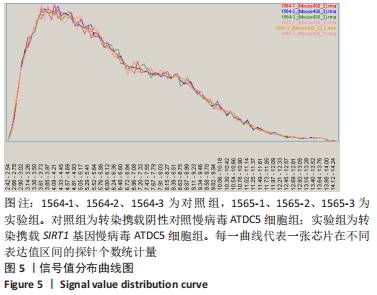
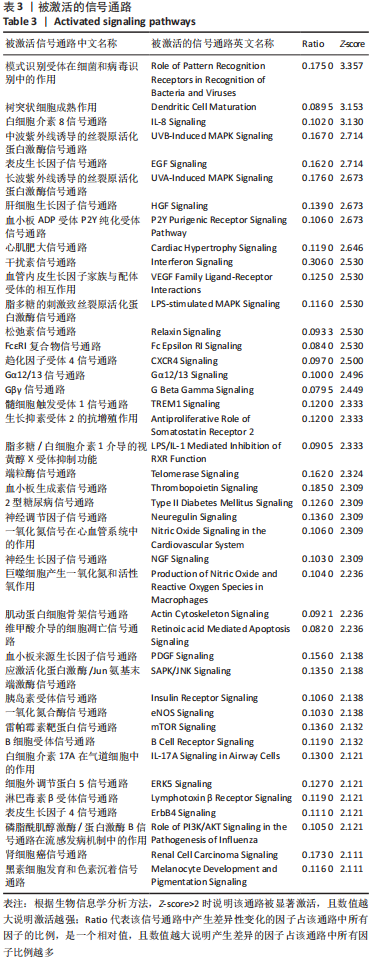
[1] KRYCH AJ, SARIS DBF, STUART MJ, et al. Cartilage Injury in the Knee: Assessment and Treatment Options. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020; 28(22):914-922.
[2] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:33-43.
[3] CORYELL PR, DIEKMAN BO, LOESER RF. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(1):47-57.
[4] CHEN DH, ZHENG G, ZHONG XY, et al. Oroxylin A attenuates osteoarthritis progression by dual inhibition of cell inflammation and hypertrophy. Food Funct. 2021;12(1):328-339.
[5] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452.
[6] YU H, YAO S, ZHOU C, et al. Morroniside attenuates apoptosis and pyroptosis of chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritic development by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;266:113447.
[7] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101249.
[8] TSINGAS M, OTTONE OK, HASEEB A, et al. Sox9 deletion causes severe intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by apoptosis, matrix remodeling, and compartment-specific transcriptomic changes. Matrix Biol. 2020;94:110-133.
[9] WANG J, ROBERTS S, KUIPER JH, et al. Characterization of regional meniscal cell and chondrocyte phenotypes and chondrogenic differentiation with histological analysis in osteoarthritic donor-matched tissues. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21658.
[10] YU F, YUAN Y, LI D, et al. The Effect of Lentivirus-mediated SIRT1 Gene Knockdown in the ATDC5 Cell Line via inhibition of the Wnt Signaling Pathway. Cell Signal. 2019;53:80-89.
[11] 于斐,曾晖,雷鸣,等.SIRT1基因敲除对骨关节炎小鼠VEGF/AKT信号通路的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(1):31-37.
[12] 袁昊,曾晖,肖德明,等.白藜芦醇通过NF-κB信号通路抑制软骨细胞炎症因子的表达[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(1):75-79.
[13] SUN K, LUO J, JING X, et al. Hyperoside ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Phytomedicine. 2021; 80:153387.
[14] ZHANG L, SUI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Knockdown of hsa_circ_0134111 alleviates the symptom of osteoarthritis via sponging microRNA-224-5p. Cell Cycle. 2021;20(11):1052-1066.
[15] DAI J, ZHANG Y, CHEN D, et al. Glabridin inhibits osteoarthritis development by protecting chondrocytes against oxidative stress, apoptosis and promoting mTOR mediated autophagy. Life Sci. 2021; 268:118992.
[16] BATSHON G, ELAYYAN J, QIQ O, et al. Serum NT/CT SIRT1 ratio reflects early osteoarthritis and chondrosenescence. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(10):1370-1380.
[17] DUAN R, XIE H, LIU ZZ. The Role of Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:608388.
[18] WANG FS, KUO CW, KO JY, et al. Irisin Mitigates Oxidative Stress, Chondrocyte Dysfunction and Osteoarthritis Development through Regulating Mitochondrial Integrity and Autophagy. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(9):810.
[19] YAO Y, ZHANG T, CHEN H, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis in a coculture system with genetically manipulated dedifferentiated chondrocytes and ATDC5 cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2020;117(10):3173-3181.
[20] ZHAO J, DUAN L, WANG R, et al. Roflumilast prevents lymphotoxin α (TNF-β)-induced inflammation activation and degradation of type 2 collagen in chondrocytes. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(12):1191-1199.
[21] 于斐,曾晖,翁鉴,等.慢病毒介导SIRT1基因表达降低的ATDC5细胞模型建立[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(2):154-158.
[22] PAN XH, LIN QK, YAO X, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect thymus structure and function in aged C57 mice by downregulating aging-related genes and upregulating autophagy- and anti-oxidative stress-related genes. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(17): 16899-16920.
[23] ZEMEL MB. Modulation of Energy Sensing by Leucine Synergy with Natural Sirtuin Activators: Effects on Health Span. J Med Food. 2020; 23(11):1129-1135.
[24] LUO D, FAN H, MA X, et al. miR-1301-3p Promotes Cell Proliferation and Facilitates Cell Cycle Progression via Targeting SIRT1 in Gastric Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:664242.
[25] CHEN C, ZHOU M, GE Y, et al. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;187:111215.
[26] MA S, FENG J, ZHANG R, et al. SIRT1 Activation by Resveratrol Alleviates Cardiac Dysfunction via Mitochondrial Regulation in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:4602715.
[27] ISIDE C, SCAFURO M, NEBBIOSO A, et al. SIRT1 Activation by Natural Phytochemicals: An Overview. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1225.
[28] ALVES-FERNANDES DK, JASIULIONIS MG. The Role of SIRT1 on DNA Damage Response and Epigenetic Alterations in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3153.
[29] TANG BL. Sirt1 and the Mitochondria. Mol Cells. 2016;39(2):87-95.
[30] SINGH V, UBAID S. Role of Silent Information Regulator 1 (SIRT1) in Regulating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Inflammation. 2020; 43(5):1589-1598.
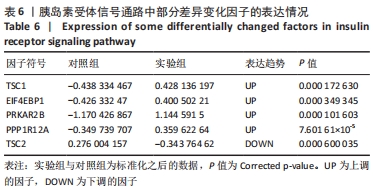
[31] YU F, ZENG H, LEI M, et al. Effects of SIRT1 Gene Knock-Out via the Activation of SREBP2 Protein Mediated PI3K/AKT Signal Pathway on Osteoarthritis in Mice. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016; 36(5):683-690.
[32] YU F, LI M, YUAN Z, et al. Mechanism Research on a Bioactive Resveratrol-PLA-Gelatin Porous Nano-scaffold in Promoting the Repair of Cartilage Defect. Int J Nanomed. 2018;13:7845-7858.
[33] 刘玉峰, 许肈初, 马海燕. 基因芯片技术在中药现代化研究中的应用进展[J]. 辽宁大学学报(自然科学版),2021,48(3):254-262.
[34] YIN G, BIE S, GU H, et al. Application of gene chip technology in the diagnostic and drug resistance detection of Helicobacter pylori in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;35(8):1331-1339.
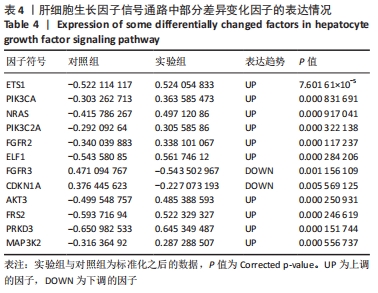
[35] TONOMURA H, NAGAE M, TAKATORI R, et al. The Potential Role of Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Degenerative Disorders of the Synovial Joint and Spine. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8717.
[36] SAHU N, AGARWAL P, GRANDI F, et al. Encapsulated Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Microbeads Promote Endogenous Regeneration of Osteoarthritic Cartilage Ex Vivo. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(8): e2002118.
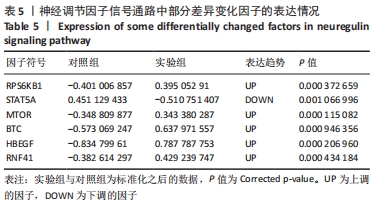
[37] SHI L, XU X, MENG B, et al. Neuregulin 4 Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression by Inhibiting Inflammation and Apoptosis of Chondrocytes in Mice. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021.doi: 10.1007/s00223-021-00897-2.
[38] CINQUE L, DE LEONIBUS C, IAVAZZO M, et al. MiT/TFE factors control ER-phagy via transcriptional regulation of FAM134B. EMBO J. 2020; 39(17):e105696.
[39] HALLETT SA, ONO W, ONO N. The hypertrophic chondrocyte: To be or not to be. Histol Histopathol. 2021;18355.
[40] KUMAR A, PALIT P, THOMAS S, et al. Osteoarthritis: Prognosis and emerging therapeutic approach for disease management. Drug Dev Res. 2021;82(1):49-58.
[41] GALDERISI S, CICALONI V, MILELLA MS, et al. Homogentisic acid induces cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix alteration in alkaptonuric cartilage.J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(8):6011-6024.
[42] LEE W, NIMS RJ, SAVADIPOUR A, et al. Inflammatory signaling sensitizes Piezo1 mechanotransduction in articular chondrocytes as a pathogenic feed-forward mechanism in osteoarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(13):e2001611118.
[43] DING C, ZOU Q, WANG F, et al. HGF and BFGF Secretion by Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Improves Ovarian Function During Natural Aging via Activation of the SIRT1/FOXO1 Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(4):1316-1332.
[44] GU A, JIE Y, SUN L, et al. RhNRG-1β Protects the Myocardium against Irradiation-Induced Damage via the ErbB2-ERK-SIRT1 Signaling Pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0137337.
[45] CHEN CC, KUO CH, LEU YL, et al. Corylin reduces obesity and insulin resistance and promotes adipose tissue browning through SIRT-1 and β3-AR activation. Pharmacol Res. 2021;164:105291.
[46] HESHMATI M, SOLTANI A, SANAEI MJ, et al. Ghrelin induces autophagy and CXCR4 expression via the SIRT1/AMPK axis in lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Cell Signal. 2020; 66:109492.
[47] MOTONISHI S, NANGAKU M, WADA T, et al. Sirtuin1 Maintains Actin Cytoskeleton by Deacetylation of Cortactin in Injured Podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26(8):1939-1959.
|