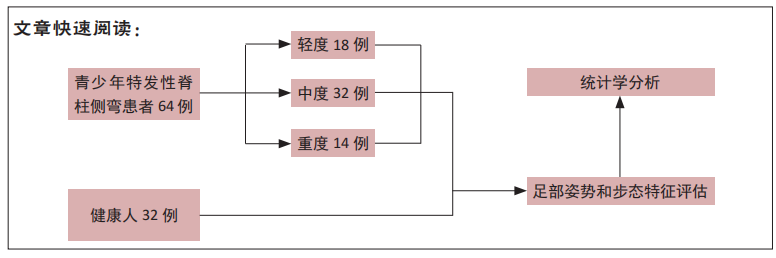
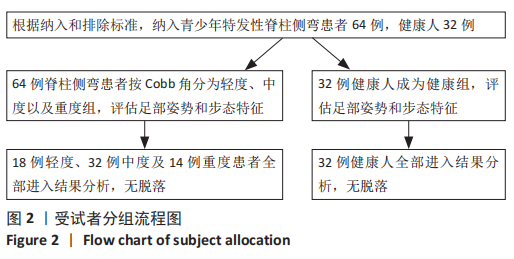
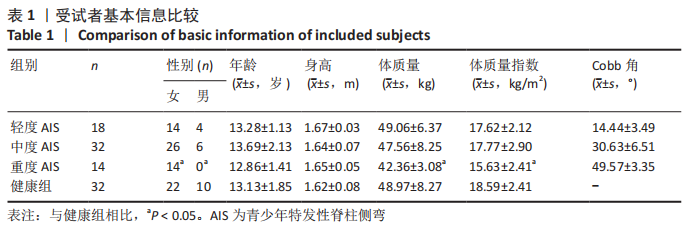
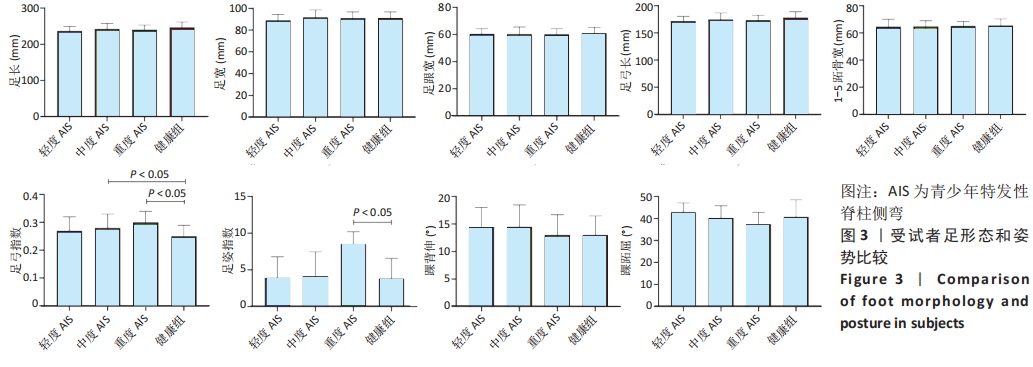
[1] ADDAI D, ZARKOS J, BOWEY AJ. Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020;36(6):1111-1119.
[2] PENG Y, WANG SR, QIU GX, et al. Research progress on the etiology and pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(4):483-493.
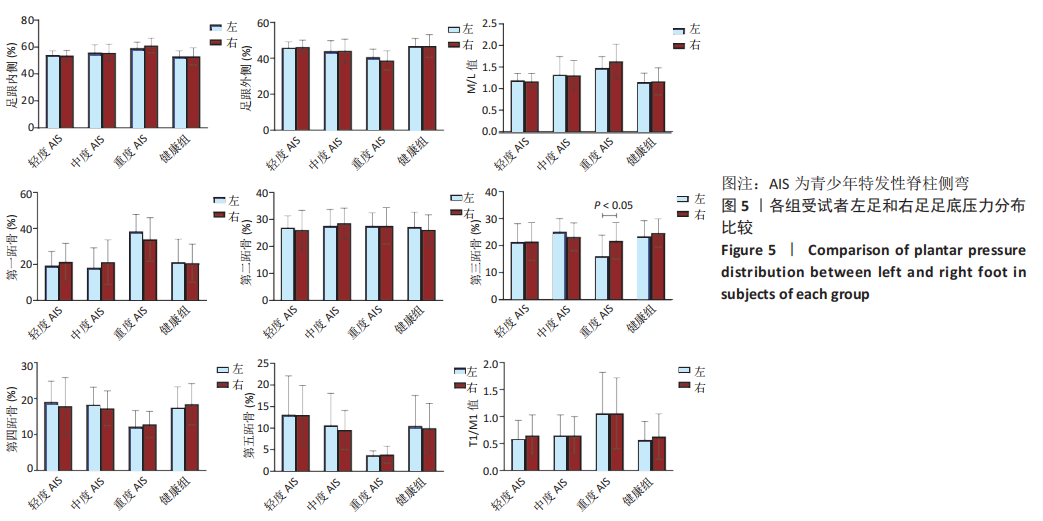
[3] 陈梦婕,罗义,马琪超,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧弯的冠状位平衡与足底压力的相关性 [J].中华全科医学,2020,18(4):542-546.
[4] KUZNIA AL, HERNANDEZ AK, LEE LU. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: common questions and answers. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(1): 19-23.
[5] WU KW, WANG TM, HU CC, et al. Postural adjustments in adolescent idiopathic thoracic scoliosis during walking. Gait Posture. 2019;68: 423-429.
[6] 游国鹏,杜青,陈楠,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者步态运动学及足底压力特征分析[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(7): 537-541.
