中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (23): 3728-3732.doi: 10.12307/2022.674
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
CTLA4.FasL促进异种肝卵圆细胞在大鼠脾脏的定植
万 真1,王旭珍2,张晓刚3
- 南昌大学第一附属医院,1普外科,2重症医学科,江西省南昌市 330006;3西安交通大学第一附属医院肝胆外科,陕西省西安市 710061
CTLA4.FasL promotes the engraftment of xenogeneic hepatic oval cells in rat spleen
Wan Zhen1, Wang Xuzhen2, Zhang Xiaogang3
- 1Department of General Surgery, 2Department of Critical Care Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
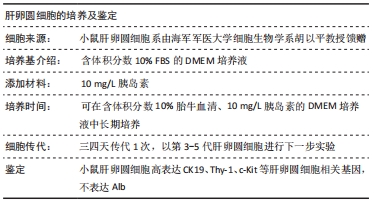
肝卵圆细胞(hepatic oval cells,HOCs):来源于成体肝脏赫令管,是肝脏祖细胞,细胞体积小,增殖能力较强,具有双分化潜能。在急性肝坏死、慢性病毒性肝炎等疾病导致的肝功能衰竭时,成熟肝细胞增殖受抑制,门管区肝卵圆细胞活化增殖并可分化为肝细胞和胆管上皮细胞,促进受损肝脏的修复。
CTLA4.FasL:CTLA4(Cytotoxic Lymphocyte Antigen 4)是细胞毒性T淋巴细胞中发现的第四种特异性抗原基因。CTLA4阻断协同刺激信号通路B7-CD28,T淋巴细胞不能活化,进入克隆无能状态。此外,FasL是能够结合到死亡受体TNFRSF6/FAS的细胞因子。FasL与其受体Fas结合介导的活化T淋巴细胞凋亡也可显著抑制免疫排斥反应。而CTLA4.FasL融合蛋白分子整合了CTLA4和FasL两个功能域,可抑制T细胞活化并诱导活化T细胞的凋亡,其效能远远超过单个CTLA4和FasL分子或两者联合应用。
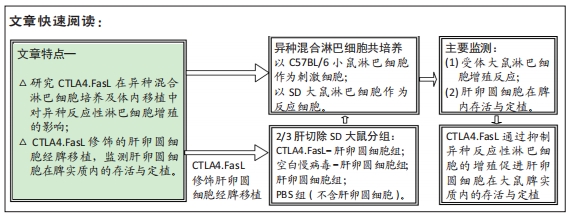
背景:CTLA4.FasL可有效抑制同种反应性T淋巴细胞及自身反应性T淋巴细胞,但CTLA4.FasL在异种肝卵圆细胞经脾移植中对异种反应性T淋巴细胞的抑制作用还不明确。
目的:研究CTLA4.FasL对异种反应性淋巴细胞增殖的作用,监测CTLA4.FasL修饰的小鼠肝卵圆细胞(CTLA4.FasL-肝卵圆细胞)在大鼠脾脏内的存活与定植。
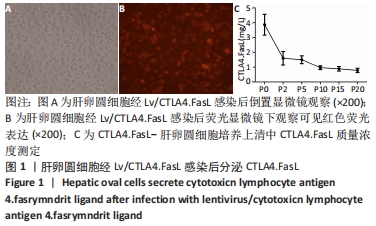
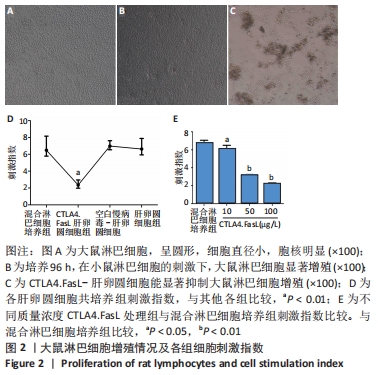
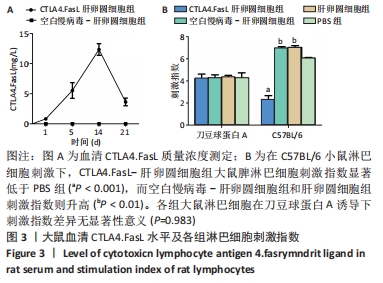
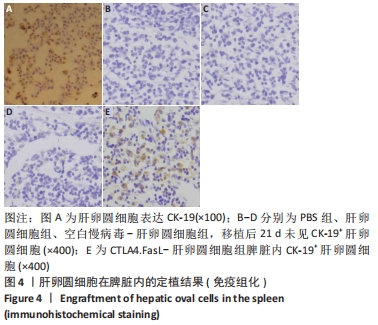
方法:①于小鼠肝卵圆细胞悬液中,加入携带CTLA4.FasL融合基因的重组慢病毒载体Lv/CTLA4.FasL和聚凝胺进行感染,以未感染慢病毒的肝卵圆细胞和感染空白慢病毒-肝卵圆细胞为对照;在荧光显微镜下观察肝卵圆细胞的活力和红色荧光蛋白慢病毒载体的表达;②对行2/3肝切除的SD大鼠分别经脾移植CTLA4.FasL-肝卵圆细胞、空白慢病毒-肝卵圆细胞、肝卵圆细胞和PBS(不含肝卵圆细胞),分别于肝切除术后1,5,14和21 d,采用ELISA法测定大鼠血清CTLA4.FasL浓度,取受体大鼠脾脏进行CK-19的免疫组化检测;③以C57BL/6小鼠淋巴细胞作为刺激细胞,以SD大鼠淋巴细胞作为反应细胞;在混合淋巴细胞反应中,分别接种CTLA4.FasL-肝卵圆细胞,空白慢病毒-肝卵圆细胞及肝卵圆细胞,或分别加入CTLA4.FasL-肝卵圆细胞(质量浓度分为10,50和100 μg/L)、空白慢病毒-肝卵圆细胞及肝卵圆细胞培养上清液,培养96 h后,用5-Brdu法测定各组大鼠淋巴细胞的增殖情况。
结果与结论:①在异种混合淋巴细胞培养体系中,CTLA4.FasL-肝卵圆细胞及培养上清均能有效抑制大鼠淋巴细胞的增殖;②CTLA4.FasL-肝卵圆细胞移植受体大鼠的脾脏淋巴细胞对小鼠淋巴细胞低免疫应答,而空白慢病毒-肝卵圆细胞和肝卵圆细胞移植受体大鼠来源的脾细胞则表现出强应答;③CTLA4.FasL-肝卵圆细胞组移植后21 d大鼠脾脏实质内可见CK-19阳性细胞,而在PBS组、肝卵圆细胞组和空白慢病毒-肝卵圆细胞组术后21 d未见CK-19阳性细胞;④结果说明,CTLA4.FasL可有效抑制异种反应性淋巴细胞的增殖,促进小鼠肝卵圆细胞在大鼠脾实质内的存活及定植。
缩略语:肝卵圆细胞:hepatic oval cells,HOCs
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4818-1296 (万真)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: