2.1 运动与脂肪氧化研究的前沿热点与演进趋势 运动与脂肪代谢一直是运动科学领域的关注重点,前期虽有一些综述总结了这方面的研究,但距今时间较长,且内容不全面不深入,所以有必要收集近年的研究对运动与脂肪氧化的问题进行系统分析和全面总结。该部分主要梳理了国内外近10年来运动与脂肪氧化的代表性成果,旨在反映近些年该领域研究的前沿热点和演进趋势,见表1。
2.2 运动方式与脂肪氧化 运动方式一般指人体参与运动的途径或方法。既往关于运动方式的研究存在概念混用甚至误用的情况,如运动方式、运动项目、运动形式、运动类型以及运动种类等概念的使用不统一,有些研究甚至误用动作模式、运动模式等不规范术语。概言之,运动方式多种多样,依据不同的分类标准可划分为不同类型。
根据运动过程中有无时间间歇,运动方式可划分为中等强度持续运动、高强度间歇运动和冲刺间歇运动等。一般而言,当运动时间较短(< 30 min)时,由于高强度间歇运动和冲刺间歇运动的运动强度更大,因此其燃脂效果要优于中等强度持续运动;当运动时间足够长(1 h以上)时,中等强度持续运动的脂肪氧化效果要优于高强度间歇运动和冲刺间歇运动,其原因是运动中机体的总能耗比不同底物的动员顺序和运动后过量氧耗(excess post-exercise oxygen consumption,EPOC)更为重要。文献报道,高强度间歇运动和冲刺间歇运动的EPOC高于中等强度持续训练,但从总能量消耗角度而言,高强度间歇运动和冲刺间歇运动的总能量消耗与中等强度持续运动相差无几[8]。有学者认为高强度间歇运动减脂的机制是刺激了脂解激素的分泌,且运动后持续较长时间,但缺乏实验数据支撑[9]。有研究从运动间歇期和运动后过量氧耗两个方面对高强度运动的减脂效果进行了分析,认为运动后过量氧耗大可能是高强度运动促进脂肪氧化的原因,但新近研究表明,与运动中的能耗相比,高强度运动后的EPOC只占较小部分[8]。
目前运动科学和健康促进领域测量能耗的经典方式为跑台测试和功率自行车测试,因此根据运动中主要肌群的参与情况,运动方式可划分为局部肌群参与的自行车运动和全身肌群参与的跑步运动等。就脂肪氧化效果而言,在运动强度和运动时间相同的情况下,跑步运动的燃脂效果要优于自行车运动,这可能与跑步运动时神经动员范围更广、参与运动的肌纤维数量多有关;但自行车运动的局部减脂效果更佳,且安全性更高。
根据发展人体各生理系统的功能分类,运动方式可以划分为发展心血管功能的有氧运动、发展肌肉功能的抗阻运动以及发展其他功能的身心运动和混合运动等。有氧运动具有减脂效果好、应用范围广、安全系数高等优点,并且可以有效改善心肺功能,但运动时间较长,受试者依从性较低,难以长时间坚持;抗阻运动的负荷强度一般大于有氧运动,机体较多依靠糖类供能,故其减脂效果一般,但抗阻运动持续时间短、愉悦感强,有助于促进骨骼和肌肉健康,肌肉含量增多会提高人体的基础代谢率,从而达到减脂的目标。新近研究(2021)发现[10],抗阻训练减脂增肌的机制是运动增加了肌肉中α-酮戊二酸的合成和血液α-酮戊二酸水平,α-酮戊二酸促进的肾上腺激素的分泌,肾上腺激素通过与肾上腺2-氧戊二酸受体结合,进而刺激棕色脂肪产热和脂肪代谢[10]。瑜伽、普拉提、太极和气功等身心运动具有较好的减脂效果,但身心运动一般需要专业训练或专业人士指导,因而其应用范围相对较小;运动联合药物、运动联合营养等混合运动干预的减脂效果一般优于运动、热量限制或药物等单一干预方式,但其效果易受其他因素影响,且实施过程相对较为繁琐,其作用机制仍需全面系统的研究。