[7] ZHANG H, GUO Y, ZANOTTO D. Accurate ambulatory gait analysis in walking and running using machine learning models. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2020;28(1):191-202.
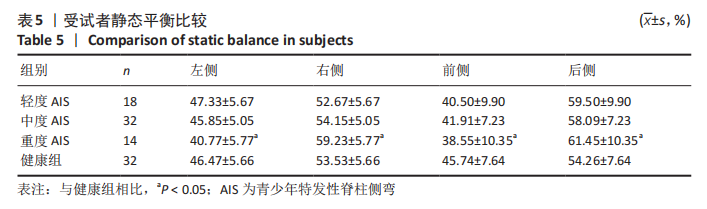
[8] 李省华,王连成,申慧圆.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸48例患者的静态平衡能力研究[J].医学综述,2019,25(14):2897-2902.
[9] 成西侠,徐超,白建萍.青少年脊柱侧弯患者足底压力分析[J].当代临床医刊,2018,31(4):3925-3926.
[10] 韩秀兰,许轶,李小金,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧弯症患者的足底压力差异分析及穿戴矫形鞋垫的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2017,38(4):582-589.
[11] 周璇,杜青,赵黎,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸患者的静态平衡功能研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(10):953-956.
[12] MA Q, LIN H, WANG L, et al. Correlation between spinal coronal balance and static baropodometry in children with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Gait Posture. 2020;75:93-97.
[13] CATAN L, CERBU S, AMARICAI E, et al. Assessment of static plantar pressure, stabilometry, vitamin d and bone mineral density in female adolescents with moderate idiopathic scoliosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(6):2167.
[14] WIERNICKA M, KOTWICKI T, KAMINSKA E, et al. Postural Stability in Adolescent Girls with Progressive Idiopathic Scoliosis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:7103546.
[15] KIM K, MULLINEAUX DR, JEON K. A comparative study of spinal deformity and plantar pressure according to the static standing posture of female adolescents with or without idiopathic scoliosis. Iran J Public Health. 2019;48(2):345-346.
[16] LEE, JEONG UK. Comparison of dynamic plantar foot pressure in normal subjects and patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis for health science research. Toxicol Environ Health Ences. 2017;9(5):269-278.
[17] DARYABOR A, ARAZPOUR M, SHARIFI G, et al. Gait and energy consumption in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a literature review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2017;60(2):107-116.
[18] LEE J, KIM M, KIM J. Comparison of static plantar foot pressure between healthy subjects and patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Toxicol Environ Health Sci. 2014;6(2):127-132.
[19] CHERN JS, KAO CC, LAI PL, et al. Severity of spine malalignment on center of pressure progression during level walking in subjects with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:5888-5891.
[20] YANG JH, SUH SW, SUNG PS, et al. Asymmetrical gait in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(11):2407-2413.
[21] MAHAUDENS P, BANSE X, MOUSNY M, et al. Gait in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: kinematics and electromyographic analysis. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(4):512-521.
[22] KRAMERS-QUERVAIN IA, MULLER R, STACOFF A, et al. Gait analysis in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2004;13(5):449-456.
[23] WOZNIACKA R, OLEKSY L, JANKOWICZ-SZYMANSKA A, et al. The association between high-arched feet, plantar pressure distribution and body posture in young women. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17187.
[24] Horne JP, Flannery R, Usman S. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2014;89(3):193-198.
[25] FORCE-USPST, GROSSMAN DC, CURRY SJ, et al. Screening for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;319(2):165-172.
[26] ALTAF F, GIBSON A, DANNAWI Z, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. BMJ. 2013;346:f2508.
[27] CHO Y, PARK JW, NAM K. The relationship between foot posture index and resting calcaneal stance position in elementary school students. Gait Posture. 2019;74:142-147.
[28] REDMOND AC, CRANE YZ, MENZ HB. Normative values for the Foot Posture Index. J Foot Ankle Res. 2008;1(1):6.
[29] CAVANAGH PR, RODGERS MM. The arch index: a useful measure from footprints. J Biomech. 1987;20(5):547-551.
[30] GIJON-NOGUERON G, MARCHENA-RODRIGUEZ A, MONTES-ALGUACIL J, et al. Evaluation of the paediatric foot using footprints and foot posture index: a cross-sectional study. J Paediatr Child Health. 2020;56(2): 201-206.
[31] HABER CK, SACCO M. Scoliosis: lower limb asymmetries during the gait cycle. Arch Physiother. 2015;8(5):4.
[32] YAZDANI S, FARAHPOUR N, HABIBI M, et al. Spatiotemporal Variables of Gait in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Healthy Individuals. J Sport Biomech. 2016;2(3):5-14.
[33] HAGEDORN TJ, DUFOUR AB, RISKOWSKI JL, et al. Foot disorders, foot posture, and foot function: the Framingham foot study. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74364.
[34] BULDT AK, ALLAN JJ, LANDORF KB, et al. The relationship between foot posture and plantar pressure during walking in adults: a systematic review. Gait Posture. 2018;62:56-67.
[35] HERONEMUS MJ, RABE K, TOLSTYKH I, et al. The association of parity with greater dynamic pronation of the feet. PM R. 2021;13(2):144-152.
[36] JANDOVA S, GAJDOS M, URBANOVA K, et al. Temporal and dynamic changes in plantar pressure distribution, as well as in posture during slow walking in flat and high-heel shoes. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2019; 21(4):131-138.
[37] GIMUNOVA M, ZVONAR M, MIKESKA O. The effect of aging and gender on plantar pressure distribution during the gait in elderly. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2018;20(4):139-144.
(责任编辑:WJ,ZN,ZH)
|