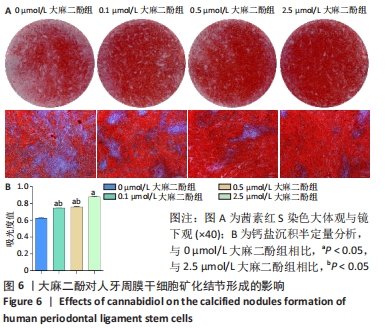
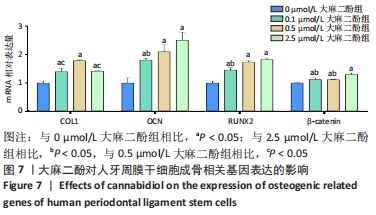
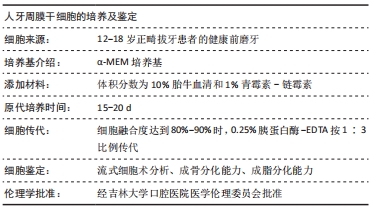
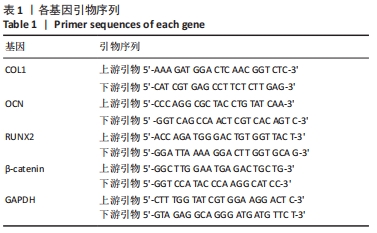
[1] KNIGHT ET, MURRAY THOMSON W. A public health perspective on personalized periodontics. Periodontol 2000. 2018;78(1):195-200.
[2] BOSSHARDT DD, STADLINGER B, TERHEYDEN H. Cell-to-cell communication-periodontal regeneration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015; 26(3):229-239.
[3] XU XY, LI X, WANG J, et al. Concise Review: Periodontal Tissue Regeneration Using Stem Cells: Strategies and Translational Considerations. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(4):392-403.
[4] SEO BM, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155.
[5] ZHANG Y, XING Y, JIA L, et al. An In Vitro Comparative Study of Multisource Derived Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Bone Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(23):1634-1645.
[6] ZHENG C, CHEN J, LIU S, et al. Stem cell-based bone and dental regeneration: a view of microenvironmental modulation. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11(3):23.
[7] LIU AQ, HU CH, JIN F, et al. Contributions of Bioactive Molecules in Stem Cell-Based Periodontal Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1016.
[8] BERGAMASCHI MM, QUEIROZ RH, ZUARDI AW, et al. Safety and side effects of cannabidiol, a Cannabis sativa constituent. Curr Drug Saf. 2011;6(4):237-249.
[9] ATALAY S, JAROCKA-KARPOWICZ I, SKRZYDLEWSKA E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;9(1):21.
[10] PISANTI S, MALFITANO AM, CIAGLIA E, et al. Cannabidiol: State of the art and new challenges for therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;175:133-150.
[11] BRITCH SC, BABALONIS S, WALSH SL. Cannabidiol: pharmacology and therapeutic targets. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021;238(1):9-28.
[12] KOGAN NM, MELAMED E, WASSERMAN E, et al. Cannabidiol, a Major Non-Psychotropic Cannabis Constituent Enhances Fracture Healing and Stimulates Lysyl Hydroxylase Activity in Osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(10):1905-1913.
[13] KAMALI A, ORYAN A, HOSSEINI S, et al. Cannabidiol-loaded microspheres incorporated into osteoconductive scaffold enhance mesenchymal stem cell recruitment and regeneration of critical-sized bone defects. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101:64-75.
[14] LI D, LIN Z, MENG Q, et al. Cannabidiol administration reduces sublesional cancellous bone loss in rats with severe spinal cord injury. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;809:13-19.
[15] NAPIMOGA MH, BENATTI BB, LIMA FO, et al. Cannabidiol decreases bone resorption by inhibiting RANK/RANKL expression and pro-inflammatory cytokines during experimental periodontitis in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009;9(2):216-222.
[16] KANG MA, LEE J, PARK SH. Cannabidiol induces osteoblast differentiation via angiopoietin1 and p38 MAPK. Environ Toxicol. 2020;35(12):1318-1325.
[17] SCHMUHL E, RAMER R, SALAMON A, et al. Increase of mesenchymal stem cell migration by cannabidiol via activation of p42/44 MAPK. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;87(3):489-501.
[18] QI X, LIU C, LI G, et al. Investigation of in vitro odonto/osteogenic capacity of cannabidiol on human dental pulp cell. J Dent. 2021;109: 103673.
[19] GIBON E, LU L, GOODMAN SB. Aging, inflammation, stem cells, and bone healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:44.
[20] SUI BD, HU CH, LIU AQ, et al. Stem cell-based bone regeneration in diseased microenvironments: Challenges and solutions. Biomaterials. 2019;196:18-30.
[21] APOSTU D, LUCACIU O, MESTER A, et al. Cannabinoids and bone regeneration. Drug Metab Rev. 2019;51(1):65-75.
[22] PAGANO S, CONIGLIO M, VALENTI C, et al. Biological effects of Cannabidiol on normal human healthy cell populations: Systematic review of the literature. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;132:110728.
[23] MILLER H, DE LEO N, BADACH J, et al. Role of marijuana components on the regenerative ability of stem cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021; 39(3):432-441.
[24] VIMALRAJ S. Alkaline phosphatase: Structure, expression and its function in bone mineralization. Gene. 2020;754:144855.
[25] GREGORY CA, GUNN WG, PEISTER A, et al. An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells in culture: comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction. Anal Biochem. 2004;329(1):77-84.
[26] ALFORD AI, KOZLOFF KM, HANKENSON KD. Extracellular matrix networks in bone remodeling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;65:20-31.
[27] KOMORI T. Regulation of Proliferation, Differentiation and Functions of Osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1694.
[28] HAN Y, YOU X, XING W, et al. Paracrine and endocrine actions of bone-the functions of secretory proteins from osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Bone Res. 2018;6:16.
[29] CLEVERS H, NUSSE R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192-1205.
[30] DUAN P, BONEWALD LF. The role of the wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in formation and maintenance of bone and teeth. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;77(Pt A):23-29.
[31] MAO L, LIU J, ZHAO J, et al. Effect of micro-nano-hybrid structured hydroxyapatite bioceramics on osteogenic and cementogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cell via Wnt signaling pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:7031-7044.
[32] ZHENG DH, WANG XX, MA D, et al. Erythropoietin enhances osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13: 2543-2552.
[33] NIE F, ZHANG W, CUI Q, et al. Kaempferol promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020;258:118143.
[34] VALLÉE A, LECARPENTIER Y, VALLÉE JN. Cannabidiol and the Canonical WNT/β-Catenin Pathway in Glaucoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3798.
[35] VALLÉE A, VALLÉE JN, LECARPENTIER Y. Potential role of cannabidiol in Parkinson’s disease by targeting the WNT/β-catenin pathway, oxidative stress and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(7): 10796-10813.
|