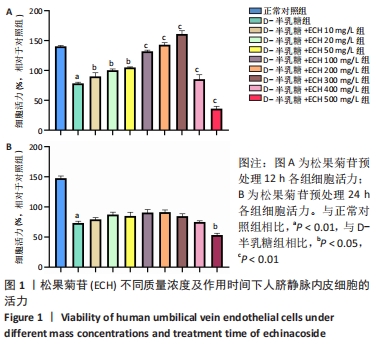
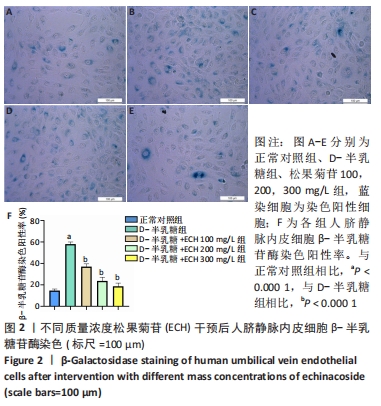
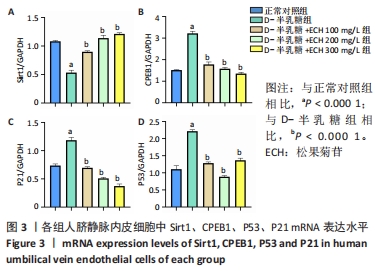
[1] SHEN CY, JIANG JG, YANG L, et al. Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals used in traditional Chinese medicine: pharmacological mechanisms and implications for drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(11):1395-1425.
[2] NORTH BJ, SINCLAIR DA. The intersection between aging and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2012;110(8):1097-1108.
[3] VAN DEURSEN JM. The role of senescent cells in ageing. Nature. 2014; 509(7501):439-446.
[4] BRUN C, JEAN-LOUIS F, ODDOS T, et al. Phenotypic and functional changes in dermal primary fibroblasts isolated from intrinsically aged human skin. Exp Dermatol. 2016;25(2):113-119.
[5] JOHMURA Y, NAKANISHI M. Multiple facets of p53 in senescence induction and maintenance. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(11):1550-1555.
[6] ZHANG R, ADAMS PD. Heterochromatin and its relationship to cell senescence and cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(7):784-789.
[7] ALIPIEVA K, KORKINA L, ORHAN IE, et al. Verbascoside--a review of its occurrence, (bio)synthesis and pharmacological significance. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(6):1065-1076.
[8] WU L, GEORGIEV MI, CAO H, et al. Therapeutic potential of phenylethanoid glycosides: A systematic review. Med Res Rev. 2020; 40(6):2605-2649.
[9] LIU J, YANG L, DONG Y, et al. Echinacoside, an Inestimable Natural Product in Treatment of Neurological and other Disorders. Molecules. 2018;23(5):1213.
[10] WANG N, JI S, ZHANG H, et al. Herba Cistanches: Anti-aging. Aging Dis. 2017;8(6):740-759.
[11] 李欢,宋安齐,薛嘉虹,等.松果菊苷对血管内皮细胞损伤的保护作用[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2013,34(3):387-392.
[12] DONATO AJ, MORGAN RG, WALKER AE, et al. Cellular and molecular biology of aging endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;89(Pt B): 122-135.
[13] LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO MA, PARTRIDGE L, et al. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013;153(6):1194-1217.
[14] 庞明,刘展,李韶山,等.同型半胱氨酸对血管内皮细胞衰老的影响[J].新疆医学,2020,50(7):670-674.
[15] LAMICHANE S, BAEK SH, KIM YJ, et al. MHY2233 Attenuates Replicative Cellular Senescence in Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells via SIRT1 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:6492029.
[16] PANG J, XIONG H, OU Y, et al. SIRT1 protects cochlear hair cell and delays age-related hearing loss via autophagy. Neurobiol Aging. 2019; 80:127-137.
[17] XIE L, HUANG R, LIU S, et al. A positive feedback loop of SIRT1 and miR17HG promotes the repair of DNA double-stranded breaks. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(17):2110-2123.
[18] NAKAGAWA T, GUARENTE L. SnapShot: sirtuins, NAD, and aging. Cell Metab. 2014;20(1):192.
[19] KASZUBOWSKA L, FOERSTER J, KWIATKOWSKI P, et al. NKT-like cells reveal higher than T lymphocytes expression of cellular protective proteins HSP70 and SOD2 and comparably increased expression of SIRT1 in the oldest seniors. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2018;56(4):231-240.
[20] GUO Y, XING L, QIAN C, et al. Involvement of Flavonoids from the Leaves of Carya cathayensis Sarg. in Sirtuin 1 Expression in HUVEC Senescence. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:8246560.
[21] SHEN P, DENG X, CHEN Z, et al. SIRT1: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;12:779177.
[22] FANG Y, WANG X, YANG D, et al. Relieving Cellular Energy Stress in Aging, Neurodegenerative, and Metabolic Diseases, SIRT1 as a Therapeutic and Promising Node. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13: 738686.
[23] YAO H, RAHMAN I. Perspectives on translational and therapeutic aspects of SIRT1 in inflammaging and senescence. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84(10):1332-1339.
[24] RAMIS MR, ESTEBAN S, MIRALLES A, et al. Caloric restriction, resveratrol and melatonin: Role of SIRT1 and implications for aging and related-diseases. Mech Ageing Dev. 2015;146-148:28-41.
[25] MAEDA M, TSUBOI T, HAYASHI T. An Inhibitor of Activated Blood Coagulation Factor X Shows Anti-Endothelial Senescence and Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects. J Vasc Res. 2019;56:181-190.
[26] WARBOYS CM, DE LUCA A, AMINI N, et al. Disturbed flow promotes endothelial senescence via a p53-dependent pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:985-995.
[27] BIAN W, JING X, SUN Y, et al. Downregulation of LncRNA NORAD promotes Ox-LDL-induced vascular endothelial cell injury and atherosclerosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(7):6385-6400.
[28] RYAN KM, PHILLIPS AC, VOUSDEN KH. Regulation and function of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13(3):332-337.
[29] MORGAN RG, IVES SJ, LESNIEWSKI LA, et al. Age-related telomere uncapping is associated with cellular senescence and inflammation independent of telomere shortening in human arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;305(2):H251-258.
[30] CASELLA G, MUNK R, KIM KM, et al. Transcriptome signature of cellular senescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(14):7294-7305.
[31] FERNÁNDEZ-MIRANDA G, MÉNDEZ R. The CPEB-family of proteins, translational control in senescence and cancer. Ageing Res Rev. 2012; 11(4):460-472.
[32] BURNS DM, RICHTER JD. CPEB regulation of human cellular senescence, energy metabolism, and p53 mRNA translation. Genes Dev. 2008;22(24):3449-3460.
[33] BURNS DM, D’AMBROGIO A, NOTTROTT S, et al. CPEB and two poly(A) polymerases control miR-122 stability and p53 mRNA translation. Nature. 2011;473(7345):105-108.
[34] XU K, REN G. Depletion of CPEB1 protects against oxidized LDL-induced endothelial apoptosis and inflammation though SIRT1/LOX-1 signalling pathway. Life Sci. 2019;239:116874.
[35] GROISMAN I, IVSHINA M, MARIN V, et al. Control of cellular senescence by CPEB. Genes Dev. 2006;20(19):2701-2712.
[36] HU GS, HUR YJ, JIA JM, et al. Effects of 2-aminoindan-2-phosphonic acid treatment on the accumulation of salidroside and four phenylethanoid glycosides in suspension cell culture of Cistanche deserticola. Plant Cell Rep. 2011;30(4):665-674.
[37] YOU SP, MA L, ZHAO J, et al. Phenylethanol Glycosides from Cistanche tubulosa Suppress Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Block the Conduction of Signaling Pathways in TGF-β1/smad as Potential Anti-Hepatic Fibrosis Agents. Molecules. 2016;21(1):102.
[38] 艾江,余扬,费蒙辉,等.松果菊苷对人增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞TGF-β1/Smads信号通路影响的实验研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2021,32(3):187-189.
[39] ZHU H, CHENG C, ZHANG C, et al. Echinacoside suppresses cellular senescence of human fibroblastic cells by down-regulation of p53. J Chin Pharm Sci. 2011;1(5):523-528.
|