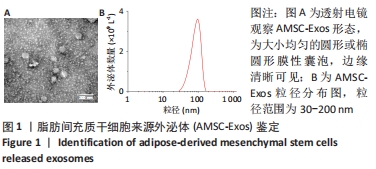
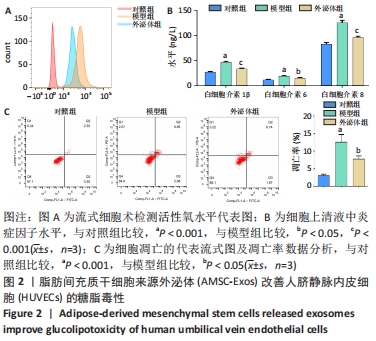
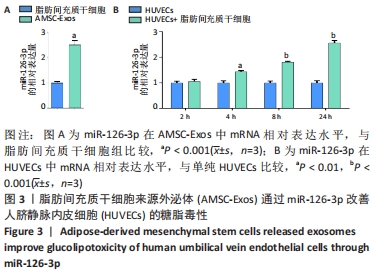
[1] REUSCH JE, MANSON JE. Management of Type 2 Diabetes in 2017: Getting to Goal. JAMA. 2017;317(10):1015-1016.
[2] MUREA M, FREEDMAN BI, PARKS JS, et al. Lipotoxicity in diabetic nephropathy: the potential role of fatty acid oxidation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5(12):2373-2379.
[3] KOJIMA H, KIM J, CHAN L. Emerging roles of hematopoietic cells in the pathobiology of diabetic complications. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014;25(4):178-187.
[4] TOUSOULIS D, PAPAGEORGIOU N, ANDROULAKIS E, et al. Diabetes mellitus-associated vascular impairment: novel circulating biomarkers and therapeutic approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(8):667-676.
[5] ROBERTSON RP, HARMON J, TRAN PO, et al. Beta-cell glucose toxicity, lipotoxicity, and chronic oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53 Suppl 1:S119-124.
[6] REBELATTO CK, AGUIAR AM, MORETÃO MP, et al. Dissimilar differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, and adipose tissue. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008;233(7): 901-913.
[7] RAO RR, STEGEMANN JP. Cell-based approaches to the engineering of vascularized bone tissue. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(11):1309-1322.
[8] HAN Y, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine. Cells. 2019;8(8):886.
[9] SCHMELZER E, MCKEEL DT, GERLACH JC. Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Different Tissues and Their Membrane Encasement for Prospective Transplantation Therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6376271.
[10] LIU X, ZHENG P, WANG X, et al. A preliminary evaluation of efficacy and safety of Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(2):57.
[11] XIE M, HAO HJ, CHENG Y, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hyperglycemia through regulating hepatic glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483(1):435-441.
[12] 赵一婷.脂肪间充质干细胞及其外泌体对炎症状态脂肪细胞及2型糖尿病大鼠的作用及机制[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2017.
[13] BHONDE RR, SHESHADRI P, SHARMA S, et al. Making surrogate β-cells from mesenchymal stromal cells: perspectives and future endeavors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;46:90-102.
[14] MOON KC, SUH HS, KIM KB, et al. Potential of Allogeneic Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Hydrogel Complex for Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes. 2019;68(4):837-846.
[15] MICHELHAUGH SA, CAMACHO A, IBRAHIM NE, et al. Proteomic Signatures During Treatment in Different Stages of Heart Failure. Circ Heart Fail. 2020;13(8):e006794.
[16] LIANG X, DING Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: current status and perspectives. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(9):1045-1059.
[17] ØVERBYE A, SKOTLAND T, KOEHLER CJ, et al. Identification of prostate cancer biomarkers in urinary exosomes. Oncotarget. 2015;6(30): 30357-30376.
[18] CHEN B, LI Q, ZHAO B, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Potential Therapeutic Tool for Tissue Repair. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(9):1753-1758.
[19] LUDWIG N, HONG CS, LUDWIG S, et al. Isolation and Analysis of Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2019;127(1):e91.
[20] ZHOU N, CHEN X, XI J, et al. Genomic characterization reveals novel mechanisms underlying the valosin-containing protein-mediated cardiac protection against heart failure. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101662.
[21] NAHID MA, SATOH M, CHAN EK. Interleukin 1β-Responsive MicroRNA-146a Is Critical for the Cytokine-Induced Tolerance and Cross-Tolerance to Toll-Like Receptor Ligands. J Innate Immun. 2015;7(4):428-440.
[22] NAHID MA, SATOH M, CHAN EK. Mechanistic role of microRNA-146a in endotoxin-induced differential cross-regulation of TLR signaling. J Immunol. 2011;186(3):1723-1734.
[23] 卢佩颖. 2型糖尿病患者血清miR-126表达的分析[D].杭州:浙江大学,2015.
[24] 邓仁生,朱小琴,刘长召,等.血浆循环miRNA-126、miRNA-28-3p的表达与糖尿病的关系研究[J].局解手术学杂志,2017,26(6):400-405.
[25] AN X, LI L, CHEN Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorated Glucolipotoxicity in HUVECs through TSG-6. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(4): 483.
[26] 张静,易阳艳,阳水发,等.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及管样分化的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(10):1351-1357.
[27] CHO BS, KIM JO, HA DH, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atopic dermatitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):187.
[28] SHI Y, WANG Y, LI Q, et al. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(8):493-507.
[29] RENDRA E, RIABOV V, MOSSEL DM, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophage activation and function in diabetes. Immunobiology. 2019;224(2):242-253.
[30] SHUKLA L, YUAN Y, SHAYAN R, et al. Fat Therapeutics: The Clinical Capacity of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Exosomes for Human Disease and Tissue Regeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:158.
[31] DALIRFARDOUEI R, JAMIALAHMADI K, JAFARIAN AH, et al. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(4):555-568.
[32] 陈子扬,蒲锐,邓爽,等.外泌体对运动介导胰岛素抵抗类疾病的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25):4089-4094.
[33] GREENING DW, GOPAL SK, XU R, et al. Exosomes and their roles in immune regulation and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:72-81.
[34] ZHANG X, PEI Z, CHEN J, et al. Exosomes for Immunoregulation and Therapeutic Intervention in Cancer. J Cancer. 2016;7(9):1081-1087.
[35] XUE WL, CHEN RQ, ZHANG QQ, et al. Hydrogen sulfide rescues high glucose-induced migration dysfunction in HUVECs by upregulating miR-126-3p. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020;318(5):C857-C869.
[36] EISSA S, MATBOLI M, ABOUSHAHBA R, et al. Urinary exosomal microRNA panel unravels novel biomarkers for diagnosis of type 2 diabetic kidney disease. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30(8): 1585-1592.
[37] BRENTNALL M, RODRIGUEZ-MENOCAL L, DE GUEVARA RL, et al. Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol. 2013;14:32.
[38] TOMITA T. Cleaved caspase-3 immunocytochemical staining for pancreatic islets and pancreatic endocrine tumors: A potential marker for biological malignancy. Islets. 2010;2(2):82-88.
[39] RANI J, MITTAL I, PRAMANIK A, et al. T2DiACoD: A Gene Atlas of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Associated Complex Disorders. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 6892.
[40] WEI F, WANG A, WANG Q, et al. Plasma endothelial cells-derived extracellular vesicles promote wound healing in diabetes through YAP and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(12): 12002-12018.
[41] BATHINA S, DAS UN. Dysregulation of PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway in brain of streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in Wistar rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):168.
|