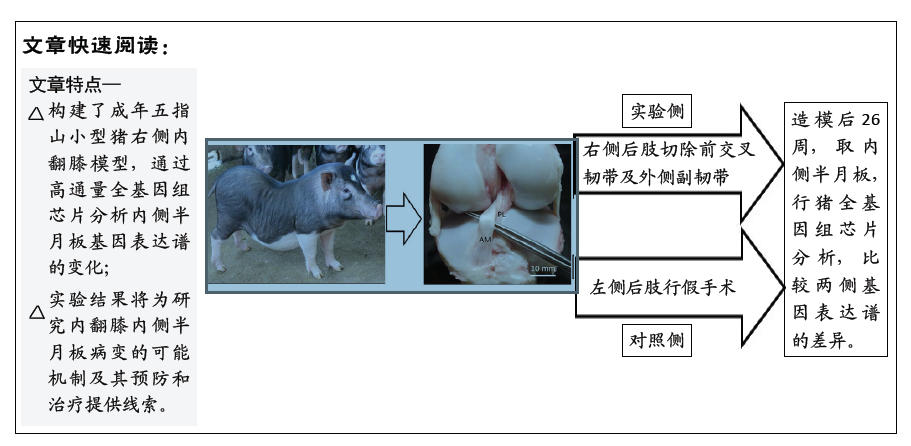
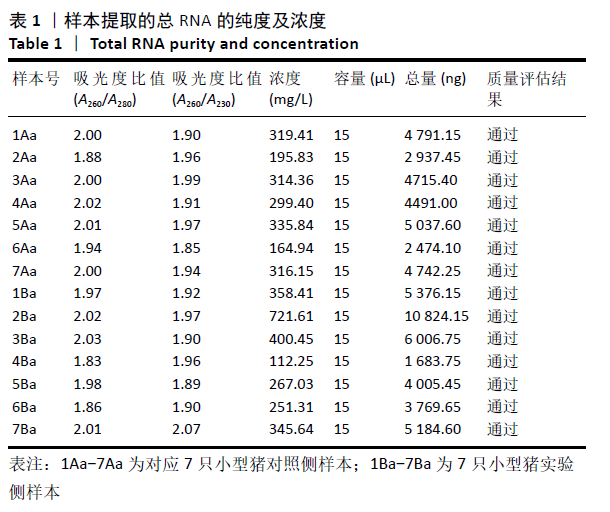
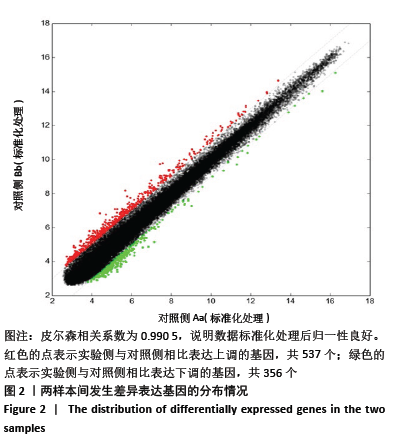
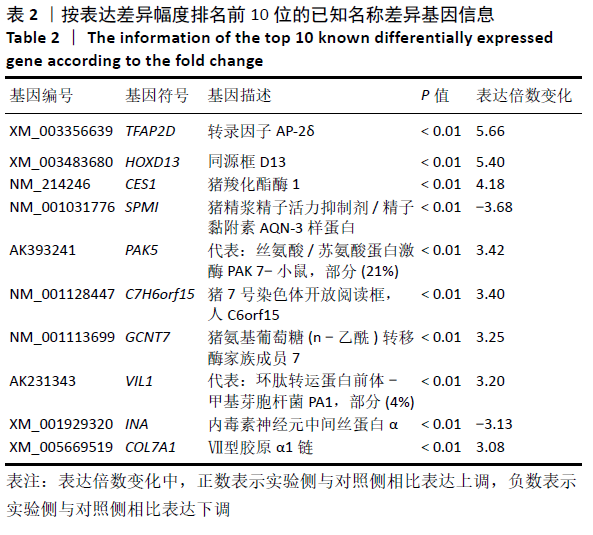
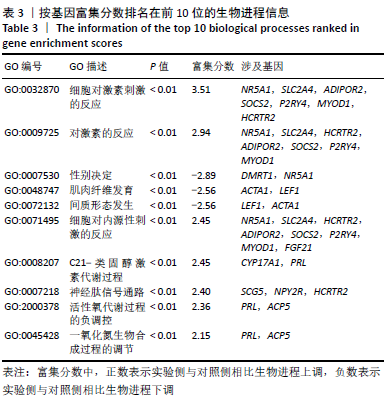
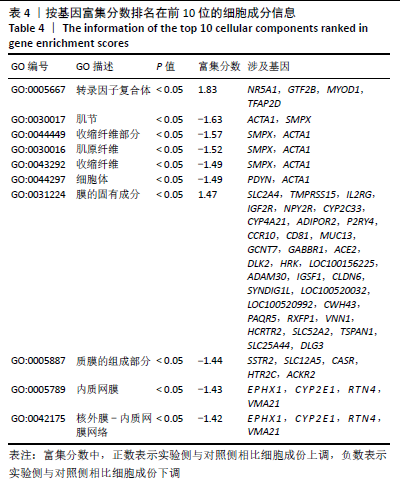
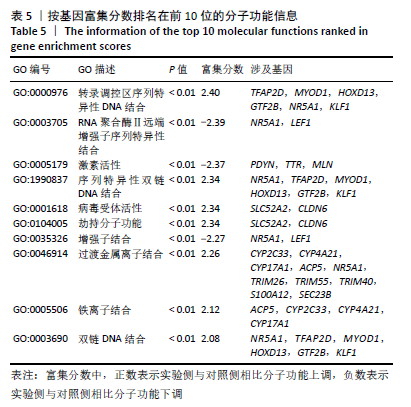
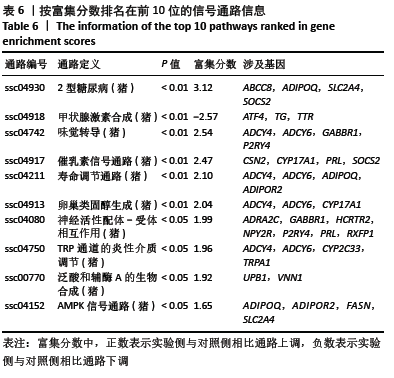
[1] DUBUC J, GIRARD C, RICHARD H, et al. Equine meniscal degeneration is associated with medial femorotibial osteoarthritis. Equine Vet J. 2018;50(1):133-140.
[2] RIBITSCH I, PEHAM C, ADE N, et al. Structure-Function relationships of equine menisci. PLoS One. 20189;13(3):e0194052.
[3] IIJIMA H, AOYAMA T, ITO A, et al. Destabilization of the medial meniscus leads to subchondral bone defects and site-specific cartilage degeneration in an experimental rat model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(7):1036-1043.
[4] FISCHENICH KM, LEWIS J, KINDSFATER KA, et al. Effects of degeneration on the compressive and tensile properties of human meniscus. J Biomech. 2015;48(8):1407-1411.
[5] BENDELE AM. Animal models of osteoarthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2001;1(4):363-376.
[6] SUN Y, MAUERHAN DR, STEUERWALD NM, et al. Expression of phosphocitrate-targeted genes in osteoarthritis menisci. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:210469.
[7] CHEUNG HS, SALLIS JD, DEMADIS KD, et al. Phosphocitrate blocks calcification-induced articular joint degeneration in a guinea pig model. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(8):2452-2461.
[8] KREINEST M, REISIG G, STRÖBEL P, et al. A Porcine Animal Model for Early Meniscal Degeneration - Analysis of Histology, Gene Expression and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Six Months after Resection of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0159331.
[9] ZHANG R, FANG H, CHEN Y, et al. Gene expression analyses of subchondral bone in early experimental osteoarthritis by microarray. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32356.
[10] GOTTERBARM T, BREUSCH SJ, SCHNEIDER U, et al. The minipig model for experimental chondral and osteochondral defect repair in tissue engineering: retrospective analysis of 180 defects. Lab Anim. 2008;42(1):71-82.
[11] BOLLEN P, ELLEGAARD L. The Göttingen minipig in pharmacology and toxicology. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1997;80 Suppl 2:3-4.
[12] ASPDEN RM, YARKER YE, HUKINS DW. Collagen orientations in the meniscus of the knee joint. J Anat. 1985;140(Pt 3):371-380.
[13] PAPAGEORGIOU CD, GIL JE, KANAMORI A, et al. The biomechanical interdependence between the anterior cruciate ligament replacement graft and the medial meniscus. Am J Sports Med. 2001;29(2):226-231.
[14] KILLIAN ML, ZIELINSKA B, GUPTA T, et al. In vitro inhibition of compression-induced catabolic gene expression in meniscal explants following treatment with IL-1 receptor antagonist. J Orthop Sci. 2011; 16(2):212-220.
[15] SHEN C, YAN J, ERKOCAK OF, et al. Nitric oxide inhibits autophagy via suppression of JNK in meniscal cells. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53(6):1022-1033.
[16] TAKAHASHI K, HASHIMOTO S, KUBO T, et al. Hyaluronan suppressed nitric oxide production in the meniscus and synovium of rabbit osteoarthritis model. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(3):500-503.
[17] HÄFELEIN K, PREUßE-PRANGE A, BEHRENDT P, et al. Selenium Reduces Early Signs of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-Induced Meniscal Tissue Degradation. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017;177(1):80-89.
[18] BEHRENDT P, HÄFELEIN K, PREUSSE-PRANGE A, et al. IL-10 ameliorates TNF-α induced meniscus degeneration in mature meniscal tissue in vitro. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):197.
[19] CHOI CJ, CHOI YJ, SONG IB, et al. Characteristics of radial tears in the posterior horn of the medial meniscus compared to horizontal tears. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(2):128-132.
[20] ZHANG F, KUMM J, SVENSSON F, et al. Risk factors for meniscal body extrusion on MRI in subjects free of radiographic knee osteoarthritis: longitudinal data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(5):801-806.
[21] LANGE AK, FIATARONE SINGH MA, et al. Degenerative meniscus tears and mobility impairment in women with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(6):701-708.
[22] ŚLIWIŃSKI L, CEGIEŁA U, PYTLIK M, et al. Effects of fenoterol on the skeletal system depend on the androgen level. Pharmacol Rep. 2017;69(2):260-267.
[23] MOBLEY CB, MUMFORD PW, KEPHART WC, et al. Effects of testosterone treatment on markers of skeletal muscle ribosome biogenesis. Andrologia. 2016;48(9):967-977.
[24] PAULI C, GROGAN SP, PATIL S, et al. Macroscopic and histopathologic analysis of human knee menisci in aging and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(9):1132-1141.
[25] DU G, ZHAN H, DING D, et al. Abnormal Mechanical Loading Induces Cartilage Degeneration by Accelerating Meniscus Hypertrophy and Mineralization After ACL Injuries In Vivo. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(3):652-663.
[26] SUN Y, ROBERTS A, MAUERHAN DR, et al. Biological activities of phosphocitrate: a potential meniscal protective agent. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:726581.
[27] CAMACHO A, SIMÃO M, EA HK, et al. Iron overload in a murine model of hereditary hemochromatosis is associated with accelerated progression of osteoarthritis under mechanical stress. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(3):494-502.
[28] KATSURAGAWA Y, SAITOH K, TANAKA N, et al. Changes of human menisci in osteoarthritic knee joints. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(9):1133-1143.
[29] NEUMANN J, GUIMARAES JB, HEILMEIER U, et al. Diabetics show accelerated progression of knee cartilage and meniscal lesions: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Skeletal Radiol. 2019;48(6):919-930.
[30] HENNERBICHLER A, MOUTOS FT, HENNERBICHLER D, et al. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit repair of the porcine meniscus in vitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(9):1053-1060.
[31] STONE AV, LOESER RF, VANDERMAN KS, et al. Pro-inflammatory stimulation of meniscus cells increases production of matrix metalloproteinases and additional catabolic factors involved in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(2): 264-274.
[32] COOK AE, COOK JL, STOKER AM. Metabolic Responses of Meniscus to IL-1β. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(9):834-840.
[33] AOKI T, CHONG LC, TAKATA K, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Disease-Defining T-cell Subsets in the Tumor Microenvironment of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(3):406-421.
|