中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (21): 3332-3337.doi: 10.12307/2022.640
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯/己二胺涂层接枝氯乙定改善种植体的抗菌性能
颜楷泉,刘惠珊,王晓玮,吴晓琴,张维波,李向阳,王银龙,陈佳龙
- 安徽医科大学口腔医学院/附属口腔医院,口腔疾病研究安徽省重点实验室,安徽省合肥市 230032
Epigallocatechin gallate/hexanediamine coating grafted chlorhexidine improves the antibacterial properties of implants
Yan Kaiquan, Liu Huishan, Wang Xiaowei, Wu Xiaoqin, Zhang Weibo, Li Xiangyang, Wang Yinlong, Chen Jialong
- Department of Stomatology/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Anhui Provincial Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯:是一种在绿茶、乌龙茶和红茶叶中广泛存在的多酚类物质,大量研究表明其具有抗癌、抗突变、预防和治疗心脑血管系统疾病以及调理内分泌、免疫系统等生物活性,同时在机体的解毒功能及药物联合应用方面有着重要应用价值。
氯己定:作为一种阳离子双胍类抗菌剂,不仅对革兰阳性菌、革兰阴性菌、酵母菌、病毒(包括人类免疫缺陷病毒和乙型肝炎病毒)有抑制能力,对细菌生物膜的形成也有抑制作用,已经作为局部抗菌剂、擦洗剂和冲洗剂被广泛运用于临床治疗。
背景:细菌感染引起的并发症严重影响种植体的长期疗效,因此抗菌性能在种植体表面设计中具有重要意义。
目的:在多孔钛表面构建载氯己定的酚胺交联涂层,评价涂层的抗菌性能及细胞相容性。
方法:将钛片打磨清洗,干燥后浸泡于NaOH溶液中,置于60 ℃干燥箱24 h,沸水清洗干燥后记为对照组;将对照组钛片浸泡于含表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与己二胺的Tris溶液中24 h,清洗干燥后记为酚胺组;将酚胺组钛片浸泡在氯己定溶液中24 h,清洗干燥后记为氯己定组。通过扫描电镜、X射线光电子能谱、水接触角测量仪、NH基团定量对3组样品进行材料学表征;采用活/死菌染色、抑菌环法及浊度法评价3组样品的抗菌能力,MTT法和细胞荧光染色评价3组样品的细胞相容性,细菌-细胞共培养评价有菌环境中3组样品的细胞黏附能力。
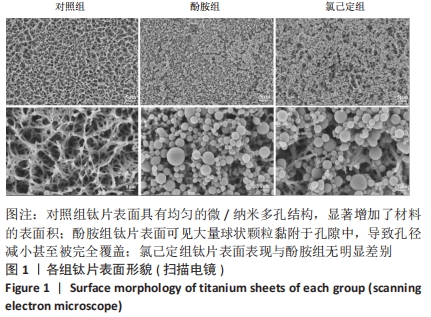
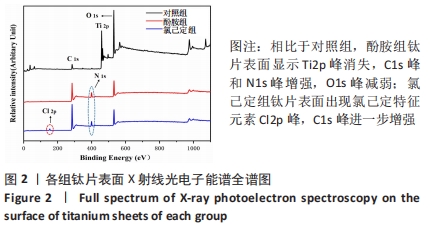
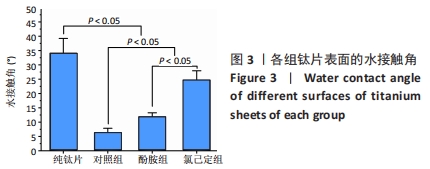
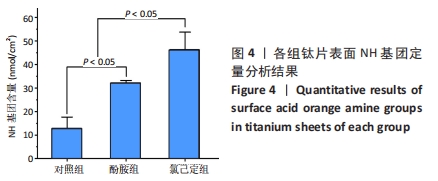
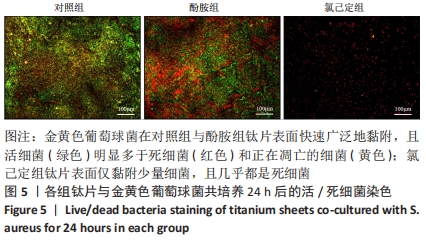
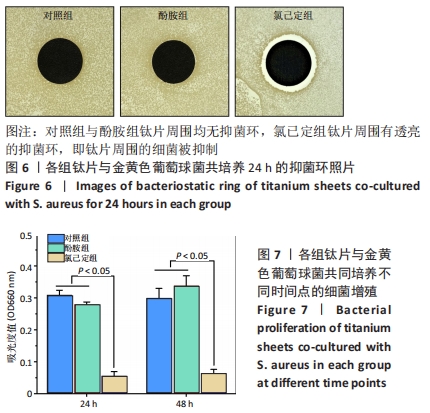
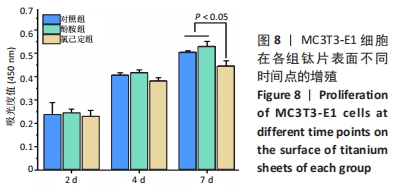
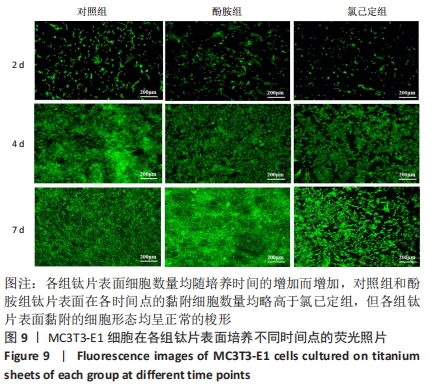
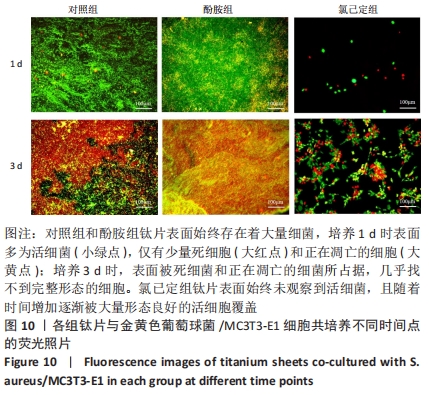
结果与结论:①氯己定组钛片表面被大量球状颗粒覆盖,出现Cl2p峰,水接触角上升至(24.6±3.3)°,表面NH密度增至(46.14±7.63) nmol/cm2,证明涂层构建成功;②抗菌结果显示,氯己定组表面细菌黏附量最低且均为死细菌,周围具有透亮的抑菌环,培养体系中细菌未增殖,证明涂层对材料表面和周围环境的细菌均具有抑制能力;对照组与酚胺组钛片表面细菌黏附较多且以活细菌多见,周围无明显的抑菌环,培养体系中细菌增殖明显;③细胞培养结果显示,氯己定组钛片轻微抑制细胞黏附但不影响细胞的增殖;④细菌-细胞共培养结果显示,仅氯己定组黏附大量细胞且细胞形态良好;⑤结果表明,氯己定接枝表面构建成功且具有良好的抗菌能力,其在有菌环境中有助于成骨细胞的黏附和增殖。
缩略语:表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯:epigallocatechin gallate,EGCG
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4466-0479 (颜楷泉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: