| [1] Gong FL. Medical Immunology. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Publishing House, 2004:1l8-121. [2] Horowitz A, Guethlein LA, Nemat-Gorgani N, et al. Regulation of Adaptive NK Cells and CD8 T Cells by HLA-C Correlates with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and with Cytomegalovirus Reactivation. J Immunol. 2015;195(9):4524-4536. [3] Bettens F, Buhler S, Tiercy JM. Allorecognition of HLA-C Mismatches by CD8+ T Cells in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Is a Complex Interplay between Mismatched Peptide-Binding Region Residues, HLA-C Expression, and HLA-DPB1 Disparities. Front Immunol. 2016;7:584. [4] Ameres S, Mautner J, Schlott F, et al. Presentation of an immunodominant immediate-early CD8+ T cell epitope resists human cytomegalovirus immunoevasion. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(5):e1003383.[5] Tan AT, Sodsai P, Chia A, et al. Immunoprevalence and immunodominance of HLA-Cw*0801-restricted T cell response targeting the hepatitis B virus envelope transmembrane region. J Virol. 2014;88(2):1332-1341. [6] Hu Z, Liu Y, Zhai X, et al. New loci associated with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Han Chinese. Nat Genet. 2013;45(12):1499-1503. [7] 杨晋,张建琼,沈宇清,等.肝癌细胞中HLA I类重链基因表达与启动子区域甲基化的相关性[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2007,23(6):582-584.[8] 高素青,邹红岩,程良红,等.应用SBT直接测序分型法研究中国南方汉族人群HLA五个基因座单倍型[J].中华医学遗传学杂志, 2009,26(2):228-232.[9] 黎燕琼.乙型肝炎病毒检测方法的研究现状[J].中外医学研究, 2016,14(8): 159-160.[10] Tan JM, Zhou YC, Tang XD. Tissue Typing Methods and the Clinical Application. Beijing: People’s Medical House,2002:91-93.[11] Müller CR, Ehninger G, Goldmann SF. Gene and haplotype frequencies for the loci hLA-A, hLA-B, and hLA-DR based on over 13,000 german blood donors. Hum Immunol. 2003;64(1):137-151. [12] 李建忠,李长缨.人群HBV易感性与HLA-Ⅰ、Ⅱ类基因相关性研究.预防医学论坛[J]. 2007,13(4):314-416.[13] Matsubara T, Nishida T, Shimoda A, et al. The combination of anti-HBc and anti-HBs levels is a useful predictor of the development of chemotherapy-induced reactivation in lymphoma patients with resolved HBV infection. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(6):6543-6552. [14] Mak LY, Wong DK, Seto WK, et al. Hepatitis B core protein as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017;21(12):1153-1159. [15] Lutomski CA, Lyktey NA, Zhao Z et al. Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Completion Occurs through Error Correction. J Am Chem Soc. 2017; 139(46):16932-16938. [16] Schöneweis K, Motter N, Roppert PL, et al. Activity of nucleic acid polymers in rodent models of HBV infection. Antiviral Res. 2018;149: 26-33. [17] Aizawa M, Tsubota A, Fujise K, et al. Clinical course and predictive factors of virological response in long-term lamivudine plus adefovir dipivoxil combination therapy for lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B patients. J Med Virol. 2011;83(6):953-961.[18] Khomeriki SG, Iakhimchuk GN, Golovanova EV. Clinical significance of intravital morphological investigation of the liver. Ter Arkh. 2011;83(4): 30-36.[19] Moretta A, Bottino C, Mingari MC, et al. What is a natural killer cell? Nat Immunol. 2002;3(1):6-8.[20] Kärre K. NK cells, MHC class I molecules and the missing self. Scand J Immunol. 2002;55(3):221-228.[21] Shah-Hosseini A, Jafari M, Mohammadi A, et al. The impact of KIR-HLA genotype on hepatitis B virus clearance in Iranian infected individuals. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2017;206(6):463-470. [22] Nakimuli A, Chazara O, Farrell L, et al. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genes and their HLA-C ligands in a Ugandan population. Immunogenetics. 2013;65(11):765-775.[23] 杨志明.丙型肝炎病毒基因型分布及HLA-Cw基因多态性的关联性分析[J].标记免疫分析与临床,2016,23(12):1395-1398.[24] 孙坚萍,孙焕芹,刘宁,等.中国北京男男同性恋艾滋病感染者HLA分型及与疾病进展分析[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2016,32(8):1183-1186,1191.[25] 田伟,李立新,周劲峰,等.中国南方汉族人群HLA-Cw座位基因多态性分析[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,2001,22(1):99-102.[26] 张洪波,赵钧海,赖江华.新疆维吾尔族HLA-Cw基因座遗传多态性调查[J].遗传,2003,25(5):549-551.[27] Rasmussen M, Harndahl M, Stryhn A, et al. Uncovering the peptide- binding specificities of HLA-C: a general strategy to determine the specificity of any MHC class I molecule. J Immunol. 2014;193(10): 4790-4802. [28] 徐小明,任雨 ,姚许平,等.供者HLA-Cw和受者KIR基因多态性以及HLA- Cw/KIR组合型对移植肾功能的影响[J]. 中华移植杂志(电子版),2014, 8(1):13-17.[29] Li J, Han Y, Jin K, et al. Dynamic changes of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), natural killer (NK) cells, and natural killer T (NKT) cells in patients with acute hepatitis B infection. Virol J. 2011;8:199. [30] Blais ME, Dong T, Rowland-Jones S. HLA-C as a mediator of natural killer and T-cell activation: spectator or key player? Immunology. 2011; 133(1):1-7. [31] Israeli M, Roelen DL, Carrington M, et al. Association between CTL Precursor Frequency to HLA-C Mismatches and HLA-C Antigen Cell Surface Expression. Front Immunol. 2014;5:547. [32] Hundhausen C, Bertoni A, Mak RK, et al. Allele-specific cytokine responses at the HLA-C locus: implications for psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132(3 Pt 1):635-641. [33] Nair RP, Stuart PE, Nistor I, et al. Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;78(5):827-851. [34] 姚叶萍,曾跃彬,赖小丽.慢性乙型肝炎患者外周血 CD8+T 淋巴细胞功能的变化[J].肝脏,2015,20(5):356-358.[35] 卢晓敏,王文远,孙成刚.HLA-A基因频率与HBV感染的相关性研究[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2006,22(2):91-92.[36] 蒋雪梅,陈士俊,旭日.山东汉族人乙肝患者与HLA-B基因型的相关性研究[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2005,43(8): 737-740.[37] 邢文斌,郭晓楠,徐慧宁.HLA-DRB多态性与HBV感染的相关性研究[J].中华实验和临床感染病杂志:电子版,2015,9(1):65-68.[38] 杨丽,李真,徐菲莉.新疆维吾尔族、汉族慢性乙型肝炎患者HLA-DQA1基因多态性研究[J].重庆医学,2016,45(1):1-4.[39] Pajewski NM, Parker SD, Poland GA, et al. The role of HLA-DR-DQ haplotypes in variable antibody responses to anthrax vaccine adsorbed. Genes Immun. 2011;12(6):457-465. [40] 杜可明,刘达庄.HLA基因分型方法进展[J].中国输血杂志, 2005,18(4): 342-345. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
乙肝病毒携带者:多指无症状乙肝病毒携带者,血液检测单独乙型肝炎表面抗原阳性,或是指乙肝抗原、抗体检测阳性者(表面抗体单项阳性除外),但无肝炎症状和体征,各项肝功能检查正常,经半年观察无变化者,肝组织学检查一般无明显异常的群体。
人类白细胞抗原C(human leucocyte antigen,HLA-C):HLA-C是人类白细胞抗原的一个基因座,属于经典的HLA-I类基因,位于6号染色体上,处于HLA-A、B位点之间,分布于各组织有核细胞及血小板和网织红细胞的表面。成熟的HLA-C蛋白会与β2微球蛋白组成异二聚体,作为一个受体锚定在细胞表面。
文题释义:
乙肝病毒携带者:多指无症状乙肝病毒携带者,血液检测单独乙型肝炎表面抗原阳性,或是指乙肝抗原、抗体检测阳性者(表面抗体单项阳性除外),但无肝炎症状和体征,各项肝功能检查正常,经半年观察无变化者,肝组织学检查一般无明显异常的群体。
人类白细胞抗原C(human leucocyte antigen,HLA-C):HLA-C是人类白细胞抗原的一个基因座,属于经典的HLA-I类基因,位于6号染色体上,处于HLA-A、B位点之间,分布于各组织有核细胞及血小板和网织红细胞的表面。成熟的HLA-C蛋白会与β2微球蛋白组成异二聚体,作为一个受体锚定在细胞表面。.jpg) 文题释义:
乙肝病毒携带者:多指无症状乙肝病毒携带者,血液检测单独乙型肝炎表面抗原阳性,或是指乙肝抗原、抗体检测阳性者(表面抗体单项阳性除外),但无肝炎症状和体征,各项肝功能检查正常,经半年观察无变化者,肝组织学检查一般无明显异常的群体。
人类白细胞抗原C(human leucocyte antigen,HLA-C):HLA-C是人类白细胞抗原的一个基因座,属于经典的HLA-I类基因,位于6号染色体上,处于HLA-A、B位点之间,分布于各组织有核细胞及血小板和网织红细胞的表面。成熟的HLA-C蛋白会与β2微球蛋白组成异二聚体,作为一个受体锚定在细胞表面。
文题释义:
乙肝病毒携带者:多指无症状乙肝病毒携带者,血液检测单独乙型肝炎表面抗原阳性,或是指乙肝抗原、抗体检测阳性者(表面抗体单项阳性除外),但无肝炎症状和体征,各项肝功能检查正常,经半年观察无变化者,肝组织学检查一般无明显异常的群体。
人类白细胞抗原C(human leucocyte antigen,HLA-C):HLA-C是人类白细胞抗原的一个基因座,属于经典的HLA-I类基因,位于6号染色体上,处于HLA-A、B位点之间,分布于各组织有核细胞及血小板和网织红细胞的表面。成熟的HLA-C蛋白会与β2微球蛋白组成异二聚体,作为一个受体锚定在细胞表面。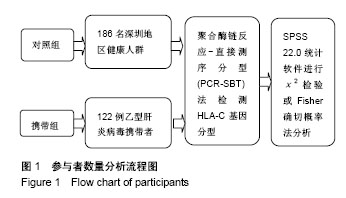
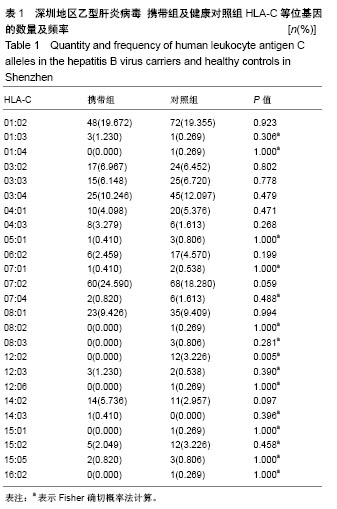
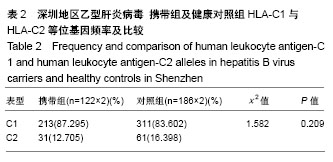
.jpg) 文题释义:
乙肝病毒携带者:多指无症状乙肝病毒携带者,血液检测单独乙型肝炎表面抗原阳性,或是指乙肝抗原、抗体检测阳性者(表面抗体单项阳性除外),但无肝炎症状和体征,各项肝功能检查正常,经半年观察无变化者,肝组织学检查一般无明显异常的群体。
人类白细胞抗原C(human leucocyte antigen,HLA-C):HLA-C是人类白细胞抗原的一个基因座,属于经典的HLA-I类基因,位于6号染色体上,处于HLA-A、B位点之间,分布于各组织有核细胞及血小板和网织红细胞的表面。成熟的HLA-C蛋白会与β2微球蛋白组成异二聚体,作为一个受体锚定在细胞表面。
文题释义:
乙肝病毒携带者:多指无症状乙肝病毒携带者,血液检测单独乙型肝炎表面抗原阳性,或是指乙肝抗原、抗体检测阳性者(表面抗体单项阳性除外),但无肝炎症状和体征,各项肝功能检查正常,经半年观察无变化者,肝组织学检查一般无明显异常的群体。
人类白细胞抗原C(human leucocyte antigen,HLA-C):HLA-C是人类白细胞抗原的一个基因座,属于经典的HLA-I类基因,位于6号染色体上,处于HLA-A、B位点之间,分布于各组织有核细胞及血小板和网织红细胞的表面。成熟的HLA-C蛋白会与β2微球蛋白组成异二聚体,作为一个受体锚定在细胞表面。