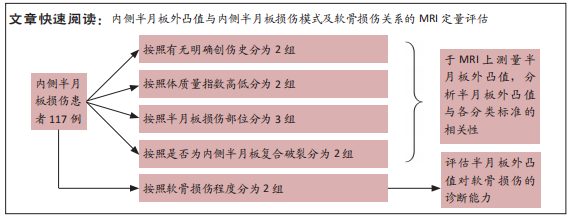
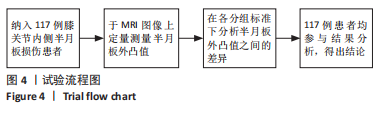
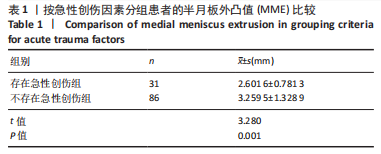
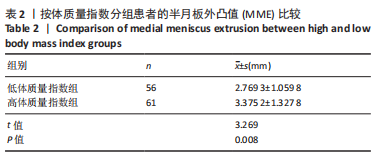
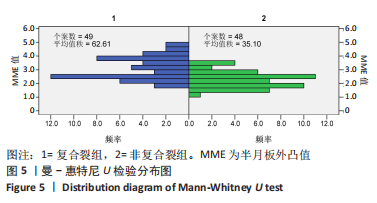
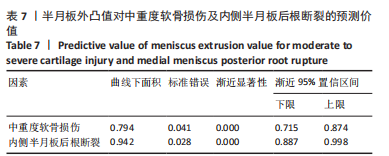
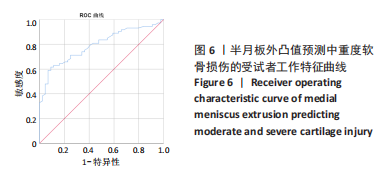
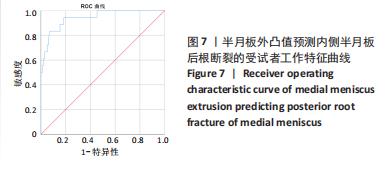
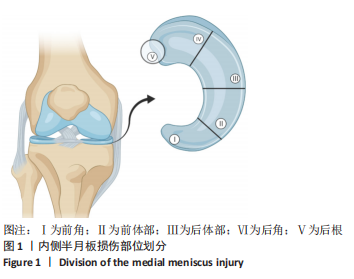
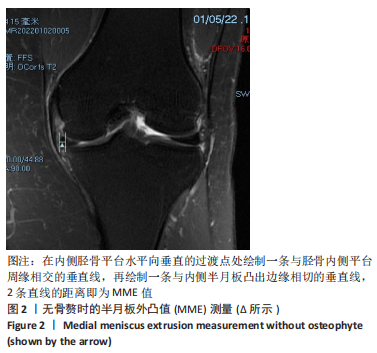
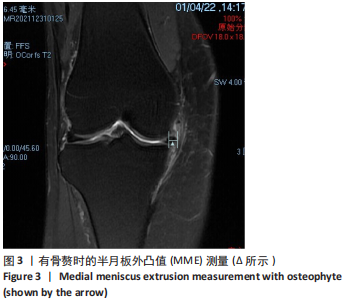
[1] THOMPSON WO, THAETE FL, FU FH, et al. Tibial meniscal dynamics using three-dimensional reconstruction of magnetic resonance images. Am J Sports Med. 1991;19(3):210-215; discussion 215-216.
[2] DASZKIEWICZ K, LUCZKIEWICZ P. Biomechanics of the medial meniscus in the osteoarthritic knee joint. Peer J. 2021;9:27.
[3] NHA KW, LEE YS, HWANG DH, et al. Second-Look Arthroscopic Findings After Open-Wedge High Tibia Osteotomy Focusing on the Posterior Root Tears of the Medial Meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(2):226-231.
[4] LEAFBLAD ND, SMITH PA, STUART MJ, et al. Arthroscopic Centralization of the Extruded Medial Meniscus. Arthrosc Tech. 2021;10(1):e43-e48.
[5] SHARIF B, ASHRAF T, SAIFUDDIN A. Magnetic resonance imaging of the meniscal roots. Skeletal Radiol. 2020;49(5):661-676.
[6] KRYCH AJ, HEVESI M, LELAND DP, et al. Meniscal Root Injuries. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(12):491-499.
[7] BHATIA S, LAPRADE CM, ELLMAN MB, et al. Meniscal Root Tears Significance, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(12): 3016-3030.
[8] SWAMY N, WADHWA V, BAJAJ G, et al. Medial meniscal extrusion: Detection, evaluation and clinical implications. Eur J Radiol. 2018;102: 115-124.
[9] OZEKI N, SEIL R, KRYCH AJ, et al. Surgical treatment of complex meniscus tear and disease: state of the art. J ISAKOS. 2021;6(1):35-45.
[10] FUJISAWA T, CHOE H, KUSABA Y, et al. Medial meniscus extrusion and stage are related to the size of spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee in patients who underwent high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2022;36:72-79.
[11] 江佩师, 陈志伟, 方玉基, 等. 602例膝关节半月板损伤流行病学调查[J]. 中南医学科学杂志,2020,48(2):160-163.
[12] GUILAK F, RATCLIFFE A, LANE N, et al. Mechanical and biochemical changes in the superficial zone of articular cartilage in canine experimental osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1994;12(4):474-484.
[13] BRUNS K, SVENSSON F, TURKIEWICZ A, et al. Meniscus body position and its change over four years in asymptomatic adults: a cohort study using data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI). BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:32.
[14] STENSBY JD, PRINGLE LC, CRIM J. MRI of the Meniscus. Clin in Sports Med. 2021;40(4):641-655.
[15] HISASHI K, MUNETA T, KOHNO Y, et al. MRI study of medial meniscus degeneration of osteoarthritic knees with or without posterior root tear. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):38.
[16] HAJEK PC, GYLYS-MORIN VM, BAKER LL, et al. The high signal intensity meniscus of the knee. Magnetic resonance evaluation and in vivo correlation. Invest Radiol. 1987;22(11):883-890.
[17] ISHII Y, ISHIKAWA M, HAYASHI S, et al. The correlation between osteoarthritis stage and the effect of the lateral wedge insole for 3 months on medial meniscus extrusion in the knee joint. Knee. 2021; 28:110-116.
[18] COSTA CR, MORRISON WB, CARRINO JA. Medial meniscus extrusion on knee MRI: Is extent associated with severity of degeneration or type of tear? Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(1):17-23.
[19] KOZAKI T, FUKUI D, YAMAMOTO E, et al. Medial meniscus extrusion and varus tilt of joint line convergence angle increase stress in the medial compartment of the knee joint in the knee extension position -finite element analysis. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):49.
[20] ZHANG F, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA SM, OEI EHG, et al. Factors associated with meniscal body extrusion on knee MRI in overweight and obese women. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(5):694-699.
[21] MUNUGODA IP, BEAVERS DP, WIRTH W, et al. The effect of weight loss on the progression of meniscal extrusion and size in knee osteoarthritis: a post-hoc analysis of the Intensive Diet and Exercise for Arthritis (IDEA) trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4):410-417.
[22] SHARMA K, ECKSTEIN F, WIRTH W, et al. Meniscus position and size in knees with versus without structural knee osteoarthritis progression - data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019; 27:S467-S468.
[23] KIM C, BIN SI, LEE BS, et al. Volumetric assessment of extrusion in medial meniscus posterior root tears through semi-automatic segmentation on 3-tesla magnetic resonance images. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2020;106(5):963-968.
[24] CHIBA D, SASAKI T, ISHIBASHI Y. Greater medial meniscus extrusion seen on ultrasonography indicates the risk of MRI-detected complete medial meniscus posterior root tear in a Japanese population with knee pain. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):4756.
[25] KRYCH AJ, BERNARD CD, LELAND DP, et al. Isolated meniscus extrusion associated with meniscotibial ligament abnormality. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(11):3599-3605.
[26] KOGA H, NAKAMURA T, NAKAGAWA Y, et al. Arthroscopic Centralization Using Knotless Anchors for Extruded Medial Meniscus. Arthrosc Tech. 2021;10(3):e639-e645.
[27] CHERNCHUJIT B, AGRAWAL S. Arthroscopic All-Inside Medial Meniscus Extrusion Reduction. Arthrosc Tech. 2019;8(5):e495-e501.
[28] HIRANAKA T, FURUMATSU T, MIYAZAWA S, et al. Transtibial pullout repair techniques using two simple stitches for medial meniscus posterior root tear can prevent the progression of medial meniscus extrusion and obtain successful outcomes. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022;32(5):795-802.
[29] WU TY. Arthroscopic Medial Meniscus Posterior Root Repair with Centralization Using Knotless Suture Anchors. Arthrosc Tech. 2022; 11(4):e661-e668.
[30] CLIFTON WILLIMON S, BUSCH MT, MURATA A, et al. Transosseous Meniscus Root Repair in Pediatric Patients and Association With Durable Midterm Outcomes and High Rates of Return to Sports. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(8):2070-2074.
[31] CHUNG KS, HA JK, RA HJ, et al. Preoperative varus alignment and postoperative meniscus extrusion are the main long-term predictive factors of clinical failure of meniscal root repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(12):4122-4130. |