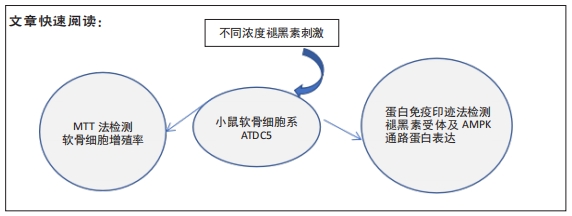
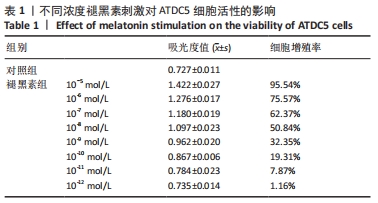
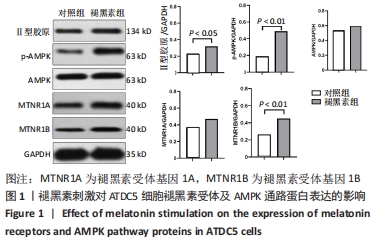
[1] ATSUMI T, MIWA Y, KIMATA K, et al. A chondrogenic cell line derived from a differentiating culture of at805 teratocarcinoma cells. Cell Differ Dev. 1990;30(2):109-116.
[2] YAO Y, WANG Y. Atdc5: An excellent in vitro model cell line for skeletal development. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(6):1223-1229.
[3] LI Q, XING W, XU X, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced damage in atdc5 cells via down-regulating myd88. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;111:104317.
[4] YIM APY, YEUNG HY, HUNG VWY, et al. Abnormal skeletal growth patterns in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis--a longitudinal study until skeletal maturity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(18):E1148-E1154.
[5] CHEUNG PWH, MANNEM A, CHEUNG JPY. Prediction of final body height for female patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Global Spine J. 2021;11(6):833-844.
[6] YAN Y, ZHOU XE, XU HE, et al. Structure and physiological regulation of ampk. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3534.
[7] TRAN QH, HOANG DH, SONG M, et al. Melatonin and doxorubicin synergistically enhance apoptosis via autophagy-dependent reduction of ampkα1 transcription in human breast cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(9):1413-1422.
[8] YU LM, DONG X, XUE XD, et al. Melatonin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy and reduces myocardial vulnerability to ischemia-reperfusion injury by improving mitochondrial quality control: Role of sirt6. J Pineal Res. 2021;70(1):e12698.
[9] ZHONG J, TAN Y, LU J, et al. Therapeutic contribution of melatonin to the treatment of septic cardiomyopathy: A novel mechanism linking ripk3-modified mitochondrial performance and endoplasmic reticulum function. Redox Biol. 2019;26:101287.
[10] MA F, HAO H, GAO X, et al. Melatonin ameliorates necrotizing enterocolitis by preventing th17/treg imbalance through activation of the ampk/sirt1 pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(17):7730-7746.
[11] PARK JH, SEO I, SHIM HM, et al. Melatonin ameliorates sglt2 inhibitor-induced diabetic ketoacidosis by inhibiting lipolysis and hepatic ketogenesis in type 2 diabetic mice. J Pineal Res. 2020;68(2):e12623.
[12] 赵菁,虞锡丹,徐纯鑫,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的国内外治疗现状[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2018,38(3):203-205.
[13] 朱泽章.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因学研究进展[J].医学研究生学报, 2016,29(2):126-132.
[14] THILLARD MJ. Vertebral column deformities following epiphysectomy in the chick. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959;248(8):1238-1240.
[15] MACHIDA M, DUBOUSSET J, IMAMURA Y, et al. An experimental study in chickens for the pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(12):1609-1615.
[16] MACHIDA M, DUBOUSSET J, IMAMURA Y, et al. Role of melatonin deficiency in the development of scoliosis in pinealectomised chickens. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(1):134-138.
[17] MACHIDA M, DUBOUSSET J, SATOH T, et al. Pathologic mechanism of experimental scoliosis in pinealectomized chickens. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(17):E385-E391.
[18] 韩啸.不同剂量褪黑素对双足直立鼠脊柱侧凸发生率的影响及脊柱侧凸临床治疗相关研究[D].南京:南京大学,2016.
[19] 吴涛,刘军,沈一燚,等.中枢高瘦素水平对低褪黑素双足直立鼠模型脊柱侧凸作用相关研究[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2013,33(6): 784-787.
[20] 朱锋,邱勇,张兴,等.褪黑素信号通路对青少年特发性脊柱侧凸软骨细胞增殖的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(2):156-160.
[21] LIU J, CLOUGH SJ, HUTCHINSON AJ, et al. Mt1 and mt2 melatonin receptors: A therapeutic perspective. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016;56:361-383.
[22] YANG M, WEI X, YANG W, et al. The polymorphisms of melatonin receptor 1b gene (mtnr1b) (rs4753426 and rs10830963) and susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A meta-analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(4):593-600.
[23] 邱旭升,邓亮生,杨晓恩,等.褪黑素受体1a基因多态性与青少年特发性脊柱侧凸相关性研究[J].中华外科杂志,2007,45(18):1264-1266.
[24] NELSON LM, WARD K, OGILVIE JW. Genetic variants in melatonin synthesis and signaling pathway are not associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(1):37-40.
|