综上所述,运动方式的种类划分繁多,不同运动方式各有其优点与局限,由“能量连续统一体”可知,任何运动方式均具有燃脂效果,都可使人体获益。但同时也应明确,运动燃脂是一个复杂的非线性过程,受多种因素的影响,运动强度、运动时长等均会对不同运动方式的燃脂效果产生影响。因此,在探讨运动燃脂时应统筹各方面的因素,从时间效益、成本效益以及实施可行性等方面进行综合选择。
2.3 运动强度与脂肪氧化 运动强度一般指单位时间内完成的运动量,它是决定运动效应的关键因素,同时也是刺激脂肪氧化的核心因素,可用最大摄氧量(VO2 max)、心率、功率和速度(m/s)等表示。以VO2 max为例,美国运动医学会认为< 64%VO2 max为中低强度、65%-90%VO2 max为较高强度、≥91%VO2 max为高强度[11]。
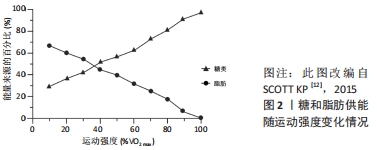
2.3.1 中低强度运动与脂肪氧化 在脂肪供能比方面,运动前的安静状态下,人体大约有33%的能量来自糖,66%来自脂肪代谢[12]。如图2所示,在10%VO2 max强度时,糖脂供能比例约为3∶7;在中低强度运动(25%-50%VO2 max)中,30%-50%的能量来自糖类,而另外50%-70%来自游离脂肪酸。随着运动强度的增加,糖代谢的比重逐渐增加,而脂肪代谢的比重却逐渐降低。在交叉点(Cross-over)以后,糖供能的比例慢慢超过脂肪,此时机体从主要脂肪供能为主逐渐向糖类供能为主进行转变,有学者称其为能量交叉调控的概念[12]。从理论上分析,上述变化持续到最大强度时,机体来自糖类的能量需求将接近100%,且普通人和运动员的这一差异不明显。
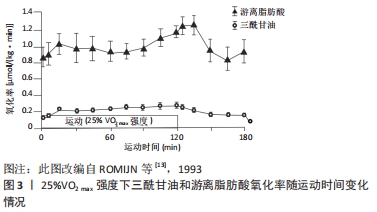
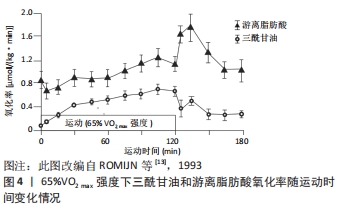
普通人在中低强度范围内的脂肪氧化率较为稳定,而高水平耐力运动员则表现出先增加后下降的趋势。ROMIJN等[13]研究发现,高水平运动员以25%VO2 max强度运动时,脂肪酸释放入血的速率和氧化速率是最高的,随着运动强度的增加,脂肪酸的生成率和氧化率逐渐下降,见图3。这提示,高水平运动员脂肪运动时间相对更早,其心肺功能较强、运动技术水平较高,完成同样的低负荷运动更为轻松。
2.3.2 较高强度运动与脂肪氧化 在较高强度运动中,随着运动强度的递增,普通人的脂肪供能比例逐渐降低(见图2)。碳水化合物通量介导的肌肉碱对线粒体肉碱棕榈酰转移酶1(carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1,CPT1)的可用性降低,可能是高强度运动中降低脂肪氧化的关键机制。有训练经历的人尤其是耐力项目运动员的脂肪供能比例较高、供能时间较长,这是由于高水平运动员利用脂肪供能的时间较早,且能维持至较高运动强度,这可能也与“两极化”训练 模式相关,即训练强度以低强度为主、高强度为辅,中强度很少。
在较高强度运动中,随着运动时间的推移,普通人的脂肪氧化率较为稳定,而高水平耐力运动员脂肪氧化率逐渐增加,见图4。ROMIJN等[13](1993)认为,对于高水平耐力运动员而言,当运动强度增加到60%-65%VO2 max时,肌肉三酰甘油作为脂肪酸的来源变得越来越重要;当运动强度达到65%VO2 max时,脂肪氧化所占供能比例最高;当运动强度达到85%VO2 max时,脂肪氧化总量逐渐下降,这可能与血液中儿茶酚胺升高刺激了肌糖原分解和葡萄糖摄取有关。上述现象表明,运动水平是影响运动强度与脂肪氧化的重要因素,随着运动水平的提高,可能会发生交叉点右移的现象,即在相同运动强度下,脂肪参与供能的比例将增大,或在更高的运动强度下更有效利用脂肪。有研究报道,有训练经历的人群在65%-70%VO2 max 的强度水平下仍可以消耗更多脂肪,这可能与耐力训练提高了乳酸水平急剧增加的临界点(称为无氧阈值),乳酸可以抑制脂肪酸代谢,因此有训练经历的人在运动中可以消耗更多脂肪[14]。从某种程度而言,这是机体对运动的适应现象,其目的是增加机体脂肪供能的比例和游离脂肪酸的动员,提高脂肪分解能力,从而延长脂肪供能时间[15]。
2.3.3 最大脂肪氧化强度运动与脂肪氧化 新近研究(2021)认为,最大脂肪氧化强度(FATmax)是减脂的最佳强度[16]。2001年,Jeukendrup和Achten最早提出的FATmax概念,它可以用最大摄氧量百分数(%VO2 max)、功率(W)、代谢当量(Mets)以及心率的百分数(%HR)来表示,最常见的为采用%VO2 max来表示。运动时脂肪代谢率随着运动强度的增加而递增,并在达到最大值后下降,一般指出现单位时间内脂肪代谢峰值或脂肪氧化利用最大化所对应的强度为最大脂肪氧化强度[16]。现有研究关于最大脂肪氧化强度的范围多集中于40%-75%VO2 max,这可能与不同试验的受试对象选取和试验方案设计不同有关。如有些研究考虑到试验过程的安全性、可行性等问题,多是在中等强度范围内预先给定不同运动强度,这并不能涵盖中等强度范围的每个强度,导致将运动强度连续变量的属性改造为分类变量。
近年,学者们对最大脂肪氧化强度的脂肪氧化效果、功能与机制进行了广泛研究。在效果方面,有研究发现当运动负荷强度保持在 50%-60%VO2 max、持续运动时间固定在 30-40 min时,机体能够更大程度地动员体内的脂肪参与氧化供能,减脂效果较好[17];张勇等[18]研究发现,10周高强度间歇运动(90%VO2 max)对皮下脂肪的减脂效果要优于最大脂肪氧化强度的持续运动;上述现象提示,现有研究结论中的最大脂肪氧化强度值可能偏小,这可能在一定程度上降低了其减脂效果。在功能方面,有研究表明,最大脂肪氧化强度训练可以有效提高脂肪细胞、肝脏和骨骼肌氧化脂肪酸的总量,改善脂质环境,进而提高脂肪的氧化能力[19];也研究发现,最大脂肪氧化强度运动能显著提高骨骼肌线粒体数量,提高脂肪酸氧化酶以及柠檬酸氧化酶活性,并降低血浆低密度脂蛋白、胆固醇、三酰甘油水平和提高高密度脂蛋白水平[20]。在机制方面,最大脂肪氧化强度运动可能通过增加骨骼肌氧化酶活性,加速运动中骨骼肌对血液中游离脂肪酸摄取和利用,进而改善整体脂代谢状态。
综上所述,脂肪供能比例和脂肪氧化率随运动强度变化的趋势有所不同,运动水平是引起上述差异的重要因素。不同人群在较低运动强度中的脂肪供能比例大致相似,而脂肪氧化率的差异较为明显;在较高强度运动中,不同人群的脂肪供能比例和脂肪氧化率差异较大,同一人群的脂肪供能比例和脂肪氧化率表现出非同步性。最大脂肪氧化强度运动的减脂效果较佳,在功能和机制方面也积累了一定成果,但现有研究多以肥胖人群为受试对象,且运动持续时间较短。在更长时间内,普通人和高水平运动员的最大脂肪氧化强度与脂肪氧化的关系仍需要进一步研究。
2.4 运动时间与脂肪氧化 在运动医学领域,运动时间(又称运动时长)一般指每次运动所持续的时间或一段时间内进行体力活动的总时间(即每次训练课的时间、每天或每周的时间),常用小时(h)或分钟(min)表示,每次运动时间的长短要根据个人运动习惯、医学检查、运动频率等因素确定。根据图3和图4的运动时间情况,该部分将运动时长≤1 h的划分为短时间运动,将运动时长> 1 h的划分为长时间运动。
2.4.1 短时间运动与脂肪氧化 如前所述,脂肪氧化利用程度包括脂肪供能比例和脂肪氧化率两个方面。一般认为,人体在运动过程中随着持续时间的延长,脂肪供能比例逐渐变大,糖类供能比例逐渐变小,不同人群的这一差异并不明显。在运动的开始阶段,机体并不会立即动员脂肪供能,这是由于脂肪的水解和脂肪酸由血液转运至肌组织需要消耗一定的时间,该时间一般大于15 min。但也有文献报道,脂肪在安静时即为人体的主要供能物质,在运动达30 min左右时,其输出功率达到最大[21]。张勇[22]研究发现,随着运动时间(≤1 h)的持续,脂肪氧化率也逐渐增加。但既往研究试验设计中运动持续时间较短(≤1 h),无法反映长时间(≥1 h)运动过程中脂肪代谢特征。
与普通人群相比,高水平运动员的脂肪氧化率的变化表现出不同趋势。ROMIJN等[13]以高水平耐力运动员为研究对象却发现不同现象,当以25%VO2 max强度运动时,脂肪供能比例呈现出先增加后下降的趋势,这可能与高水平运动员的运动经济性(running economy,RE)较高有关(见图3)。RE一般指为维持某次极限(submaximal)特定跑步时的能量需求,通常以给定速度下的摄氧量表示。高水平运动员的心肺功能较强、疲劳出现较晚、运动技术娴熟,完成定量运动负荷时机能变化幅度较小,单位时间或单位距离下的能量消耗越少,能量代偿效应也越明显[23];当以65%VO2 max强度运动时,脂肪供能比例基本呈现出逐渐增加的趋势,这与SCOTT的研究结果相似,见图5,表明运动员在完成中等负荷运动时运动经济性的优势会减弱。上述现象提示,运动强度和运动水平是影响运动时间与脂肪氧化的重要因素。
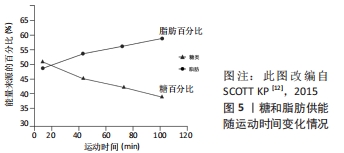
2.4.2 长时间运动与脂肪氧化 在运动持续时间较长(>1 h)的运动中,运动强度和运动水平同样是影响运动时间与脂肪氧化的重要因素。一般认为,随着运动时间的进一步延长,脂肪供能比例仍持续增加。理论上,运动时长持续到2 h左右时,机体脂肪供能的比例将达到60%左右(见图2)。有研究报道,随着运动时间的延长,脂肪供能比例增大,在40,90,180 min持续运动时,脂肪酸供能分别占总能耗的27%,37%,50%,呈现出持续增加的态势[24];SCOTT等[25]认为,中低强度运动中,普通人群的脂肪供能比例在1 h后仍呈现出上升的趋势(见图5)。高水平运动员在长时间运动中的脂肪供能比例与普通人有所不同,魏文哲等[26](2020)通过对1名肯尼亚优秀马拉松运动员的全程马拉松运动模拟测试后发现,每公里脂肪供能比例约12.2%,远低于糖供能的比例(87.8%),并且在后半程中脂肪供能比例出现明显降低,表明糖的能耗高于脂肪能耗,这可能与其运动强度较大有关。优秀马拉松运动员通常以80%-90%VO2 max的强度在2.1 h左右完成全程,运动心率高达200次/min以上,这一过程需要较高的能量消耗,主要以糖有氧氧化供能为主[27]。但人体的糖原含量有限,理论上不能够满足后半程的能量需求。稳定同位素示踪剂技术分析结果表明,运动的后半程脂肪的消耗大于糖类[27]。高水平运动员(尤其是耐力项目)在启动、超越和冲刺阶段会较多利用糖酵解供能,但运动表现提升的总体思路应是提高脂肪酸氧化,减少肌糖原利用,进而提高运动能力。这是由于人体内脂肪储量丰富,占体质量的20%左右,且单位质量供能更高。无训练经历的健康男性可储存20 kg以上的脂肪,由于人体对脂肪的储存没有限制,肥胖人群的脂肪储量甚至超过100 kg[28]。高水平耐力运动员的脂肪动员时间更早,且脂肪供能时间更长,这是机体对长时间耐力运动的有益适应,这可能与其有氧工作能力较强、疲劳较晚出现有关。上述现象提示,高水平运动员和普通人血浆中的游离脂肪酸含量差异不明显,但高水平运动员肌肉中脂肪酸含量较高,这可保证运动员在高强度或长时间运动中增加脂肪供能的比例,延长脂肪供能的时间。
普通人群长时间运动过程中的脂肪氧化率的研究相对较少,这可能与长时间运动的伤病风险较高和实验依从性较低有关。高水平运动员在长时间运动中的脂肪氧化率变化较为复杂,且表现出阶段性特征。ROMIJN等[13](1993)选取5名高水平耐力运动员研究了运动持续时长与脂肪氧化率的关系,当以25%VO2 max强度运动时,脂肪氧化率呈现出先增加后下降、趋于平稳、最后骤增的趋势,这与人体在运动过程中的进入工作状态、稳定状态和疲劳状态相对应;25%VO2 max强度运动时,运动开始30 min和2 h糖和脂肪的供能比例无差别,即脂肪供能比例在运动过程中并不是持续上升的,达到某一比例后会出现下降,在65%VO2 max强度运动时也发现了类似现象(见图4)。上述现象提示,高水平运动员在中低强度运动中脂肪供能会出现动员、活跃和衰减的倒“U”趋势。在以65%VO2 max强度中,脂肪供能比例随时间推移呈现出逐渐增加的趋势,但在运动的后半程(≥90 min),肌肉内的氧化底物(三酰甘油和糖原)在总能量供应中所占的比例反而越来越少[2]。上述现象提示,机体可能在运动90 min后出现了能量节省化或能量保护现象[29]。此外,马拉松、越野滑雪、长距离自行车和铁人三项等耐力项目运动员的脂肪供能特征也有所差异,这可能与不同运动员的肌纤维类型、动作发力部位以及发力顺序等不同有关,且男女运动员的差异也较为明显。
综上所述,运动时间与脂肪氧化同样是一个复杂的非线性过程,受运动强度、运动方式、运动水平、人种差别、测试仪器或个体差异等因素的影响。短时间运动中,随着运动时间的延长,脂肪供能比例的逐渐增大,且不同人群的差异并不明显;短时间运动中脂肪氧化率与运动强度有关,不同运动水平的人群差异较为明显。在持续时间较长(≥1 h)运动中,受试验过程的安全性和受试者的运动耐受力等因素考虑,普通人群的实证研究较少;高水平运动员的脂肪氧化特征较为复杂,且呈现出明显的阶段性特征,运动方式、发力顺序等因素均会对其产生影响。受能耗测量手段的影响,既往研究可能低估了脂肪在长时间运动中供能的比例。高水平运动员在长时间运动中脂肪供能较多,可能与其肌肉中脂肪酸含量较高有关,提示经过系统训练脂肪细胞产生了外周骨骼肌适应。
2.5 运动调控脂肪氧化的机制探讨 运动对脂肪功能的调控是一个多器官参与的生理生化调控过程,神经、运动、循环、呼吸和内分泌等系统均参与其中。运动时心率增加、血流加快、氧运输能力增强,最多可达安静时的10-20倍,物质代谢和能量代谢加速,脂肪氧化随之加强[28];运动引起交感神经兴奋,可调控多种内分泌器官分泌脂解激素如甲状腺素、肾上腺素的释放增多,激活脂肪酶,增强脂解[30];此外,脂肪本身也是内分泌器官,运动可调控内脂素(visfatin)、脂联素(adiponectin/ADPN)和瘦素(Leptin)等脂肪细胞因子的分泌,从而调节脂肪代谢。骨骼肌是运动效应的直接作用器官,而运动过程中骨骼肌也可作为内分泌器官,分泌多种肌细胞因子调控脂肪功能[31]。如运动可促进骨骼肌分泌白细胞介素15(IL-15),从而加速脂肪氧化;骨骼肌中鸢尾素(Irisin)分泌的增加可增加白色脂肪组织中解偶联蛋白1的表达,促进白色脂肪组织棕色化,进而增加脂解作用[32]。
但应注意的是运动的促脂解作用与运动方式的选择以及运动训练水平有关。长时间、低强度的有氧运动中脂肪的供能比例增加,而短时间高强度的无氧运动代谢所产生的乳酸可能会阻止脂肪组织释放游离脂肪酸[33],其机制可能与乳酸含量增加激活了其受体G蛋白偶联受体(G protein coupled receptors 81,GPR81),进而增强胰岛素的抗脂解作用有关[34]。长期耐力训练可提高乳酸水平急剧增加的临界点(无氧阈值或乳酸阈值),增强机体的脂肪动员和氧化利用能力,在运动过程中可能会消耗更多的脂肪。如高水平马拉松运动员运动后乳酸产生量极少,变化率仅为4.8%[26]。
2.6 应用启示 目前对肥胖等疾病的管理中均建议增加体育锻炼和去脂体质量,从而达到增加静息能量消耗和机体总能量消耗效果。运动时间是负荷量(运动量)的重要评价指标,流行病学和随机临床试验的研究结果显示,运动量与健康/体适能获益之间存在量效反应关系,即在一定范围内,健康/体适能获益随着身体活动的递增而增加,但是获得健康/体适能益处的运动量的上下限尚不清楚。因此,该部分结合运动科学领域和健康促进领域的最新研究进展,以有氧运动燃脂的最佳效率(运动时间)为例,探究合理运动在防治肥胖等代谢性疾病中的启示。
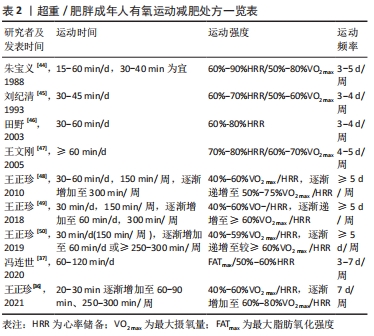
运动减肥的最终目的是减少体内的脂肪含量,从近些年减肥运动处方的发展趋势来看,运动减肥处方推荐量整体上呈现出逐渐增加的态势。早期就有学者提出,有氧运动每次运动时间应大于90 min。如Schoeller认为每天应进行80 min的中等强度运动或35 min的强健运动[35];日本爱知大学运动医学中心研究认为,运动强度为60%-80%VO2 max,每次运动150 min才有较好的减脂效果,运动频率控制在每周3次以上或5-7次更为合适,或者运动强度为10%-60%VO2 max,每次运动2.5 h,每周运动3次以上[35]。
王正珍等[36]关于减肥运动处方的推荐量从30-60 min/d上升到60-90 min/d。冯连世[37](2020)新近研究将减肥运动处方的推荐量设置为60-120 min/d,并提出成年肥胖人群减肥运动处方的每次运动时间在1-1.5 h,每周运动时长8-12 h,甚至将15岁的青少年减肥运处方设置为每天运动4 h(分2次完成)、每周运动24-26 h。FLACK等[38](2020)的新近研究发现,目前运动减肥处方的推荐运动量可能较低,每周运动时间刚超过249 min时,体脂并没有显著减少;而当每周运动时间超过320 min时,身体脂肪会显著减少。也有研究认为,每周累积运动时间超过225 min才会产生临床意义上的减重效果[39]。WHO颁布的新版《身体活动与久坐行为指南》强调,无论是成年人、老年人,还是慢性疾病患者,每周中等强度有氧运动时间超过300 min可额外获益,但获益幅度下降[40]。因此,每周运动时间应接近300 min,同时克服约4 185.85 kJ/周的能量补偿。
有研究报道,运动减肥不成功是由于代偿反应抵消了运动产生的能量负平衡[41],这一观点得到了以50%、100%和150%的公共健康推荐运动量进行运动时或分别以每周58.6 kJ/kg和96.3 kJ/kg的强度进行运动时体质量下降差异的支持[42-43]。现阶段关于运动中能量代偿的大小尚存争议,这可能是由于受试者的性别、年龄、运动水平、运动习惯和实验设计不同有关。现行成人运动减肥处方总结,见表2
。
学术界最近提出的“能量保护”观点认为,人体的运动量与能量消耗之间并不是简单的等比例或线性关系,它们之间存在动态的、非线性的复杂关系,并认为能量消耗越大,能量代偿便越多[29,51]。新近研究(2021)发现,人体会通过降低基础代谢的方式产生28%能量来代偿体力活动的能耗,肥胖人群的这一比例高达49%[52]。运动科学领域最近提出的能量保护模式和抑制性能量消耗模型是该领域的典型代表[50]。上述现象提示,虽然减肥运动处方的推荐活动量逐步增加,但受机体能量保护机制的影响,这一运动量并非越大越好[53]。运动量过大时会激发能量保护,产生“运动抵抗”现象,从而降低减肥效率。有鉴于此,该文建议以有氧运动为例,遵循安全性、渐进性和有效性原则,运动减肥的每日理想运动时长在90 min左右为宜,尽量不超过2 h,每周3-5次,逐渐增加至每日1次。