中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (30): 4857-4861.doi: 10.12307/2022.766
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
新等位基因HLA-DRB1*12:02:10的序列分析及确认
武君华,王天菊,王满妮,徐 华,齐 珺,尚利侠,陈 乐
- 陕西省血液中心西安市中心血站白细胞研究室,陕西省西安市 710061
Sequence analysis and identification of a new allele HLA-DRB1*12:02:10
Wu Junhua, Wang Tianju, Wang Manni, Xu Hua, Qi Jun, Shang Lixia, Chen Le
- Leukocyte Research Laboratory, Xi’an Central Blood Station, Shaanxi Provincial Blood Center, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
完全缓解:目前国内使用的急性白血病的疗效标准分为完全缓解、部分缓解和未缓解。完全缓解是指经治疗后,白血病患者临床、血象、骨髓象均得到改善,其中血象结果表现为血红蛋白> 90 g/L,白细胞正常或减低,分类无幼稚细胞,血小板>100×109 L-1。文中先证者在进行HLA配型时处于完全缓解状态,因此排除了病理细胞对于分型结果的干扰,便于更加准确区分先证者的新等位基因是来自于遗传因素还是基因突变。
新等位基因:在人类进化过程中,为了适应某种外界环境,新近产生而不曾被人们发现的等位基因称为新等位基因,其形成机制有点突变、重组和交换。一般新基因在人群中频率极低,在 IMGT/HLA 数据库中正式命名的等位基因约有40%仅被报道过1次,随着HLA分型检测技术的进步和造血干细胞志愿捐献者的不断增多,新等位基因不断被发现,人类基因库数据不断完善。
背景:人类白细胞抗原(human leukocyte antigen,HLA)个体遗传学差异的本质是在编码其抗原产物的基因水平上,各种诱导因素下所产生的新等位基因,在人群中的频率分布、抗原的血型血清学检测和生物学功能等均有待进一步研究。
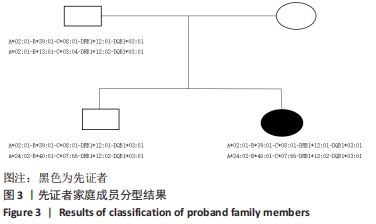
目的:HLA新等位基因HLA-DRB1*12:02:10的确认及序列分析。
方法:采用多聚酶链式反应-基于测序的分型技术(PCR-SBT)、单链测序和下一代测序(NGS)方法对常规检测中HLA-DRB1位点无匹配结果的移植配型样本进行确证实验,并运用聚合酶链式反应-序列特异性寡核苷酸探针技术(PCR-SSO)进行对照实验。
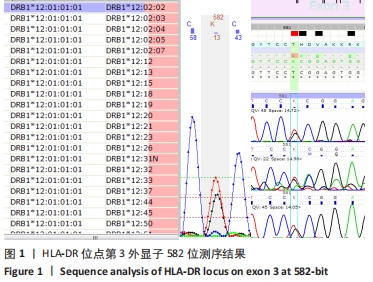
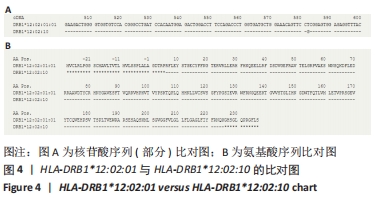
结果与结论:①实验发现先证者的HLA-DRB1位点在第3外显子582位置发生了T>G碱基突变,造成第3外显子194位密码子由CCT>CCG,为同义突变,未造成氨基酸改变;②实验最终确定了HLA-DRB1位点新的HLA等位基因,并被世界卫生组织HLA因子命名委员会正式命名为HLA-DRB1*12:02:10。
缩略语:人类白细胞抗原:human leukocyte antigen,HLA
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3310-6648 (武君华)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: