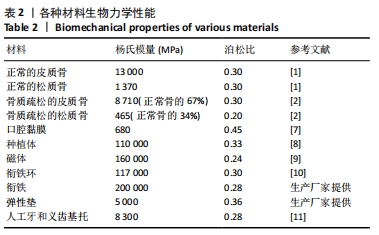
[1] DENNISON E, COLE Z, COOPER C. Diagnosis and epidemiology of osteoporosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17(4):456-461.
[2] XIAO JR, KONG L, CHEN YX, et al. Selection of Optimal Expansion Angle and Length of an expandable Implant osteoporotic Mandible: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28:e88-e97.
[3] TAMAMURA N, KURODA S, SUGAWARA Y, et al. Use of palatal minis- crew anchorage lingual multi-bracket appliances to enhance efficiency of molar scissors-bite correction. Angle Orthod. 2009;79(3):577.
[4] WU AY, HSU JT, FUH LJ, et al. Biomechanical effect of implant design on four implants supporting mandibular full-arch fixed dentures: In vitro test and finite element analysis. Formos Med Assoc. 2020; 119(10):1514-1523.
[5] AMANDA RP, YOAN PR, LAURA MSR, et al. The effect of diameter, length and elastic modulus of a dental implant on stress and strain levels in peri-implant bone: A 3D finite element analysis. Biomed Mater Eng. 2020;30(5-6):541-558.
[6] GENG JP, TAN KB, LIU GR. Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent. 2001; 85(6):585-598.
[7] 胡凤玲,龚逸明,张建国,等.种植磁性覆盖义齿的三维有限元模型的建立[J].口腔医学,2015,35(12):1025-1027.
[8] KITAMURA E, STEGAROIU R, NOMURA S, et al. Influence of marginal bone resorption on stress around an implant———A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Rehabil. 2005;32(4):279-286.
[9] POLIKEIT A, NOLTE LP, FERGUSON SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: Finite-element analysis. Spine. 2003;28(10):991-996.
[10] BARÃO VA, ASSUNÇÃO WG, TABATA LF, et al. Effect of different mucosa thickness and resiliency on stress distribution of implant- retained overdentures-2D FEA. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2008;92:213-223.
[11] SCHWITALLA AD, ABOU-EMARA M, SPINTIG T, et al. Finite element analysis of the biomechanical effects of PEEK dental implants on the peri-implant bone. J Biomech. 2015;48(1):1-7.
[12] JOHN J, RANGARAJAN V, SAVADI RC, et al. A finite element analysis of stress distribution in the bone, around the implant supporting a mandibular overdenture with ball/o ring and magnetic attachment.Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2012;12:37-44.
[13] DARBAR UR, HUGGETT R, HARRISON A, et al. Finite element analysis of stress distribution at the tooth-denture base interface of acrylic resin teeth debonding from the denture base. J Prosthet Dent. 1995;74(6): 591-594.
[14] ACHARYA PH, PATEL VV, DUSEJA SS, et al. Comparative evaluation of peri-implant stress distribution in implant protected occlusion and cuspally loaded occlusion on a 3 unit implant supported fixed partial denture: A 3D finite element analysis study. J Adv Prosthodont. 2021;13(2):79-88.
[15] HU F, GONG Y, BIAN Z, et al. Comparison of Three Different Types of Two-Implant-Supported Magnetic Attachments on the Stress Distribution in Edentulous Mandible. Comput Math Methods Med. 2019:6839517. doi: 10.1155/2019/6839517. eCollection 2019.
[16] CRUZ M, WASSALL T, TOLEDO EM, et al. Finite element stress analysis of dental prostheses supported by straight and angled implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(3):391-403.
[17] LIU J, PAN S, DONG J, et al. Influence of implant number on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular implant-retained/supported overdentures: a three- dimensional finite element analysis. J Dent. 2013;41:241-249.
[18] OGATA K, SATOH M. Centre and magnitude of vertical forces in complete denture wearers. J Oral Rehabil. 1995;22(2):113-119.
