1.1 设计 体外细胞学实验,组间差异性分析采用非配对t检验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2019年1月至2020年12月在深圳市中医院中心实验室、威斯腾生物实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 健康新西兰大白兔10只,雌雄各半,两三个月龄,体质量(1.660±0.368) kg,由广东省实验动物中心提供,动物生产许可证号:SCXK(粤)2019-0035。实验通过广州中医药大学实验动物伦理委员会批准,实验操作符合2006年中华人民共和国科学技术部颁布的《关于善待实验动物的指导性意见》。
1.3.2 实验试剂 L-DMEM培养基(Gbico,美国,批号11995-065)、胎牛血清(Gibco,美国,批号10099-141);0.25%胰蛋白酶(碧云天,中国,批号C0201)、青霉素-链霉素溶液(100X)(碧云天,中国,批号C0222);PBS(上海生工,中国,批号B040100);EDTA(Sigma,美国,批号EDS-100G);兔来源一抗(Abcam,英国):RAB39B(批号ab151591)、GAPDH(批号ab181602)、RHOA(批号ab187027)、LIMK(批号ab95186)、Sox9(批号ab185966);山羊抗兔IgG二抗(碧云天,中国,批号A0468);PVDF膜(Bio-Rad,美国,批号1620177);ECL增强化学发光检测试剂盒(PIERCE,美国,批号32106);30%丙烯酰胺(29∶1)(上海生工,批号B546017-0500);甲基磺酰氟(Sigma,美国,批号52201-00-0);TEMED、牛血清白蛋白(Sigma,美国,批号A7030);Easye-see预染蛋白质Marker(Bio-Rad,美国,批号1610374); Western blot裂解液(碧云天,中国,批号P0013);CCK-8试剂盒(Sigma,美国,批号C2581);Annexin V-PE/7-AAD流式试剂盒(Vazyme,中国,批号A213-01); DEPC(Sigma,美国,批号D5758);RNA提取试剂盒(Takara,日本,批号6769);HiScript® II Q RT SuperMix for qRT-PCR(Vazyme,中国,批号R123-01);AceQ® qRT-PCR SYBR® Green Master Mix(Vazyme,中国,批号Q111-02);引物(ThermoFisher);慢病毒(威斯腾生物);质粒(淼灵生物),等。
1.3.3 实验仪器 电热压力蒸汽消毒器(YXQ-LS-100A,上海博讯实业有限公司);电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(GZX-9140MBE,上海博讯实业有限公司);台式高速微量迷你离心机(MiniAtarPlus,湖南可成仪器设备有限公司);低速台式离心机(TDL-50B,上海安亭科学仪器厂);高速台式离心机(TG16-WS,湘仪离心机仪器有限公司);生物安全柜(BSC-1300ⅡA2,上海博讯实业有限公司);双人双面垂直洁净工作台(SW-CJ-2F,
