中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (33): 5312-5316.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1836
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
亚甲基蓝可拮抗苯胺致小鼠骨髓细胞DNA的损伤
姜 超,胡玉龙
- 扬州大学体育学院,江苏省扬州市 225000
Antagonistic effect of methylene blue on aniline-induced DNA damage of mouse bone marrow cells
Jiang Chao, Hu Yulong
- Sports College of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 单细胞凝胶电泳:细胞膜和核膜在裂解液的作用下被破坏,其中的RNA和蛋白质等从细胞逸出,扩散到裂解液中,而只有核DNA仍停留在细胞核原位。如果细胞完整,经荧光染色后核会呈现圆形;反之,如果细胞受损,那么DNA双链在碱性条件解旋成单链,断片就会进入凝胶,在电泳时,相对分子质量较小、本身带负电荷的断片,在电泳场作用下离开主核向阳极移动,形成不同层次的电泳条带。这些条带经荧光染料染色后,其形状犹如彗星一般,因此也称彗星实验。 DNA损伤:利用gel red染液对电泳条带进行染色,细胞受损越严重,产生断片越多,彗星的尾越长。通过彗星尾长、尾距及荧光强度等指标综合评估DNA损伤及其修复的程度。
摘要
背景:采用单细胞凝胶电泳技术应用于DNA损伤与修复的研究,探讨苯胺遗传毒性的靶器官及亚甲基蓝修复动力学效应,为治疗苯胺中毒提供基础数据和新的策略。
目的:探讨亚甲基蓝对苯胺致小鼠骨髓细胞DNA损伤的拮抗作用。
方法:采用不同浓度苯胺5,50,100,200 mg/kg对昆明小鼠进行灌胃(苯胺灌胃组),同时设置相对应的亚甲基蓝治疗组、阴性对照组以及空白对照组,每组10只小鼠,持续染毒6 d,取小鼠骨髓细胞进行单细胞凝胶电泳实验,观察骨髓细胞DNA的损伤及修复情况。
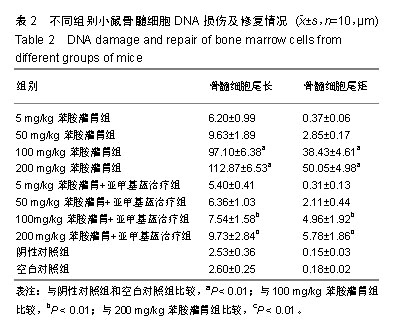
结果与结论:①与阴性对照组和空白对照组相比,100,200 mg/kg苯胺灌胃组小鼠骨髓细胞DNA尾长、尾矩增加(P < 0.01),5,50 mg/kg亚甲基蓝治疗组尾长、尾矩分别较对应的苯胺灌胃组稍微减少(P > 0.05),而100,200 mg/kg苯胺灌胃组尾长、尾矩与对应的亚甲基蓝治疗组比较显著增加(P < 0.01);②结果表明,小鼠骨髓细胞DNA损伤程度随着苯胺浓度的增加而逐渐加重;亚甲基蓝对苯胺致小鼠骨髓细胞DNA损伤具有一定的修复效果。该实验方案已于2018-07-01经扬州大学动物科学与技术学院伦理委员会批准。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID:0000-0001-7590-3608(姜超)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)