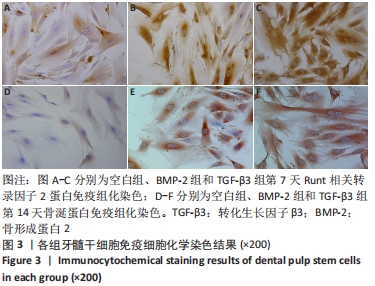
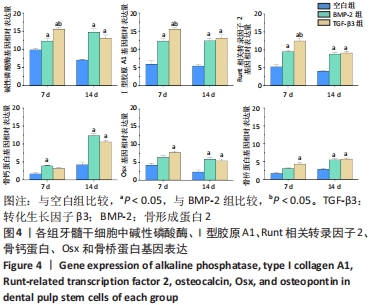
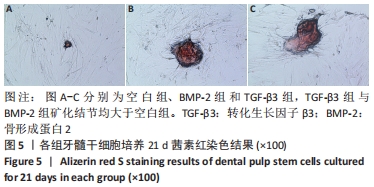
[1] LIU T, XU J, PAN X, et al. Advances of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-based biomaterial scaffolds for oral and maxillofacial tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8):2467-2478.
[2] POURLAK T, POURLAK T, GHODRATI M, et al. Usage of stem cells in oral and maxillofacial region. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;122(4):441-452.
[3] ADAMIČKA M, ADAMIČKOVÁ A, DANIŠOVIČ L, et al. Pharmacological Approaches and Regeneration of Bone Defects with Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021; 2021:4593322.
[4] ALONZO M, PRIMO FA, KUMAR SA, et al. Bone tissue engineering techniques, advances and scaffolds for treatment of bone defects. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2021;17:100248.
[5] MAREW T, BIRHANU G. Three dimensional printed nanostructure biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Regen Ther. 2021;18:102-111.
[6] SAMIEI M, FATHI M, BARAR J, et al. Bioactive hydrogel-based scaffolds for the regeneration of dental pulp tissue. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2021;64(1):102600.
[7] MAGALHÃES FD, SARRA G, CARVALHO GL, et al. Dental tissue-derived stem cell sheet biotechnology for periodontal tissue regeneration: A systematic review. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;129:105182.
[8] ZHAO H, WEI J, SUN J. Roles of TGF-beta signaling pathway in tumor microenvirionment and cancer therapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;89(Pt B):107101.
[9] BOYE A. A cytokine in turmoil: Transforming growth factor beta in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;139:111657.
[10] 艾力麦尔旦·艾尼瓦尔, 张晓莉, 卡米力江·买买提明, 等.转化生长因子 β3 促进兔牙髓干细胞成骨向分化的体外实验研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2019, 35(4):485-489.
[11] CHEN S, SHI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Evaluation of BMP-2 and VEGF loaded 3D printed hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds with enhanced osteogenic capacity in vitro and in vivo. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;112:110893.
[12] BERBÉRI A, FAYYAD-KAZAN M, AYOUB S, et al. Osteogenic potential of dental and oral derived stem cells in bone tissue engineering among animal models: An update. Tissue Cell. 2021;71:101515.
[13] MOLLENTZE J, DURANDT C, PEPPER MS. An In Vitro and In Vivo Comparison of Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:9919361.
[14] LICHTMAN MK, OTERO-VINAS M, FALANGA V. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) isoforms in wound healing and fibrosis. Wound Repair Regen. 2016;24(2):215-222.
[15] LI M, QIU L, HU W, et al. Genetically-modified bone mesenchymal stem cells with TGF-β3 improve wound healing and reduce scar tissue formation in a rabbit model. Exp Cell Res. 2018;367(1):24-29.
[16] MARTIN AR, PATEL JM, LOCKE RC, et al. Nanofibrous hyaluronic acid scaffolds delivering TGF-β3 and SDF-1α for articular cartilage repair in a large animal model. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:170-182.
[17] LI D, MA X, ZHAO T. Mechanism of TGF-β3 promoting chondrogenesis in human fat stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;530(4):725-731.
[18] QASIM M, LE NXT, NGUYEN TPT, et al. Nanohybrid biodegradable scaffolds for TGF-β3 release for the chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Pharm. 2020;581:119248.
[19] MOIOLI EK, HONG L, GUARDADO J, et al. Sustained release of TGFbeta3 from PLGA microspheres and its effect on early osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(3):537-546.
[20] DENG M, MEI T, HOU T, et al. TGFβ3 recruits endogenous mesenchymal stem cells to initiate bone regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):258.
[21] 艾力麦尔旦·艾尼瓦尔,木合塔尔·霍加.转化生长因子β3促进兔牙髓干细胞成骨向分化机制的初步研究[J].口腔医学,2019,39(2):97-102.
[22] 艾力麦尔旦·艾尼瓦尔,王玲,古丽,等.转化生长因子 β3 对成骨细胞增殖和成骨能力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(17):2664-2669.
[23] LI Y, QIAO Z, YU F, et al. Transforming Growth Factor-β3/Chitosan Sponge (TGF-β3/CS) Facilitates Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):4982.
[24] HRUBI E, IMRE L, ROBASZKIEWICZ A, et al. Diverse effect of BMP-2 homodimer on mesenchymal progenitors of different origin. Hum Cell. 2018;31(2):139-148.
[25] TÓTH F, GÁLL JM, TŐZSÉR J, et al. Effect of inducible bone morphogenetic protein 2 expression on the osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells in vitro. Bone. 2020;132:115214.
[26] MARUPANTHORN K, TANTRAWATPAN C, KHEOLAMAI P, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhances the osteogenic differentiation capacity of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from human bone marrow and umbilical cord. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(3):654-662.
[27] WANG Y, HE T, LIU J, et al. Synergistic effects of overexpression of BMP-2 and TGF-beta3 on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(6):5514-5520.
[28] ROEDER E, MATTHEWS BG, KALAJZIC I. Visual reporters for study of the osteoblast lineage. Bone. 2016;92:189-195.
[29] KOMORI T. Molecular Mechanism of Runx2-Dependent Bone Development. Mol Cells. 2020;43(2):168-175.
[30] HE W, CHEN L, HUANG Y, et al. Synergistic effects of recombinant Lentiviral-mediated BMP2 and TGF-beta3 on the osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Cytokine. 2019;120:1-8.
[31] 周武,王彬娉,王雅雯,等.转化生长因子 β 和骨形成蛋白 2 联合诱导小鼠成骨细胞系 MC3T3-E1 细胞的增殖与分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3630-3635.
|