上海博讯实业有限公司);二氧化碳培养箱(MCO-15AC-SC,Sanyo,日本);电子分析天平(XB120A,Precisa,瑞士);移液器(Research Plus系列,Eppendorf,德国);荧光倒置显微镜(ECLIPSE Ti-sNikon,日本);正置显微镜(CX22RFS1,OLYMPUS,日本);纯水仪(ELIX3,Millipore,美国);0.22 μm混合纤维素滤膜(Millipore,美国);细胞计数板(上海医用仪器厂);细胞培养瓶及培养板(Costar,美国);垂直板电泳转移装置(Bio-Rad,美国);Trans-Blot转膜装置(Bio-Rad,美国);图像分析系统(LabworksTM Analysis Softwar,美国);电泳仪(Bio-Rad,美国);多功能酶标仪(Thermo Fisher,美国);Tanon-4200凝胶成像系统(Tanon,中国);除热原超纯水系统(Millipore,美国);-80 ℃冰箱(Sanyo-382AT,日本);低温高速离心机(GS-15R,Beckman,美国);电子分析(Precisa12A,瑞士);电子酸度计(Beckman,美国);电热恒温水浴箱(DK-8D,上海博讯实业有限公司);旋涡振荡器(QL-901,江苏海门其林贝尔);脱色摇床(麒麟医用仪器厂);多功能酶标仪(Thermo Fisher,美国);倒置显微镜(Nikon,日本);流式细胞仪(CytoFLEX,Beckman,美国);高速台式离心机(microfuge 20R,Beckman,美国);电泳仪(Bio-rad,美国);凝胶成像仪稳压DNA电泳仪(Tanon,中国);Tanon-1600凝胶成像系统(Tanon,中国);实时荧光定量PCR仪(ABI Stepone plus,美国)等。
1.4 方法
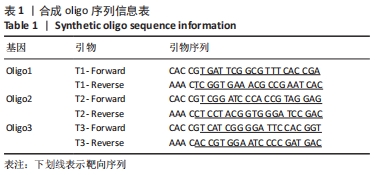
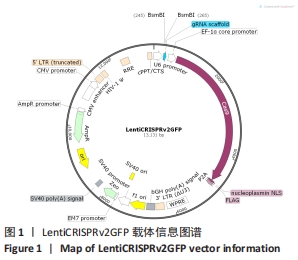
1.4.1 重组真核表达质粒sgRNA的构建 通过NCBI网站查询RAB39B mRNA基因组信息,用在线工具:http://crispor.tefor.net/进行靶点基因设计,基因靶点序列:Target 1为TGA TTC GGC GTT TCA CCG A;Target 2为TCG GAT CCC ACC GTA GGA G;Target 3为GTC ATC GGG GAT TCC ACG GT,合成Oligo,见表1,磷酸化Oligo,退火,载体线性化,构建载体:lentiCRISPRV2GFP-T1、lentiCRISPRV2GFP-T2、lentiCRISPRV2GFP-
T3,通过载体连接,转化,挑取单克隆分别进行扩增及测序,载体内源活性检测选择高活性载体,见图1。
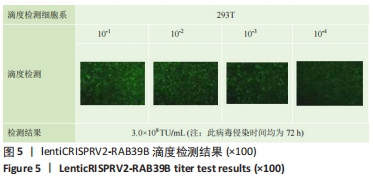
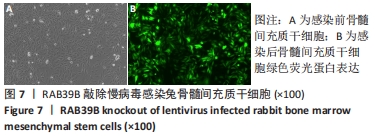
1.4.2 RAB39B敲除慢病毒包装 制备慢病毒穿梭质粒及其辅助包装原件载体质粒,3种质粒载体分别进行高纯度无内毒素大量抽提,共转染293T细胞,转染后16-24 h更换为完全培养基,继续培养48 h后,第一次收集全部富含慢病毒颗粒的细胞上清液;往培养基中添加新鲜完全培养基继续培养24 h后,第二次收集全部富含慢病毒颗粒的细胞上清液;对2次收集的病毒上清液进行浓缩后通过荧光显微镜计数荧光细胞,结合稀释倍数计算病毒滴度,得到高滴度的慢病毒浓缩液。
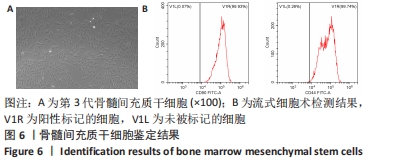
1.4.3 骨髓间充质干细胞培养和转染 从两三个月龄健康新西兰实验兔髂骨穿刺抽吸骨髓液,采用 Percoll 密度梯度离心法和细胞贴壁法分离出骨髓间充质干细胞,并用流式细胞仪检测第3代骨髓间充质干细胞抗原表型CD90、CD44的表达。
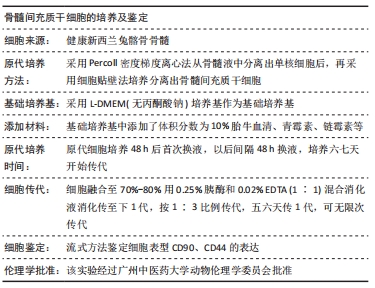
收集第3代骨髓间充质干细胞,L-DMEM培养液重悬,调整细胞浓度为0.5×108 L-1,以每孔500 μL细胞悬液接种于6孔板中,进行病毒感染时细胞的融合度为70%左右。第2天观察细胞生长状态,如细胞状态较好则开始实验,感染复数为50进行后续实验,准确计算好每孔所需病毒原液量。吸取病毒液加入细胞中,同时加入5 mg/L聚凝胺助转染试剂,以提高感染效率。混匀后将6孔板放在37 ℃培养箱中孵育,定期更换培养液,感染48-96 h后荧光显微镜观察荧光表达,估计慢病毒感染目的细胞的效率。同时,使用含5 mg/L嘌呤霉素的培养基筛选掉未感染的细胞。
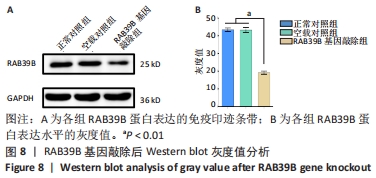
1.4.4 Western blot鉴定CRISPR/Cas9系统对RAB39B的敲除效果 将骨髓间充质干细胞分为正常对照组、空载对照组、RAB39B基因敲除组,细胞培养7 d,提取各组细胞蛋白,用BCA法测蛋白浓度,绘制标准曲线,进行SDS-PAGE电泳,将ECL曝光液按A液∶B液(1∶1)混匀后均匀覆盖在整片膜上,反应2 min放入曝光仪曝光检测RAB39B蛋白条带灰度值。
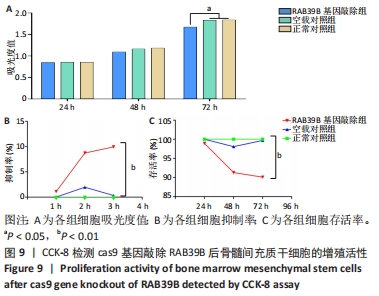
1.4.5 CCK-8检测CRISPR/Cas9系统敲除RAB39B基因后骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖活性 取正常对照组、空载对照组、RAB39B基因敲除组兔骨髓间充质干细胞,计数调整细胞浓度至0.5×108 L-1,分别接种于96孔板中,每孔100 μL,每组细胞设3个复孔,将细胞培养板置于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱24,48,72 h。培养结束后每孔加入10 μL CCK-8溶液(注意不要产生气泡),于培养箱内孵育1-4 h。用酶标仪测定450 nm处的吸光度值。细胞活力(%)=[A(实验组)-A(空白组)]/[A(对照组)-A(空白组)] ×100%。细胞抑制率(%)=[A(对照组)-A(实验组)]/[A(对照组)-A(空白组)]=1-细胞活力(注:细胞活力指细胞增殖活力或细胞毒性活力)。A(实验组):孔内含有经过处理的细胞、CCK-8溶液的吸光度值;A(空白组):孔内含有培养基和CCK-8溶液而没有细胞的吸光度值;A(对照组):孔内含有未经过处理的细胞、CCK-8溶液的吸光度值。
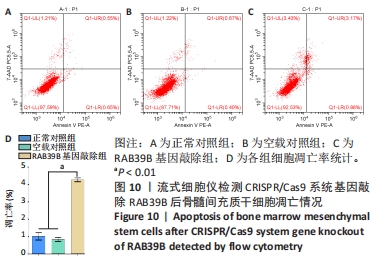
1.4.6 流式细胞仪检测CRISPR/Cas9系统敲除RAB39B基因后骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡率 取正常对照组、空载对照组、RAB39B基因敲除组兔骨髓间充质干细胞,计数调整细胞浓度至5×107 L-1,分别接种于6孔板,每孔接种2 mL,待细胞生长达到80%-90%,收集细胞培养基上清和细胞沉淀,
2 000 r/min离心5 min;PBS洗涤细胞2次,2 000 r/min离心5 min,收集(1-5)×105个细胞;在50 μL的Binding Buffer中加入7-AAD染液5 μL,混匀;收集细胞中加入上述7-AAD染液,混匀;室温、避光、反应5-15 min;反应后再加入450 μL的Binding Buffer混匀;加入1 μL AnnexinV-PE混匀;室温、避光、反应5-15 min;1 h内进行流式细胞仪检测,激发波长Ex=488 nm;发射波长Em=578 nm,Annexin V-PE的橙红色荧光建议使用FL2通道检测;激发波长Ex=546 nm;发射波长Em=647 nm,7-AAD红色荧光建议使用FL3通道检测。使用未经凋亡诱导处理的正常细胞作为对照进行荧光补偿调节,去除光谱重叠和设定十字门的位置。
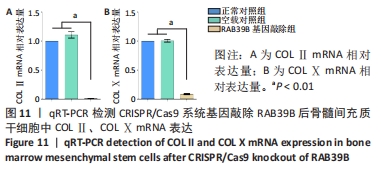
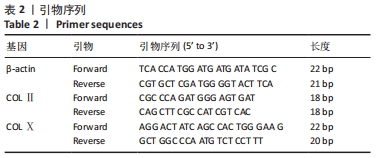
1.4.7 qRT-PCR检测CRISPR/Cas9系统敲除RAB39B基因后骨髓间充质干细胞的成软骨分化能力 取正常对照组、空载对照组、RAB39B基因敲除组兔骨髓间充质干细胞,用胰酶消化,以5×107 L-1细胞浓度接种于24孔板中,每孔接种1 mL,在含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的L-DME培养液中培养,并加入含地塞米松(39.25 mg/L)、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(10 μg/L)、维生素C(50 mg/L),在37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2孵箱内培养1周,从第2周起用转化生长因子β1(10 μg/L)替换碱性成纤维细胞生长因子继续培养3周,每日用倒置相差显微镜观察细胞形态变化并摄片。3周后收集3组细胞,检测β-actin、COLⅡ、COLⅩmRNA表达,用Trizol试剂提取各组细胞总RNA,再用随机引物、反转录酶转录为cDNA,然后以此cDNA第1链为模板进行qRT-PCR扩增。根据NCBI所公布的基因登录号设计内参和目的基因引物,该实验目的基因引物序列(5’ to 3’)见表2。
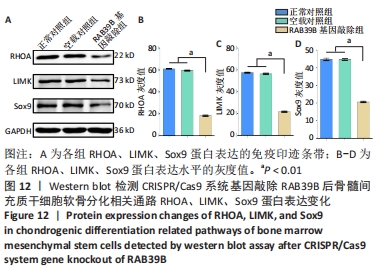
1.4.8 Western blot检测RAB39B基因敲除后骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化相关通路RHOA、LIMK、Sox9蛋白表达变化 按照之前Western blot检测方法,细胞培养3周后提取各组细胞蛋白,用BCA法测蛋白浓度,绘制标准曲线,进行SDS-PAGE电泳,将ECL曝光液按A液∶B液(1∶1)混匀后均匀覆盖在整片膜上,反应2 min放入曝光仪曝光检测RHOA、LIMK、Sox9蛋白条带灰度值。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①qRT-PCR检测CRISPR/Cas9系统敲除RAB39B基因后骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化相关基因β-actin、COLⅡ、COLⅩ mRNA表达;②Western blot检测RAB39B基因敲除后骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化相关通路RHOA、LIMK、Sox9蛋白表达变化。
1.6 统计学分析 采用 SPSS 23.0统计学软件对数据进行统计,计量资料用x±s表示,组间差异性分析采用非配对t检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义,P < 0.01为差异有非常显著性意义。