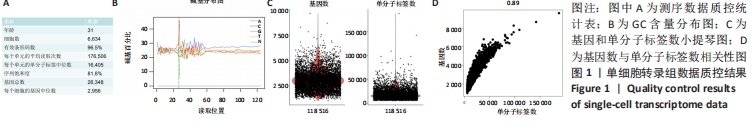
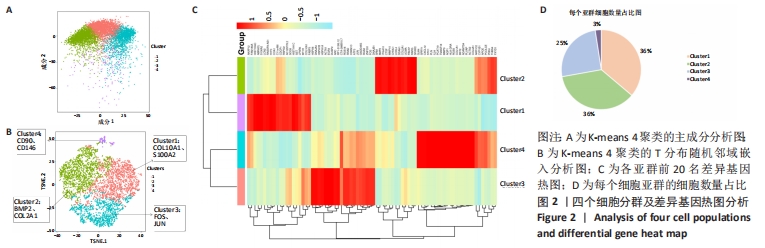
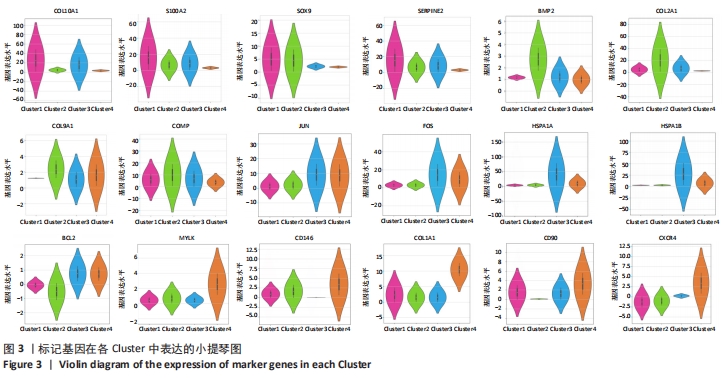
[1] VILA PM, JEANPIERRE LM, RIZZI CJ, et al. Comparison of Autologous vs Homologous Costal Cartilage Grafts in Dorsal Augmentation Rhinoplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;146(4):347-354.
[2] CHOI SW, HONG KY, MINN KW, et al. Chondrogenesis of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on Irradiated Cartilage. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020; 145(2):409-418.
[3] JUNG SN, RHIE JW, KWON H, et al. In vivo cartilage formation using chondrogenic-differentiated human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells mixed with fibrin glue. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21(2):468-472.
[4] ZHAO M, CHEN Z, LIU K, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defects in rabbits through tissue-engineered cartilage constructed with chitosan hydrogel and chondrocytes. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015;16(11):914-923.
[5] SAN-MARINA S, SHARMA A, VOSS SG, et al. Assessment of Scaffolding Properties for Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Nasal Reconstruction. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2017;19(2):108-114.
[6] DION J, COSTEDOAT-CHALUMEAU N, SÈNE D, et al. Relapsing Polychondritis Can Be Characterized by Three Different Clinical Phenotypes: Analysis of a Recent Series of 142 Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(12):2992-3001.
[7] ENOMURA M, MURATA S, TERADO Y, et al. Development of a Method for Scaffold-Free Elastic Cartilage Creation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22): 8496.
[8] 靳小兵.自体组织工程生长板修复兔长骨生长板损伤的实验研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2004.
[9] 姜疆.在体构建组织工程软骨的实验研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2012.
[10] CHEN R, WU X, JIANG L, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals Hypothalamic Cell Diversity. Cell Rep. 2017;18(13):3227-3241.
[11] HWANG B, LEE JH, BANG D. Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and bioinformatics pipelines. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(8):1-14.
[12] GULATI GS, SIKANDAR SS, WESCHE DJ, et al. Single-cell transcriptional diversity is a hallmark of developmental potential. Science. 2020;367 (6476):405-411.
[13] MAHMOUDI S, MANCINI E, XU L, et al. Heterogeneity in old fibroblasts is linked to variability in reprogramming and wound healing. Nature. 2019;574(7779):553-558.
[14] QI F, QIAN S, ZHANG S, et al. Single cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and receptors of human coronaviruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(1):135-140.
[15] JI Q, ZHENG Y, ZHANG G, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis reveals the progression of human osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(1):100-110.
[16] SUN H, WEN X, LI H, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies meniscus progenitors and reveals the progression of meniscus degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(3):408-417.
[17] 胡坤,陈竹,罗栩伟,等.组织工程软骨的研究新进展[J].西部医学, 2020,32(6):927-932.
[18] FU S, KUWAHARA M, UCHIDA Y, et al. Circadian production of melatonin in cartilage modifies rhythmic gene expression. J Endocrinol. 2019:JOE-19-0022.R2.
[19] MEI R, LOU P, YOU G, et al. 17β-Estradiol Induces Mitophagy Upregulation to Protect Chondrocytes via the SIRT1-Mediated AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:615250.
[20] 杨美蓉.先天性小耳畸形伴发胸廓畸形的临床研究及初步遗传学分析[D].北京:协和医学院,2018.
[21] PRETEMER Y, KAWAI S, NAGATA S, et al. Differentiation of Hypertrophic Chondrocytes from Human iPSCs for the In Vitro Modeling of Chondrodysplasias. Stem Cell Reports. 2021;16(3):610-625.
[22] 薛松,姜亚飞,桑伟林,等.肥大软骨细胞在骨关节炎发病中的作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(6):522-526.
[23] 陈海涛,倪曲波,陈廖斌.关节软骨的发育及调控[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2021,42(2):333-337.
[24] SANTORO A, CONDE J, SCOTECE M, et al. SERPINE2 Inhibits IL-1α-Induced MMP-13 Expression in Human Chondrocytes: Involvement of ERK/NF-κB/AP-1 Pathways. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0135979.
[25] DANG QT, HUYNH TD, INCHINGOLO F, et al. Human Chondrocytes from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Seeded on a Dermal-Derived Collagen Matrix Sheet: Our Preliminary Results for a Ready to Go Biotechnological Cartilage Graft in Clinical Practice. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6664697.
[26] ZHAO C, WANG E. Heat shock protein 90 suppresses tumor necrosis factor alpha induced apoptosis by preventing the cleavage of Bid in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Cell Signal. 2004;16(3):313-321.
[27] 杜俊杰,罗卓荆,胡蕴玉,等.rhBMP-2在体内诱导成骨中I,II型胶原及碱性磷酸酶的表达[J].第四军医大学学报,2001,22(11):981-983.
[28] 张艳,柴岗,刘伟,等.人肋软骨细胞体外培养中生长代谢及功能的变化[J].中华整形外科杂志,2004,20(5):372-376.
[29] IANNONE F, CORRADO A, GRATTAGLIANO V, et al. Phenotyping of chondrocytes from human osteoarthritic cartilage: chondrocyte expression of beta integrins and correlation with anatomic injury. Reumatismo. 2001;53(2):122-130.
[30] KURKOV A, GULLER A, FAYZULLIN A, et al. Amianthoid transformation of costal cartilage matrix in children with pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum. PLoS One. 2021;16(1):e0245159.
[31] KATO Y, GOSPODAROWICZ D. Effect of exogenous extracellular matrices on proteoglycan synthesis by cultured rabbit costal chondrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985;100(2):486-495.
[32] SATO K, MOY OJ, PEIMER CA, et al. An experimental study on costal osteochondral graft. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(2):172-183.
[33] 赵琴琴,蔡震,游晓波,等.不同性别不同层次肋软骨的生物力学性能研究[J].中华整形外科杂志,2020,36(9):1042-1046.
[34] FORMAN JL, KENT RW. The effect of calcification on the structural mechanics of the costal cartilage. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2014;17(2):94-107.
[35] KIM A, MOON J, LIM SY, et al. The Interchondral Joints of Thorax in Microtia Surgery: Classification and Fabrication Strategies. Ann Plast Surg. 2021 Feb 1. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002582.
[36] 周志文,鞠黎,楼跃.不同年龄软骨组织多肽的定量分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(8):1178-1183.
[37] 吴迎,王先成,熊祥,等.70例女性第6-8肋软骨组织量及钙化特点分析[J].中华整形外科杂志,2019,35(8):764-771.
[38] GUO F, YU X, CHEN W, et al. Preliminary Analysis on Characteristics of Rib Cartilage Calcification in Patients With Congenital Microtia. J Craniofac Surg. 2019;30(1):e28-e32.
|