[19] GOIATO MC, SÔNEGO MV, PELLIZZER EP, et al. Clinical outcome of removable prostheses supported by mini dental implants. A systematic review. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica. 2018;76(8):628-637.
[20] CRISTACHE CM, MUNTIANU LA, BURLIBASA M, et al. Five-year clinical trial using three attachment systems for implant overdentures. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;25(2):e171-e178.
[21] GONDA T, IKEBE K, ONO T, et al. Effect of magnetic attachment with stress breaker on lateral stress to abutment tooth under overdenture. J Oral Rehabil. 2004;31(10):1001-1006.
[22] GILLINGS BR. Magnetic denture retention systems: inexpensive and efficient. Int Dent J. 1984;34(3):184-197.
[23] TORRES Y, TRUEBA P, PAVON J, et al. Designing,processing and characterisation of titanium cylinders with graded porosity:An alternative to stress-shielding solution. Mater Des. 2014;(63):316-324.
[24] 刘世军,王立军,顾晓鸣,等.下颌骨骨折内固定术后应力遮挡效应的临床研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2010,45(8):474-476.
[25] ASGHARZADEH SHIRAZI H, AYATOLLAHI MR, ASNAFI A. To reduce the maximum stress and the stress shielding effect around a dental implant-bone interface using radial functionally graded biomaterials. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2017;20(7):750-759.
[26] DUYCK J, RØNOLD HJ, VAN OOSTERWYCK H, et al. The influence of static and dynamic loading on marginal bone reactions around osseointegrated implants: an animal experimental study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12(3):207-218.
[27] DE MEDEIROS FCFL, KUDO GAH, LEME BG, et al. Dental implants in patients with osteoporosis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;47(4):480-491.
[28] DUYCK J, VAN OOSTERWYCK H, VANDER SLOTEN J, et al. Magnitude and distribution of occlusal forces on oral implants supporting fixed prostheses: an in vivo study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11(5): 465-475.
[29] ZHAO JH, ZHOU YM, LI CY. Finite element analysis of the effects of implant thread locations on stress distribution. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;26(6):584-587.
[30] MAEDA Y, MIURA J, TAKI I, et al. Biomechanical analysis on platform switching: is there any biomechanical rationale. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18(5):581-584.
[31] BARÃO VA, ASSUNÇÃO WG, TABATA LF, et al. Finite element analysis to compare complete denture and implantretained overdentures with different attachment systems. J Craniofac Surg. 2009;20(4):1066-1071.
[32] CRISTACHE CM, MUNTIANU LAS, BURLIBASA M, et al. Five-year clinical trial using three attachment systems for implant overdentures. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;25(2):e171-e178.
[33] TURKER N, BUYUKKAPLAN US. Effects of overdenture attachment systems with different working principles on stress transmission: A three-dimensional finite element study. J Adv Prosthodont. 2020; 12(6):351-360.
[34] ZHOU H, JIAO Y, MA CF, et al. Clinical outcomes of implant-retained mandibular overdentures using the bar and magnetic attachment systems: an up to 5-year retrospective study. Ann Transl Med. 2020; 8(21):1360.
[35] MAEDA Y, YANG TC, KINOSHITA Y. Development of a self-adjusting magnetic attachment for implant overdentures. Int J Prosthodont. 2011;24:241-243.
[36] YANG TC, MAEDA Y, GONDA T, et al. Attachment systems for implant overdenture: influence of implant inclination on retentive and lateral forces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(11):1315-1319.
[37] TAKESHITA S, KANAZAWA M, MINAKUCHI S. Stress analysis of mandibular two-implant overdenture with different attachment systems. Dent Mater J. 2011;30:928-934.
[38] SONG SY, KANG KH, LEE JY, et al. Effects of type of magnet attachment and implant angulation in two implant overdenture models. J Adv Prosthodont. 2020;12(1):33-37.
[39] 王倩倩,陈中中,杨亚茹,等.基于FEA的种植体个性化选择及力学性能评价[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(3):307-310.
[40] TURKER N, BUYUKKAPLAN US. Effects of overdenture attachment systems with different working principles on stress transmission: A three-dimensional finite element study.J Adv Prosthodont. 2020;12(6):351-360.
|